About the architecture
About the architecture
This page covers the architecture of Coveo for Sitecore. You’ll learn about its different parts and how they interact with each other. This can be valuable if you need to troubleshoot issues.
The building blocks
From a conceptual point of view, Coveo for Sitecore is made of the following building blocks.
Block 1: Coveo Search Provider
This module is deployed as a Sitecore package (ZIP file). The Coveo Search Provider acts as a bridge between Sitecore and the Coveo Platform. It’s responsible for handling queries originating from within Sitecore and for synchronizing your Coveo organization indexes with your Sitecore search indexes.
Block 2: Coveo Platform
This module is responsible for creating, managing, and maintaining your index. The Coveo Platform also handles all search queries in the background.
Among other things, it contains:
-
a Push API, which is used to index your Sitecore items.
-
a Sitecore security provider, which handles Sitecore security permissions and lets you find only what you’re allowed to see when you perform a query.
Event workflow
Depending on the type of action that you trigger in Coveo for Sitecore, a different sequence of events occur under the cover. Here are explained the most common scenarios.
Scenario 1: Rebuilding your search indexes
Rebuilding your search indexes causes these events to occur:
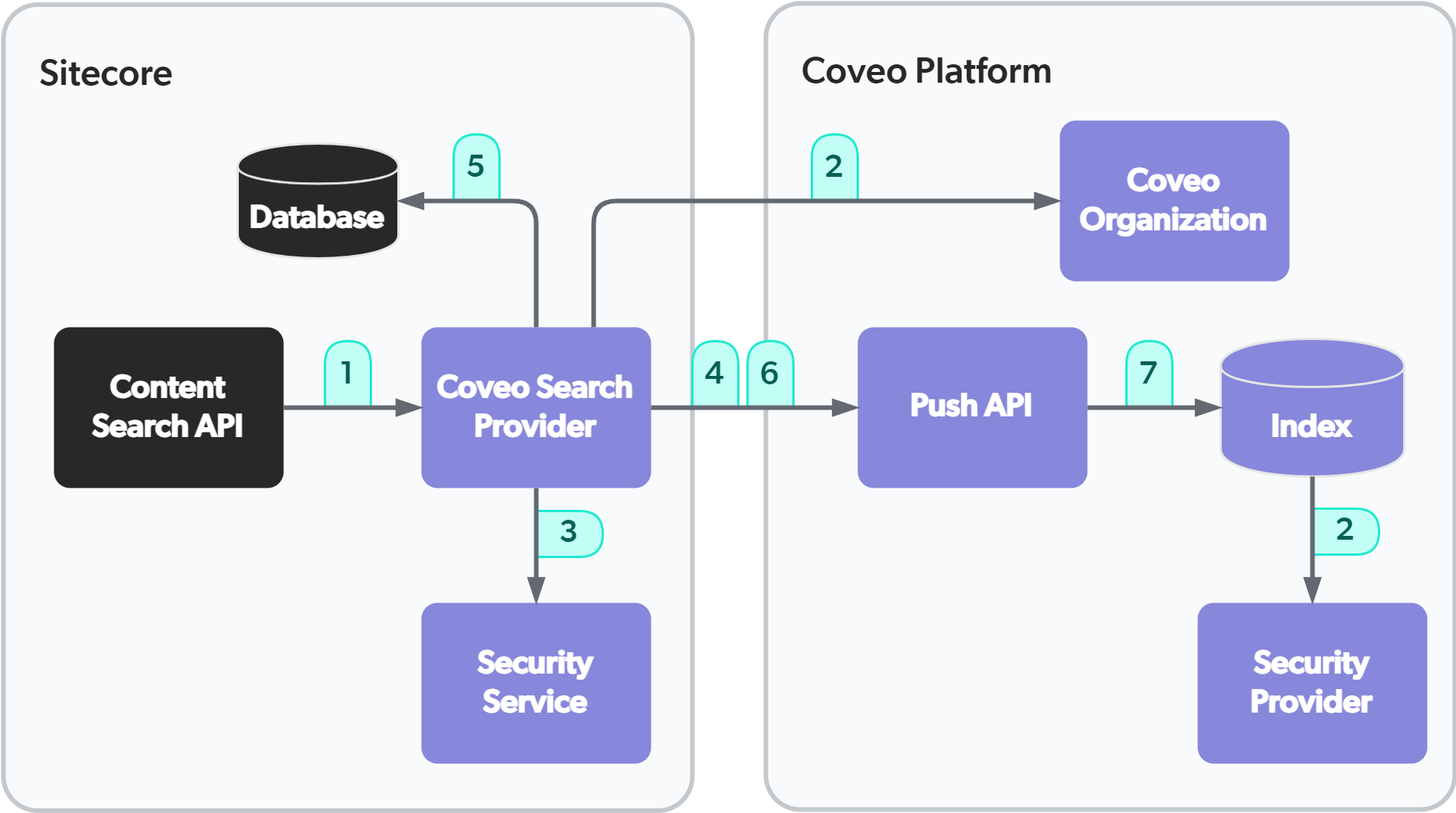
-
The Sitecore application from where you performed the rebuild (Sitecore Desktop or Content Editor) tells the Search Provider to rebuild the chosen search index (for example,
Coveo_master_index). -
The Coveo Search Provider tells the Coveo Platform to create everything necessary on the Coveo Platform side to begin indexing Sitecore items. This includes:
-
One Coveo field for each one of the Sitecore fields selected in the Fields section of the Indexing Manager (see About the Indexing Manager - Fields).
-
A field mapping for each Coveo organization field to map it to the corresponding Sitecore field.
-
A source of type Sitecore (for example,
Coveo_master_index - <farmname>). -
If the Sitecore security permissions are indexed, an Expanded Sitecore Security Provider (for example,
Expanded Sitecore Security Provider for <farmname>). The Sitecore Security Provider expands security permissions found on Sitecore items.
-
-
If Sitecore permissions are indexed, the Coveo Search Provider begins to retrieve the users and roles (known as identities) from Sitecore.
-
If Sitecore permissions are indexed, the Coveo Search Provider pushes those identities to the Push API.
-
The Coveo Search Provider begins to retrieve Sitecore items from the database corresponding to the chosen search index (for example,
master). -
The Coveo Search Provider pushes those Sitecore items to the Push API.
-
The Push API indexes those Sitecore items, including their selected fields and their security permissions, if applicable.
Scenario 2: Performing a query from a Coveo Hive search page through the proxy
|
|
Legacy feature
This section pertains to the Coveo Hive framework which is now in maintenance mode. Choose one of Coveo’s more modern, lightweight, and responsive libraries for any future search interface development. See the search interface Implementation guide for more details. |
Performing a query from a Coveo Hive search page when the Coveo for Sitecore REST Endpoint Proxy (typically located at http://<INSTANCE_HOSTNAME>/coveo/rest) is enabled causes these events to occur:
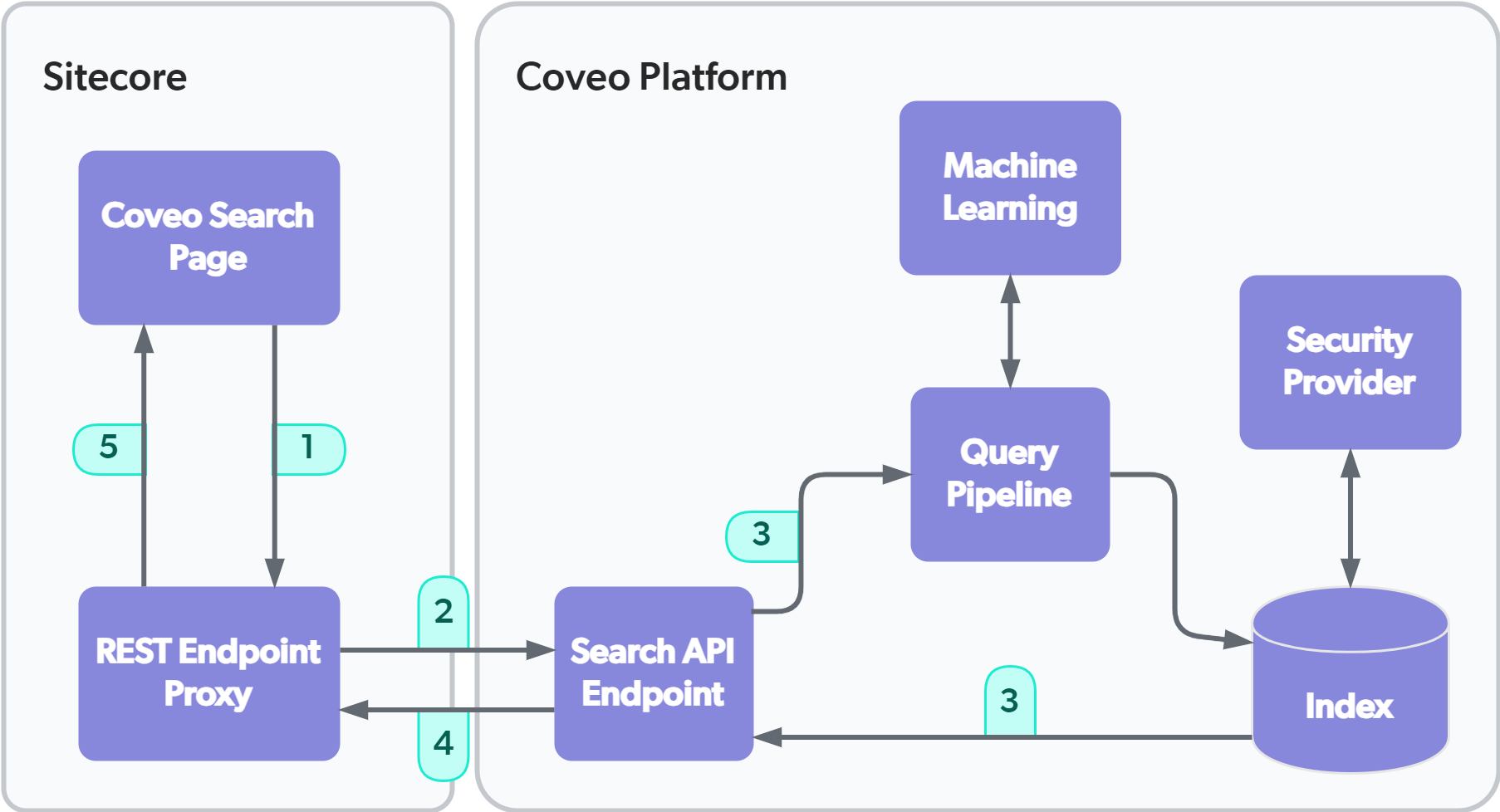
|
|
Note
When a user requests a Coveo-powered search page, a client-side process generates a search token using the API key and the user identities. The token is visible to the user in search page calls, but the API key isn’t. |
-
The Coveo Search Page sends the query to the Coveo for Sitecore REST Endpoint Proxy (typically located at
http://<INSTANCE_HOSTNAME>/coveo/rest). -
The REST Endpoint Proxy forwards the query to the Coveo Search API Endpoint.
-
The Coveo Platform processes the query and returns only the results that the user is allowed to view (see What’s a query pipeline?).
-
The Coveo Platform returns search results to the REST Endpoint Proxy in a JSON format.
-
The REST Endpoint Proxy returns the search results to the Coveo Search Page.
Scenario 3: Performing a query from a Coveo Hive search page directly to the Coveo Platform
|
|
Legacy feature
This section pertains to the Coveo Hive framework which is now in maintenance mode. Choose one of Coveo’s more modern, lightweight, and responsive libraries for any future search interface development. See the search interface Implementation guide for more details. |
You can now configure Coveo for Sitecore to bypass the REST Endpoint Proxy and have your Coveo Hive search pages perform calls directly to the Coveo Search API endpoint.
Performing a query from a Coveo Hive search page with the proxy disabled causes these events to occur:
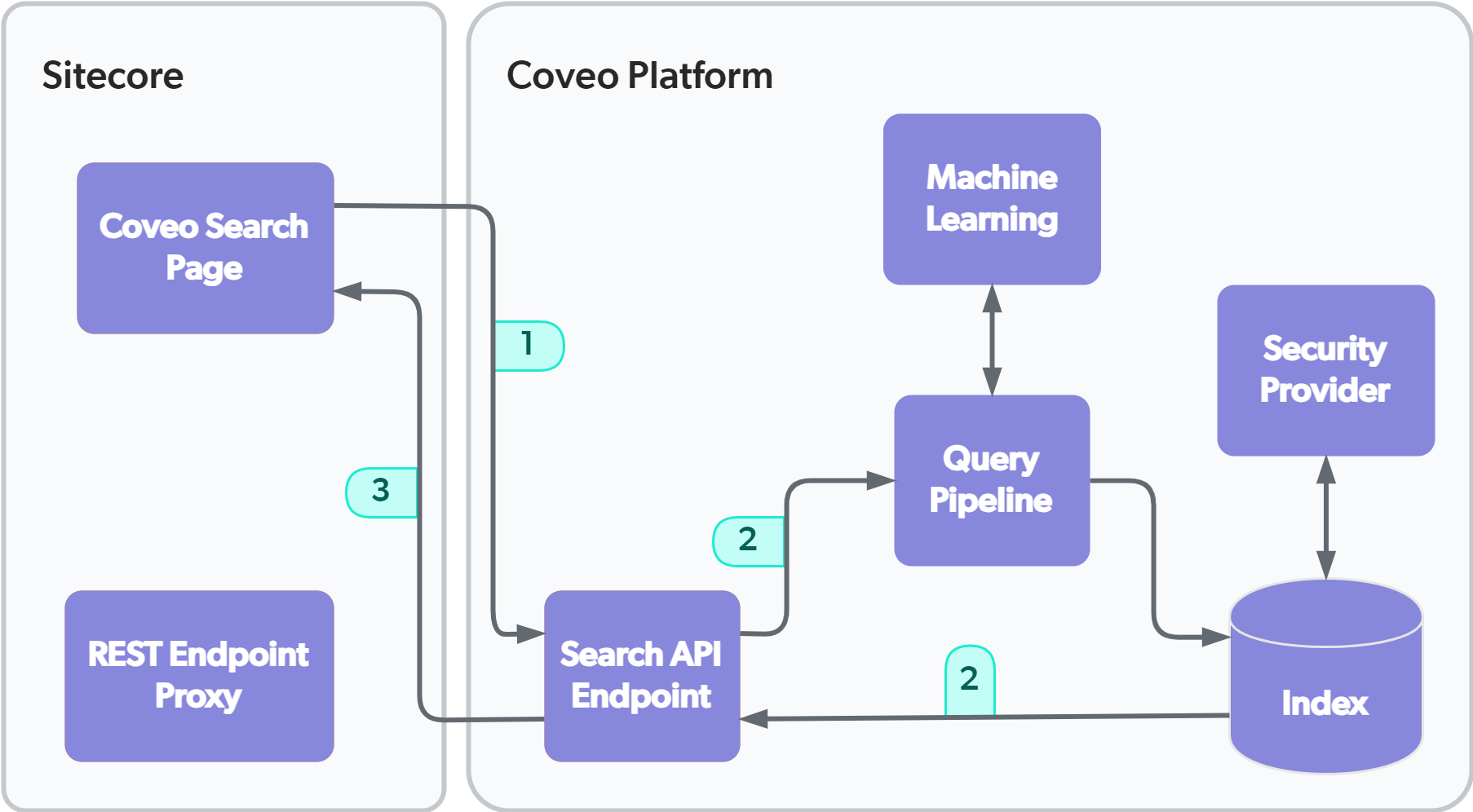
|
|
Note
When a user requests a Coveo-powered search page, a client-side process generates a search token using the API key and the user identities. The token is visible to the user in search page calls, but the API key isn’t. |
-
The Coveo Search Page sends the query to the Coveo Search API Endpoint.
-
The Coveo Platform processes the query and returns only the results that the user is allowed to view (see What’s a query pipeline?).
-
The Coveo Platform returns search results to the Coveo Search Page in a JSON format.