Sitecore XM Cloud migration guide
Sitecore XM Cloud migration guide
Coveo offers a flexible, CMS-agnostic search and personalization platform that enables the delivery of exceptional customer experiences in Sitecore XM Cloud. This guide is primarily intended for existing Coveo for Sitecore package users who are transitioning to Sitecore XM Cloud and want a Coveo Platform relevance solution that has feature parity with their current Coveo-powered implementation. In many ways, the following migration roadmap results in an easier-to-maintain, more modern, powerful, flexible, standards-compliant, and future-ready solution, mostly because it’s a move away from the Coveo JavaScript Search Framework, a technology that Coveo is no longer actively developing.
This guide focuses on:
-
Assisting Coveo for Sitecore users in the implementation decision-making process, depending on specific requirements.
-
Explaining key Coveo Platform concepts to support common migration tasks.
-
Mapping Coveo for Sitecore features to their equivalents in the Coveo Administration Console. Among the advantages, this may facilitate the auditing of the current Coveo-powered implementation.
Implementation steps are in logical order as follows:
Set up your Coveo organization
The Coveo for Sitecore integration serves as a bridge between a Sitecore XP or XM instance and a Coveo organization in the Coveo Platform.
If you still have access to the Coveo organization that you used with Coveo for Sitecore, use it to set up the new Coveo implementation for your Sitecore XM Cloud deployment. This will allow you to reuse existing resources and reduce the time required to set up your new Coveo implementation. You can find your organization ID and associated URLs in the Coveo for Sitecore Command Center.
If you no longer have access to your Coveo organization, reach out to your Customer Success Manager. You can also create a new trial organization, which you can upgrade later.
In either case, you should add a few members to the appropriate built-in groups to support your new implementation.
Index Sitecore XM Cloud content
To index your Sitecore XM Cloud content, you’ll need to add a source in your Coveo organization. The first step is to choose the appropriate source type.
Choosing the source type
The choice of source type depends on whether:
-
You need to index Sitecore XM Cloud permissions.
-
You have configured sitemap files in Sitecore XM Cloud.
If you don’t need to index Sitecore XM Cloud permissions, the recommended source types are Sitemap and Web. These two types of sources have very similar indexing features, but the Sitemap source is more efficient and supports refresh content updates, whereas the Web source doesn’t. Consider generating sitemaps in Sitecore XM Cloud and using the Sitemap source as the preferred approach.
If you need to index Sitecore XM Cloud permissions, the recommended source type is the Push source. This source type requires you to implement custom code to collect your Sitecore items along with their permissions, and then use the Coveo Push API to index them. You must also use the Push API to push the security identities referenced in your item permissions.
|
|
Indexing items with the Push source is a complex and high-effort task. |
Source type selection decision flow
| Need to index Sitecore XM Cloud permissions? | Sitemaps configured in Sitecore XM Cloud? | Source type to choose |
|---|---|---|
Sitemap (cloud |
||
Web (cloud |
||
|
With the Sitemap and Web sources, a Coveo crawler will retrieve your Sitecore XM Cloud content and index it according to schedules you define. For more specifics on the content update operations for these sources, see:
For general information on the source content update operations available in the Coveo Administration Console, see Refresh, rescan, and rebuild.
When using a Web or Sitemap source, make sure your robots.txt file settings in Sitecore XM Cloud allow the Coveo crawler to access your content.
The user agent strings used by these sources are configured in the Edit configuration with JSON panel.
To review or edit these strings, see:
For the list of Coveo IP addresses to allow for inbound communication to your Sitecore XM Cloud content, see IP addresses to allowlist.
Number of sources to create
As mentioned in the Sitemap and Web source documentation leading practices, you should create one source per domain.
|
|
There’s no value in creating a source to index unpublished content from the Sitecore XM Cloud |
Indexing metadata to use in search interface facets and result templates
Indexing metadata from your Sitecore XM Cloud content is a prerequisite to creating facets and result templates in your search interfaces. Much of this process was handled transparently by the Coveo for Sitecore integration. In your new implementation, you’ll use the Coveo Administration Console features related to metadata extraction and indexing. This involves understanding key Coveo Platform concepts and terminology, that is, metadata, fields, and mappings.
As demonstrated in the following animation, before you can use values from your Sitecore XM Cloud data template fields in your Coveo-powered search interfaces (for example, as facet values), you need to:
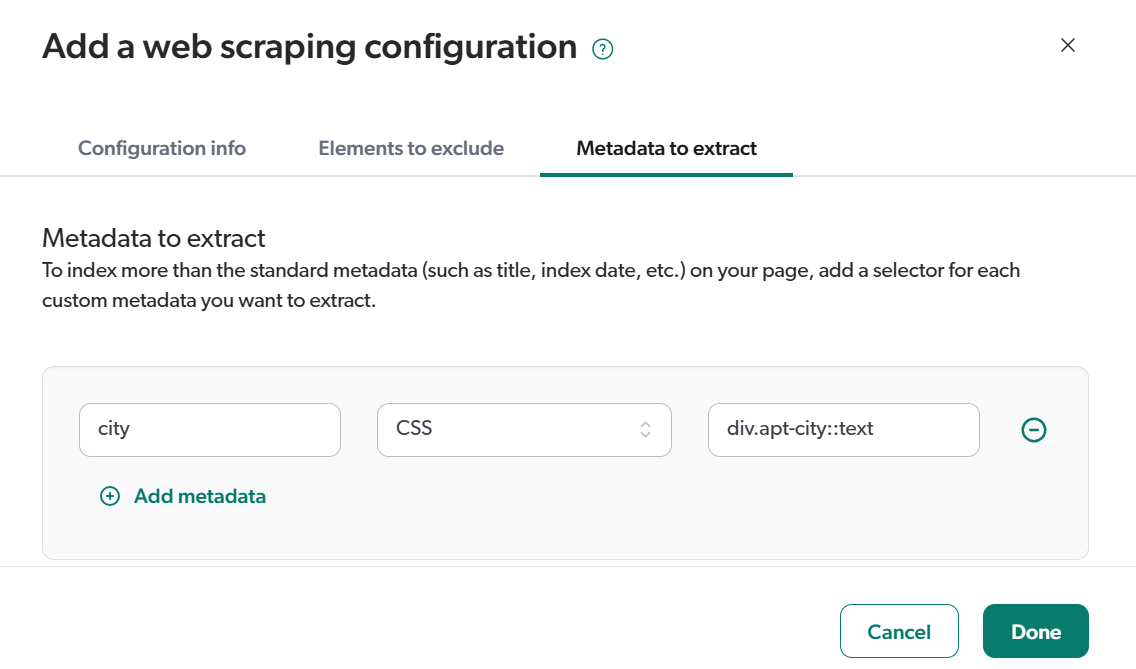
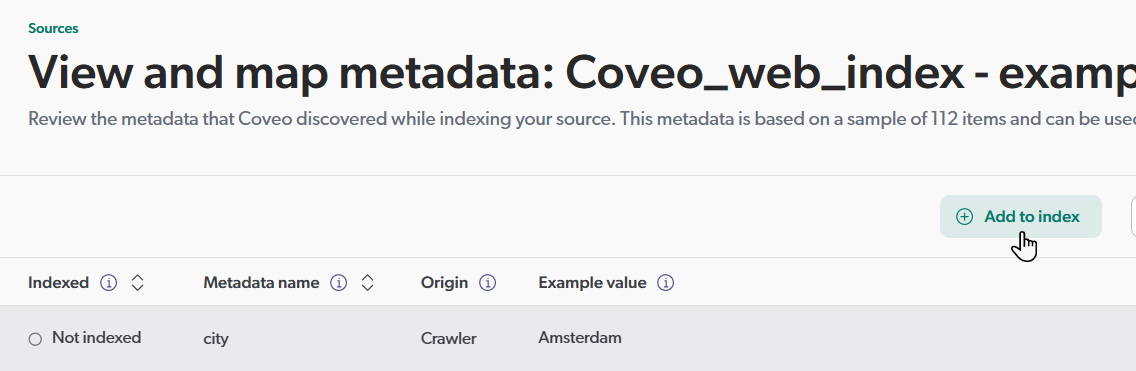
1 Extract the metadata you want to use as a facet from Sitecore XM Cloud.
2 Create a source mapping and a field to store the extracted metadata.
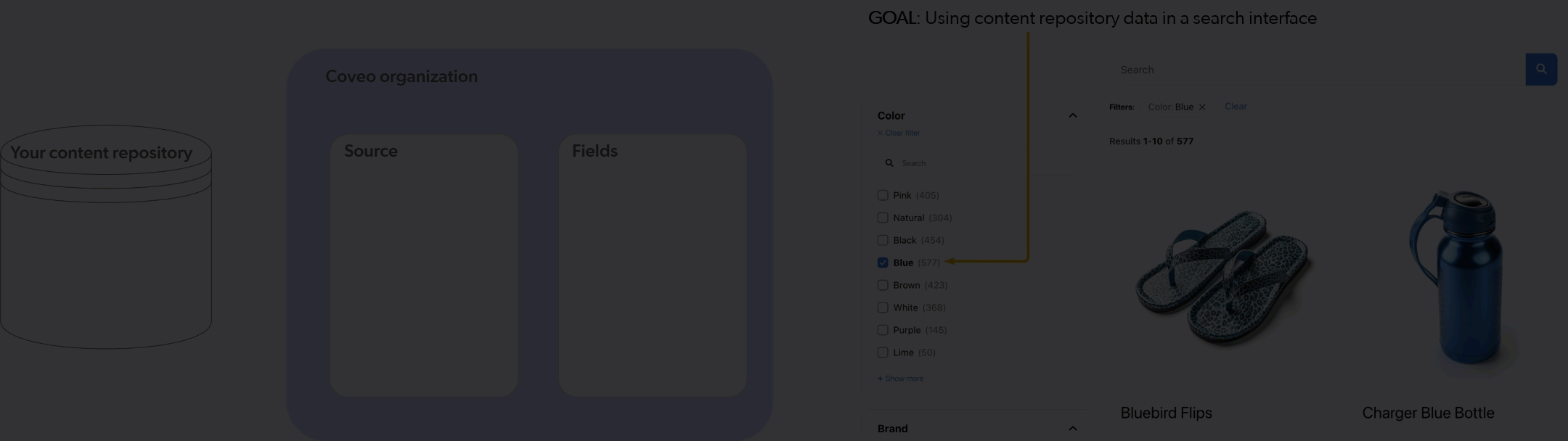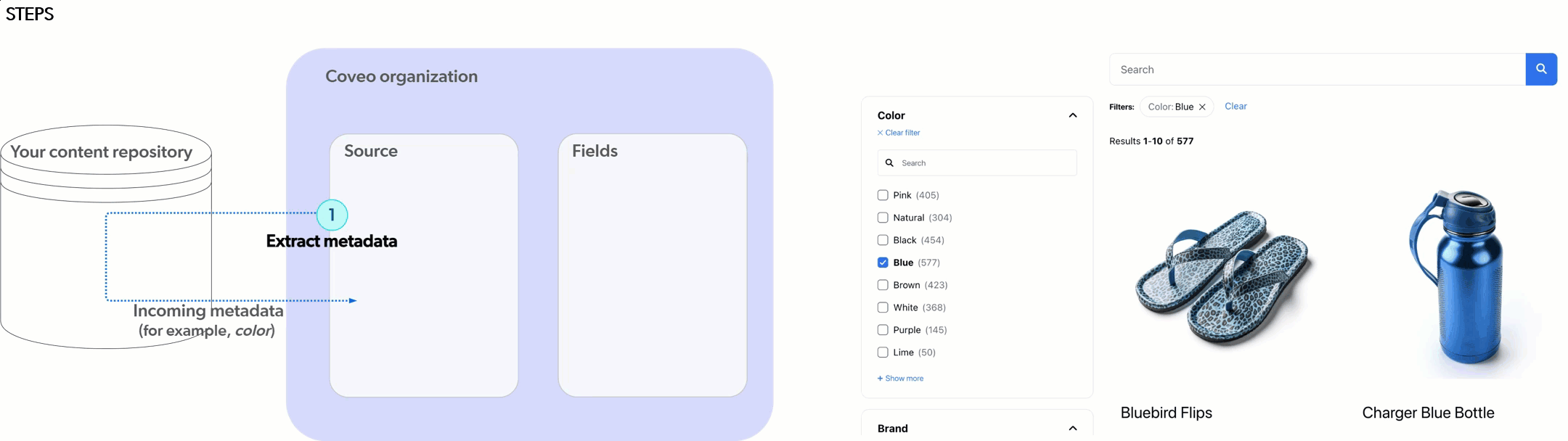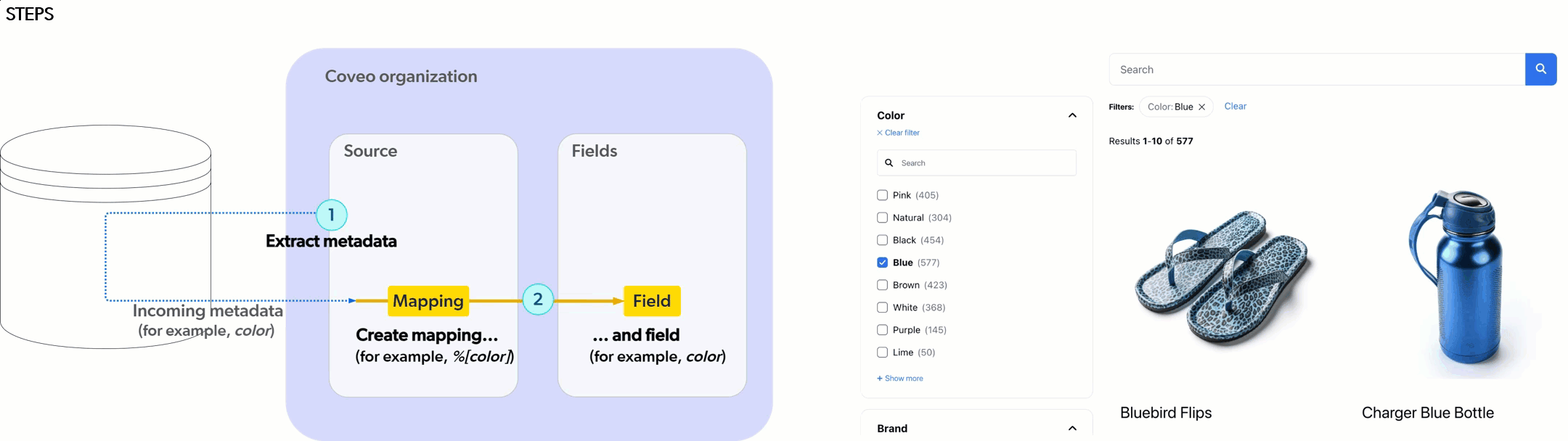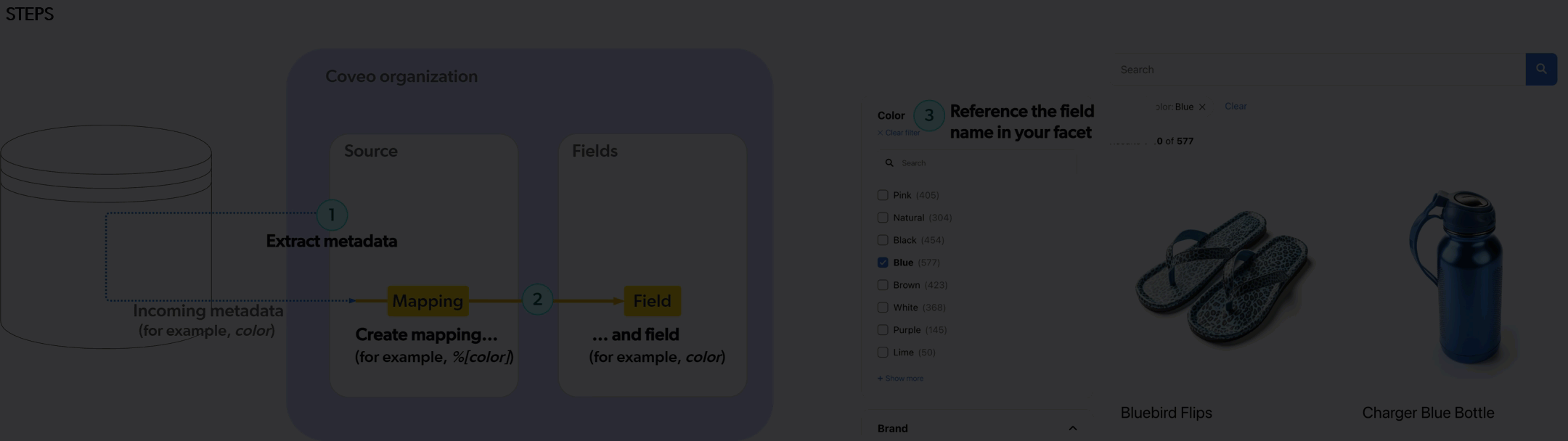
Metadata indexing in Coveo for Sitecore vs. in the Coveo Administration Console
| Step | In Coveo for Sitecore integration | In Coveo Administration Console |
|---|---|---|
1 Extracting a piece of metadata from Sitecore |
In the Command Center Fields section, you would add a Sitecore template field to the list of
On rebuilds, Coveo for Sitecore would extract the values in this field and send them to the Coveo organization as metadata, using the Command Center
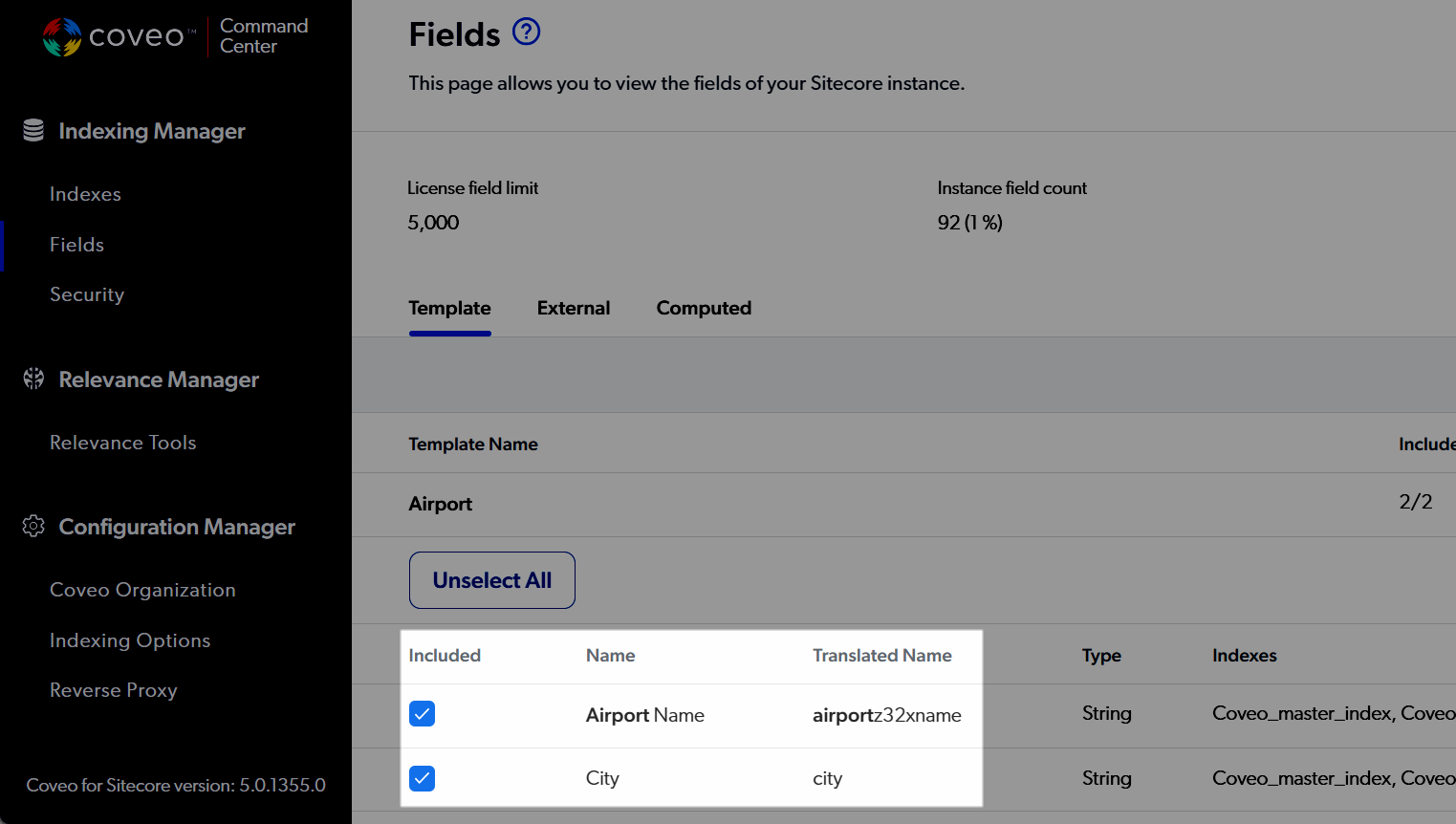
|
Metadata is extracted from your content and sent to the Coveo organization during source content updates. |
2 Creating a field and source mapping for that metadata |
In the Command Center Fields section, you would add a Sitecore template field to the list of
Coveo for Sitecore would create a field in the Coveo organization, using the Command Center |
After a source rebuild, you should see the indexed metadata when inspecting your item field values. |
The Add a Sitemap source and Add a Web source articles include complete metadata indexing instructions, in the Completion step.
|
|
If you’re still using your Coveo for Sitecore organization, that organization should still contain the fields that the integration created automatically.
If you have a lot of fields, you may be able to reuse some of them and omit step 2, the source mapping and field creation step.
To do this, access the JSON configuration of your source, and set Then, when creating your web scraping configurations, use metadata names that match the Coveo field names you want to use. |
Build search interfaces
A minimal web search solution consists of:
-
A main search page that contains a search box and a results list.
-
A standalone search box that can be placed in the header of your webpages, and which redirects users to the main search page when they submit a query.
Coveo provides a number of approaches to build search interfaces. We’ve narrowed the options to consider for your main search page to the two we consider the best for a Coveo for Sitecore audience.
For all available approaches, see the Choose the right approach article.
Main search page
Choose between using the Simple builder or the Atomic library depending on your main search page needs, especially in terms of development speed and customization. You can also use an iterative deployment strategy, using a Simple builder search page for your first iteration.
Simple builder
You can access the Simple builder from the Search Pages (platform-ca | platform-eu | platform-au) page in the Coveo Administration Console. It lets you create simple Atomic hosted search pages in a few minutes without writing any code.
Hosted search pages are ideal for test or demo purposes.
You can share a link to your search page with anyone, even people who don’t have access to the Coveo Administration Console.
You can easily consume hosted search pages using the atomic-hosted-ui component.
To create a custom search interface, you should choose the Atomic library or another library or framework. You can use an Atomic hosted search page created with the builder and customize it further, using the Coveo CLI.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
Requires no programming skills. |
Limited UI/UX customization. |
Lets you create a basic search interface within minutes. |
Atomic library
Atomic is a collection of pre-built UI components meant to quickly create versatile search interfaces. You can theme and customize the Atomic components to suit your needs. Under the hood, Atomic relies on the Coveo Headless library to interface with Coveo and handle the search application state.
Atomic supports a variety of search page development and deployment flows. For example, you can:
-
Download a hosted search page as a starting point.
-
Customize the search page locally and deploy it to your Coveo organization.
-
Consume your hosted search page using the
atomic-hosted-uicomponent.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
Requires minimal programming skills. |
Coupling between the UI and business logic. |
Faster to build than the JavaScript Search Framework. |
|
Both browser and mobile compatible. |
|
Lightweight and higher performance than the JavaScript Search Framework. |
|
Extendable through custom components. |
Do an inventory of the Coveo Hive renderings used in your current implementation by reviewing the layout details controls on your main search page item. Although it’s not a 1:1 mapping between Coveo Hive and Atomic components, you can use the list of Coveo Hive renderings as a guide to determine which Atomic components to use in your new implementation. You may also want to note the values on your rendering data sources, as these may help you when configuring your new search interface components.
Standalone search box
The Atomic standalone search box is compatible with either recommended option for your main search page. The implementation involves:
Resources
-
To get up and running quickly with Atomic, see the Level Up Coveo Atomic Tutorial.
-
Coveo provides code samples in React, Angular, Next.js, and Vue.js in its Coveo ui-kit repository.
-
For Atomic library reference documentation, see Use the Atomic library.
-
For the Atomic components reference, see Reference documentation.
-
To authenticate HTTP requests made by search interfaces that only query public content, see Use API key authentication with the Search API.
-
To authenticate HTTP requests made by search interfaces that can query private (secured) content, see Use search token authentication.
Tune the implementation
You can tune your implementation by improving the indexed content and using search optimization features.
Indexing
Your index should only include content that is relevant to your users. This means that you should exclude irrelevant items and sections of webpages from being indexed.
Excluding items from being indexed
The Sitemap and Web sources allow you to specify which pages should or shouldn’t be indexed using inclusion and exclusion crawling rules.
| In Coveo for Sitecore integration | In Coveo Administration Console | ||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Excluding sections in webpages from being indexed
The Sitemap and Web sources allow you to specify page sections to exclude using web scraping configurations. A default configuration eliminates common irrelevant sections (for example, headers and menus), but you can add your own web scraping configurations for further content cleaning.
| In Coveo for Sitecore integration | In Coveo Administration Console | ||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Miscellaneous indexing phase customizations
In the Coveo Administration Console, these customizations can only be achieved after the crawling phase of the indexing pipeline, using indexing pipeline extensions.
| In Coveo for Sitecore integration | In Coveo Administration Console | ||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Search optimization features
Coveo provides several search optimization features that you can use to improve the relevance of your search results. These features are available in the Coveo Administration Console and can be used to create a more personalized and relevant search experience for your users.
Search filter rules
The Coveo Hive Query Filter rendering provided several filtering options, including rule creation options via the Sitecore Rules Editor. In the Coveo Administration Console, you can use query pipelines filter rules for the same purposes. You can even configure filter rules to be applied only when a condition, simple or complex, is fulfilled.
| In Coveo for Sitecore integration | In Coveo Administration Console |
|---|---|
See Query Filter rendering. |
Search boosting rules
The Coveo Hive Query Ranking rendering allowed you to boost the ranking scores of items that matched a condition defined using the Sitecore Rules Editor. In the Coveo Administration Console, there are several query pipeline features that allow you to affect the ranking of search results.
| In Coveo for Sitecore integration | In Coveo Administration Console | ||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Personalization
Coveo can implicitly understand user behavior based on what users search for and click in search interfaces. Coveo also considers user page views, provided you are tracking this information.
| In Coveo for Sitecore integration | In Coveo Administration Console |
|---|---|
See Coveo Page View Analytics rendering. |
If explicit user context is available on the front end (for example, user preferences, session data), it can be leveraged as custom context and added to search and view event payloads.
| In Coveo for Sitecore integration | In Coveo Administration Console | ||
|---|---|---|---|
See Coveo User Context rendering.
|
See About custom context. |
Machine learning model-powered features
Coveo Hive supported several Coveo Machine Learning (Coveo ML) model-powered features to improve search relevance. Your new implementation will give you broader access to and better support for these features, like Relevance Generative Answering (RGA). See the Coveo Machine Learning overview article for more information.
If you’re still using your Coveo for Sitecore organization, resuming use of existing models won’t produce good results with your newly indexed content. We recommend that you delete any existing models and start fresh.