Add a Sitemap source
Add a Sitemap source
Members with the required privileges can use a Sitemap source to make the content of web pages listed in a sitemap file or sitemap index file searchable.
A sitemap file can be added to a website and is required when using a Sitemap source. The file contains a list of the website’s URLs along with their respective metadata which include the LMD (last-modified-date). This enables the Sitemap source to perform refresh updates, which the Web source doesn’t support. For this reason, although a Sitemap source requires the extra step of adding a sitemap file, it offers better performance than the Web source.
Source key characteristics
| Features | Supported | Additional information | |
|---|---|---|---|
Indexable content |
Web pages (URL) |
||
Sitemap file format |
|
Sitemap files and sitemap index files must respect the Sitemap protocol. Strict validations can be enforced by enabling the ParseSitemapInStrictMode option. |
|
The sitemap file must define the optional |
|||
Basic authentication |
Supported HTTP authentication schemes:
|
||
Form authentication |
|||
A variety of basic and advanced rules may be used to ignore the web pages you don’t want to index. |
|||
The Sitemap source automatically collects some metadata from your content. |
|||
Exclude irrelevant sections in pages and extract metadata. |
|||
Index metadata from third-party sitemap extensions or Coveo-specific metadata included in an XML sitemap file. |
|||
Web page custom metadata indexing |
Use the JSON-LD metadata feature and |
||
The Sitemap source crawler can execute JavaScript in a web page to dynamically render content before indexing the page. |
|||
Available at an extra charge. Contact Coveo Sales to add this feature to your Coveo organization license. |
|||
Default metadata
About the default metadata extracted by the Sitemap source
The Sitemap source automatically extracts metadata from HTML <meta> tags with a name attribute at the converter stage.
Given the <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /> tag, the following metadata is extracted by default:
Metadata name: viewport
Metadata value: width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0
A portion of this default metadata is automatically indexed in default fields for you. In this case, you can immediately use the indexed metadata in a search interface (for example, in a facet) by referencing the field.
The remaining default metadata is not indexed by default. In this case, you need to create a field and mapping before the metadata can be used in a search interface. This process is explained in the Completion section.
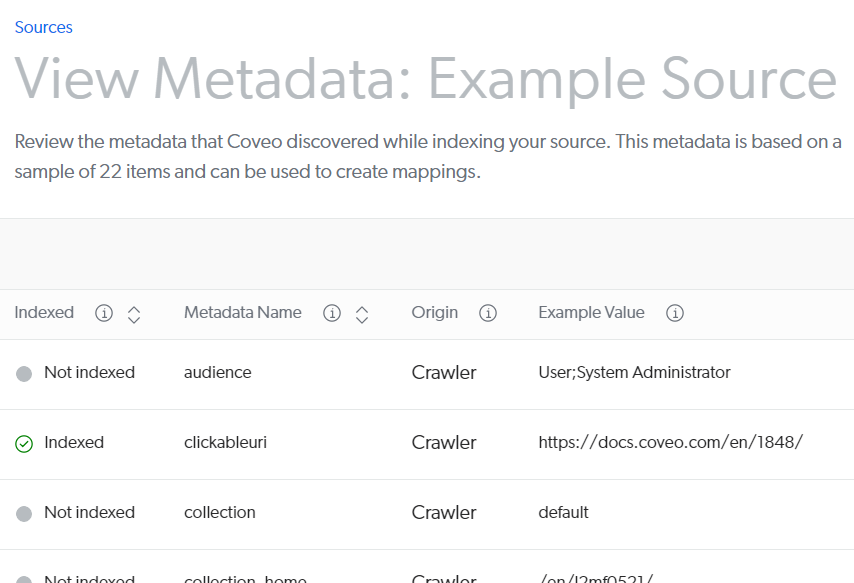
To view all the metadata a source automatically extracts (as well as the custom metadata you’re extracting), access the View and map metadata subpage after your rebuilds.
Limitations
-
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) and CAPTCHA aren’t supported.
-
Indexing page permissions isn’t supported.
-
The Sitemap source doesn’t support
robots.txtfiles. -
Content in pop-up windows and page elements requiring interaction aren’t indexed.
-
The Coveo indexing pipeline can handle web pages up to 512 MB only. Larger pages are indexed by reference (that is, their content is ignored by the Coveo crawler, and only their metadata and path are searchable). Therefore, no search result Quick view is available for these larger items.
-
When the Execute JavaScript on pages option is enabled:
-
The Sitemap source doesn’t support sending
AdditionalHeaders. -
The Sitemap source doesn’t support the
UseProxyparameter. -
Basic authentication isn’t supported.
-
-
The
UseProxyparameter can’t be used in combination with Form authentication. -
When indexing content with the Crawling Module, ensure not to change space character encoding in your items' URIs, as Coveo uses these URIs to distinguish items.
For example, an item whose URI would change from
example.com/my first itemtoexample.com/my%20first%20itemwouldn’t be recognized as the same by Coveo. As a result, it would be indexed twice, and the older version wouldn’t be deleted.Item URIs are displayed in the Content Browser (platform-ca | platform-eu | platform-au). We recommend you check where these URIs come from before making changes that affect space character encoding. Depending on your source type, the URI may be an item’s URL, or it may be built out of pieces of metadata by your source mapping rules. For example, your item URIs may consist in the main site URL, plus the item filename, due to a mapping rule such as
example.com/%[filename]. In such a case, changing space encoding in the item filename could impact the URI.
Leading practices
-
Ensure that you have the right to crawl the public content in the event where you aren’t the owner of the website. Crawling sites that you don’t own nor have the right to crawl could create reachability issues.
Furthermore, certain sites may use security mechanisms that can impact Coveo’s ability to retrieve the content. If you’re unfamiliar with these mechanisms, we recommend investigating and learning about them beforehand. For example, one impact this type of software (for example, Akamai, Cloudflare) can have is detecting our crawler as an attack and blocking us from any further crawling.
-
Always try authenticating without a custom login sequence first. You should only start working on a custom login sequence when you’re sure your form authentication details (that is, login address, user credentials, confirmation method) are accurate and that the standard form authentication process doesn’t work.
-
It’s best to create or edit your source in your sandbox organization first. Once you have confirmed that it indexes the desired content, you can copy your source configuration to your production organization, either with a snapshot or manually.
See About non-production organizations for more information and best practices regarding sandbox organizations.
-
The number of items that a source processes per hour (crawling speed) depends on various factors, such as network bandwidth and source configuration. See About Crawling Speed for information on what can impact crawling speed, as well as possible solutions.
-
Break down large sitemap files into multiple sitemap files.
-
Group your source and the other implementation resources together in a project. See Manage projects.
Add a Sitemap source
-
On the Sources (platform-ca | platform-eu | platform-au) page, click Add source.
-
In the Add a source of content panel, click the Cloud (
) or Crawling Module (
) tile, depending on your content retrieval context.
 Crawling Module Sitemap source creation requirements
Crawling Module Sitemap source creation requirements-
Make sure you meet all Crawling Module requirements.
-
Make sure you deploy the Crawling Module on your server before creating the Sitemap source.
-
-
In the Add a new Sitemap source / Add a new Crawling Module Sitemap source panel, fill in the following fields.
Name: Use a short and descriptive name, using only letters, numbers, hyphens (-), and underscores (_). The source name can’t be modified once it’s saved.
Sitemap URLs: Enter the direct sitemap URL, and not the sitemap website address. Otherwise, the source can interpret the URLs as HTML format sitemap files and crawl the links they contain.
Examples of sitemap URLs-
Public website sitemap:
http://myorgwebsite.com/sitemap.xml -
Public website sitemap compressed with GZIP:
http://myorgwebsite.com/sitemap.xml.gz
Notes-
The Sitemap source only crawls pages listed in a sitemap file. It doesn’t crawl links in the listed web pages themselves.
-
The
ParseSitemapInStrictModeJSON parameter dictates the extent of validation the Sitemap source applies on sitemap and sitemap index files, and on their referenced URLs.
-
-
If you’re creating a Crawling Module Sitemap source, in the Crawling Module dropdown menu, select the installed Crawling Module instance.
-
Click Next.
-
Select who has permission to access the content through the search interface and click Add source.
NoteThis information is editable later in the Content security tab.
-
Configure your source.
|
|
Note
You can save your source settings at any time by clicking Save. |
"Configuration" tab
The Configuration tab lets you manage the crawling rules, web scraping configurations, advanced settings, and authentication methods of your source. These configuration groups are presented in subtabs.
"Crawling rules" subtab
The Crawling rules subtab lets you define the specific pages to index.
Sitemap URLs
Enter the direct sitemap URL, and not the sitemap website address. Otherwise, the source can interpret the URLs as HTML format sitemap files and crawl the links they contain.
-
Public website sitemap:
http://myorgwebsite.com/sitemap.xml -
Public website sitemap compressed with GZIP:
http://myorgwebsite.com/sitemap.xml.gz
|
|
Notes
|
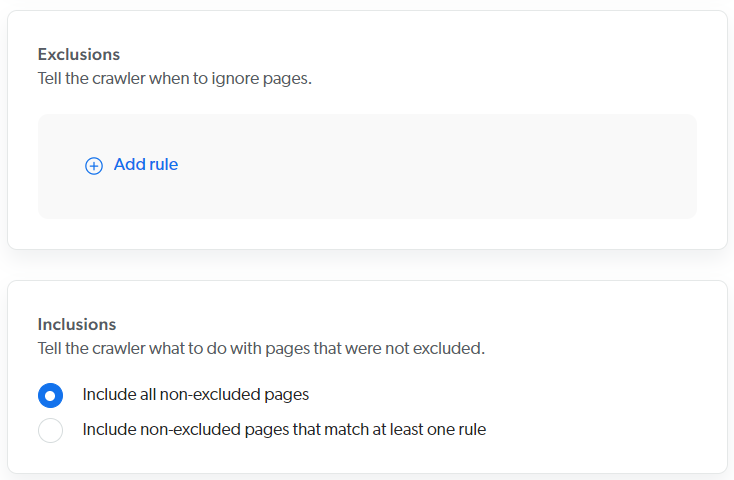
Exclusions and inclusions
Add exclusion and inclusion rules to crawl only specific items based on their URL.
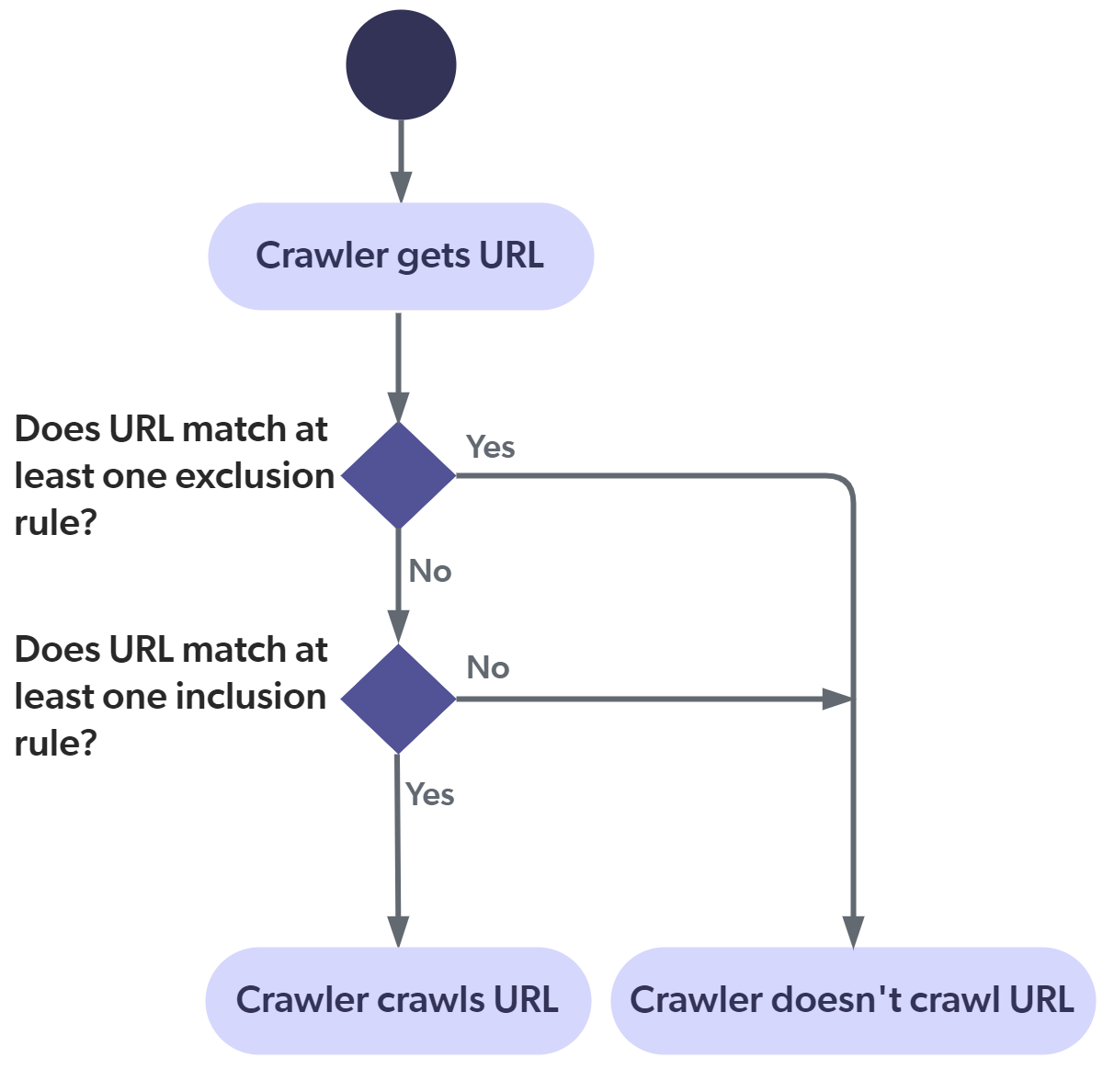
The following diagram illustrates how the Sitemap crawler applies the exclusion and inclusion rules. This flow applies to all pages, including the sitemap URLs. You must therefore pay attention to not filter out your sitemap URLs.
|
|
About the "Include all non-excluded pages" option
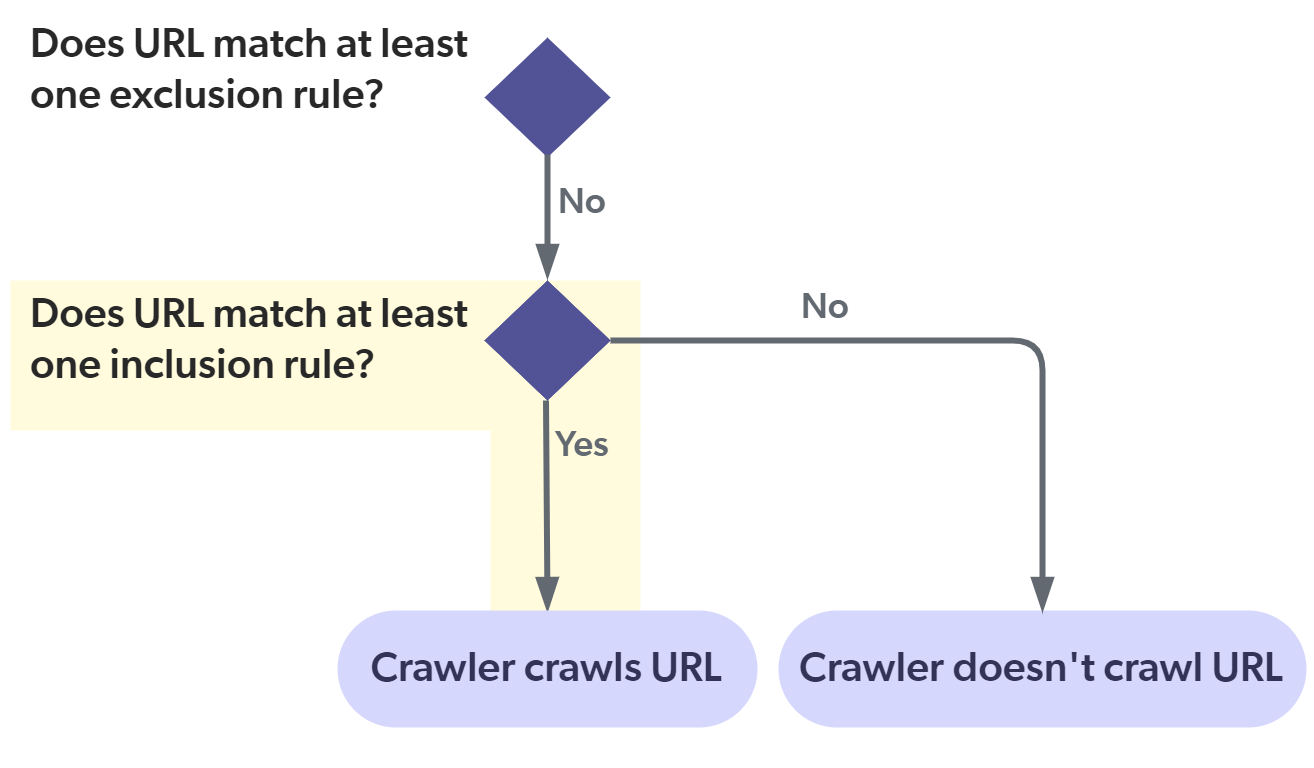
The Include all non-excluded pages option automatically adds an "include all" inclusion rule in the background.
This ensures that all sitemap URLs meet the |
You can use any of the six types of rules:
-
is and a URL that includes the protocol. For example,
https://myfood.com/. -
contains and a string found in the URL. For example,
recipes. -
begins with and a string found at the beginning of the URL and which includes the protocol. For example,
https://myfood. -
ends with and a string found at the end of the URL. For example,
.pdf. -
matches wilcard rule and a wildcard expression that matches the whole URL. For example,
https://myfood.com/recipes*. -
matches regex rule and a regex rule that matches the whole URL. For example,
^.*(company-(dev|staging)).*html.?$.When using regex rules, make sure they match the desired URLs with a testing tool such as Regex101.
"Web scraping" subtab
The Web scraping subtab lists and lets you manage web scraping configurations for your source.
When the crawler is about to index a page, it checks whether it must apply web scraping configurations that have been defined. The crawler considers the Pages to target rules of each of your web scraping configurations, starting with the configuration at the top of your list. The crawler will either apply the first matching configuration or all matching configurations.
All new Sitemap sources are created with a default web scraping configuration that excludes typical repetitive elements found in web pages that shouldn’t be indexed.
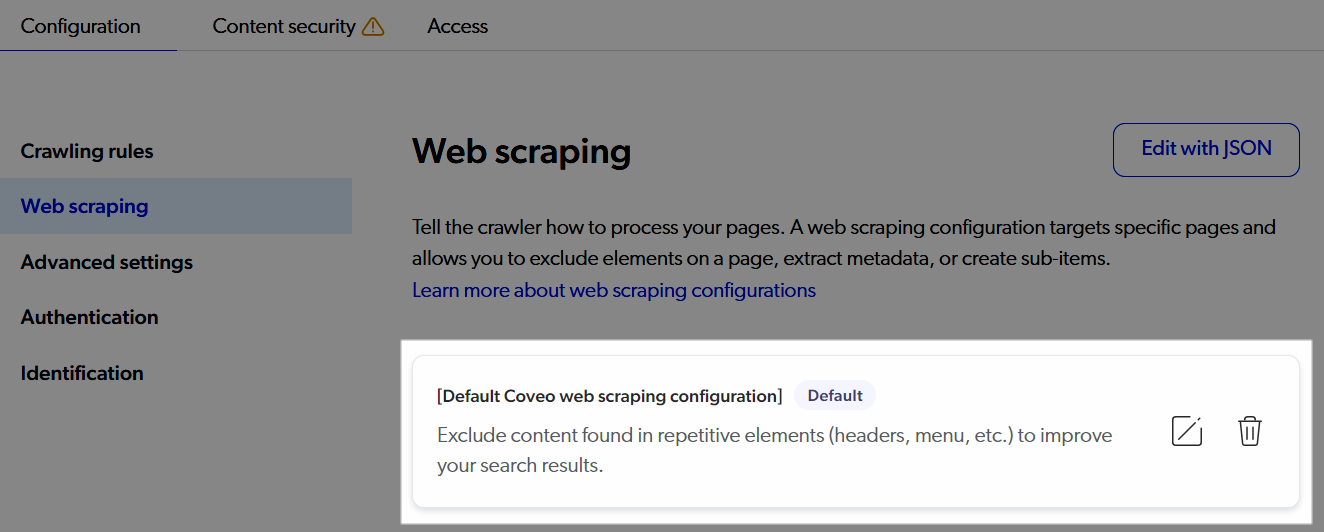
Existing Sitemap sources without a web scraping configuration prompt you to add the default configuration when you access the Web scraping subtab.
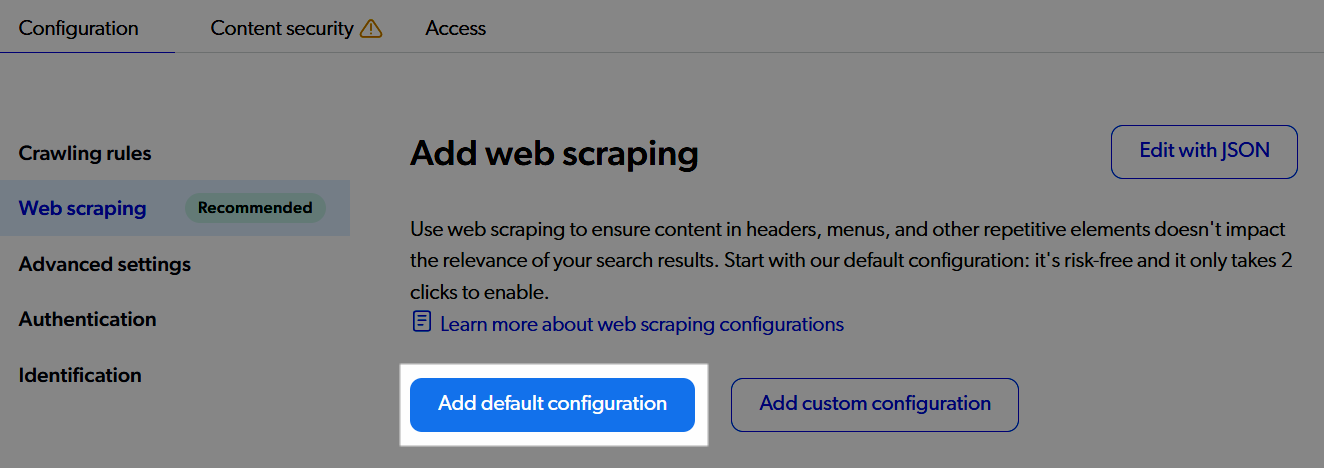
|
|
When no web scraping configuration is defined:
Indexing irrelevant page sections and not extracting custom metadata reduces quality of search results. |
The Sitemap source features two web scraping configuration management modes: UI-assisted mode and Edit with JSON mode.
UI-assisted mode
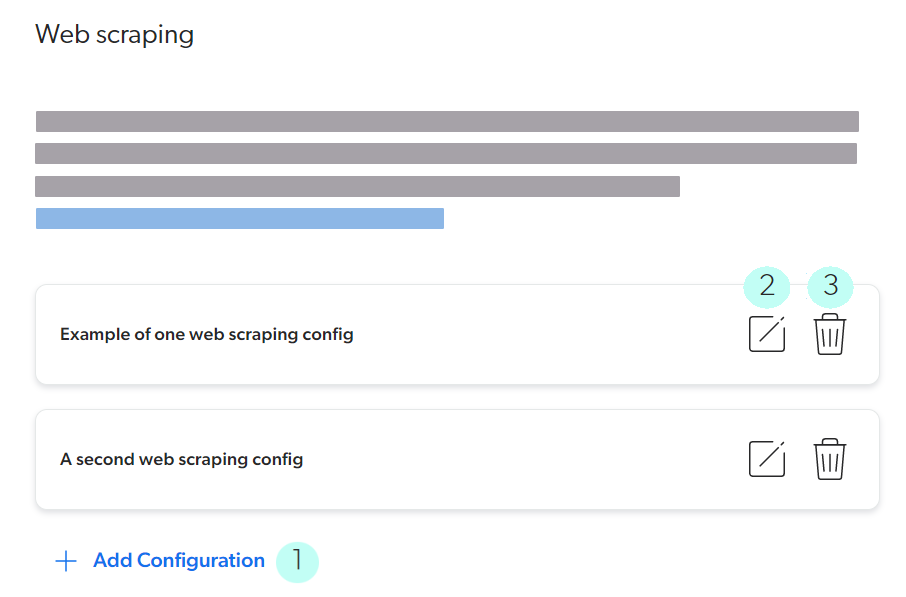
You can add (1), edit (2), and delete (3) one web scraping configuration at a time with a user interface that makes many technical aspects transparent. UI-assisted mode is easier to use and more mistake-proof than Edit with JSON mode.
This is now the recommended mode for all web scraping configurations.
When you add or edit a web scraping configuration using UI-assisted mode, the Add/Edit a web scraping configuration panel is displayed. See Configurations in UI-assisted mode for more details.
Edit with JSON mode
The Edit with JSON button gives access to the aggregated web scraping JSON configuration of the source. Adding, editing, and deleting configurations directly in the JSON requires more technical skills than using UI-assisted mode.


When you add or edit a web scraping configuration in Edit with JSON mode, the Edit a web scraping JSON configuration panel is displayed. See Configurations in Edit with JSON mode for more details.
Single-match vs multi-match
The Sitemap source can apply web scraping configurations in two ways: single-match or multi-match.
In single-match mode, the crawler applies only the first matching web scraping configuration. In multi-match mode, the crawler applies all matching web scraping configurations.
The animation below demonstrates the application of three web scraping configurations on a culinary website featuring news articles and recipe pages, in single-match mode (left) and multi-match mode (right).
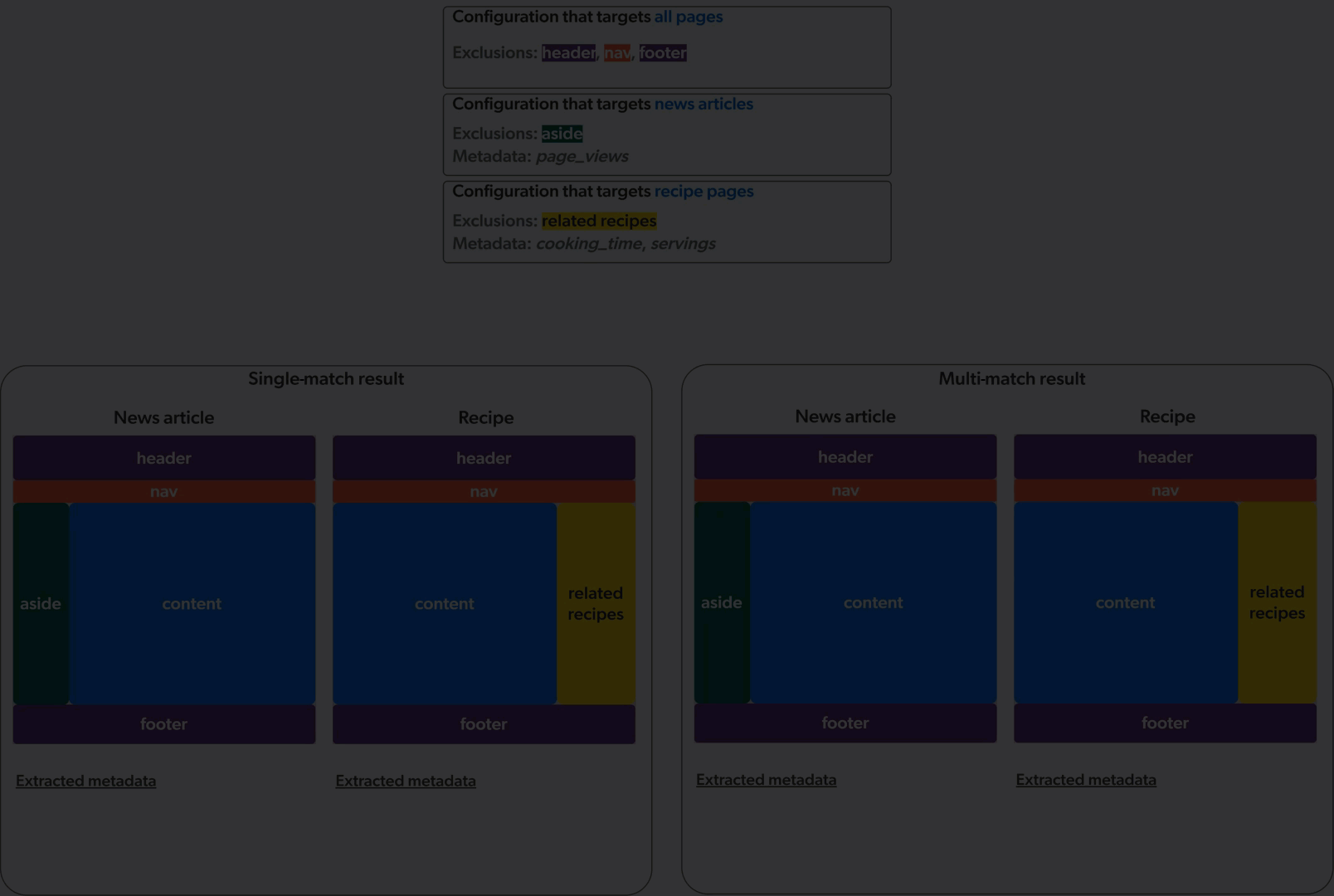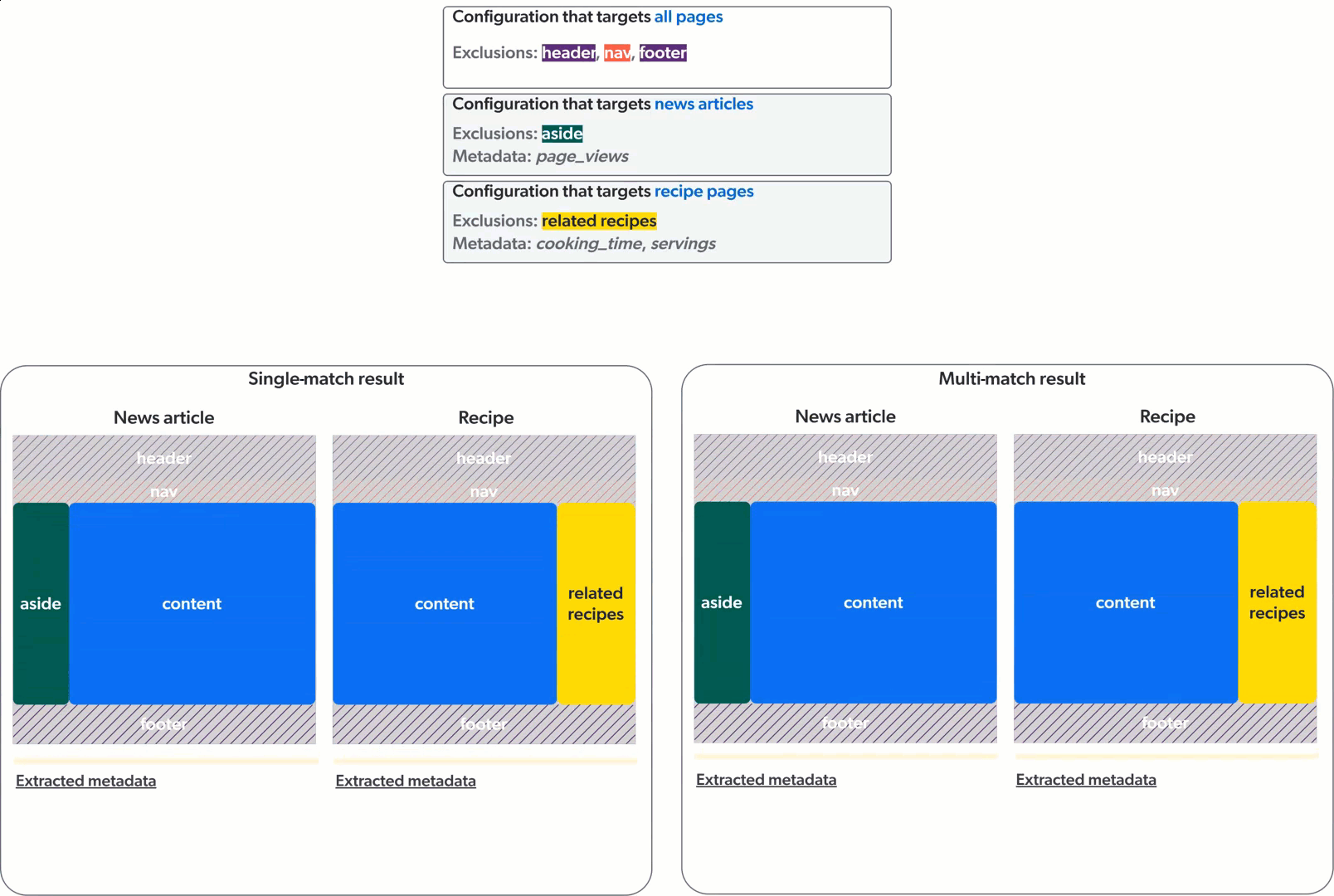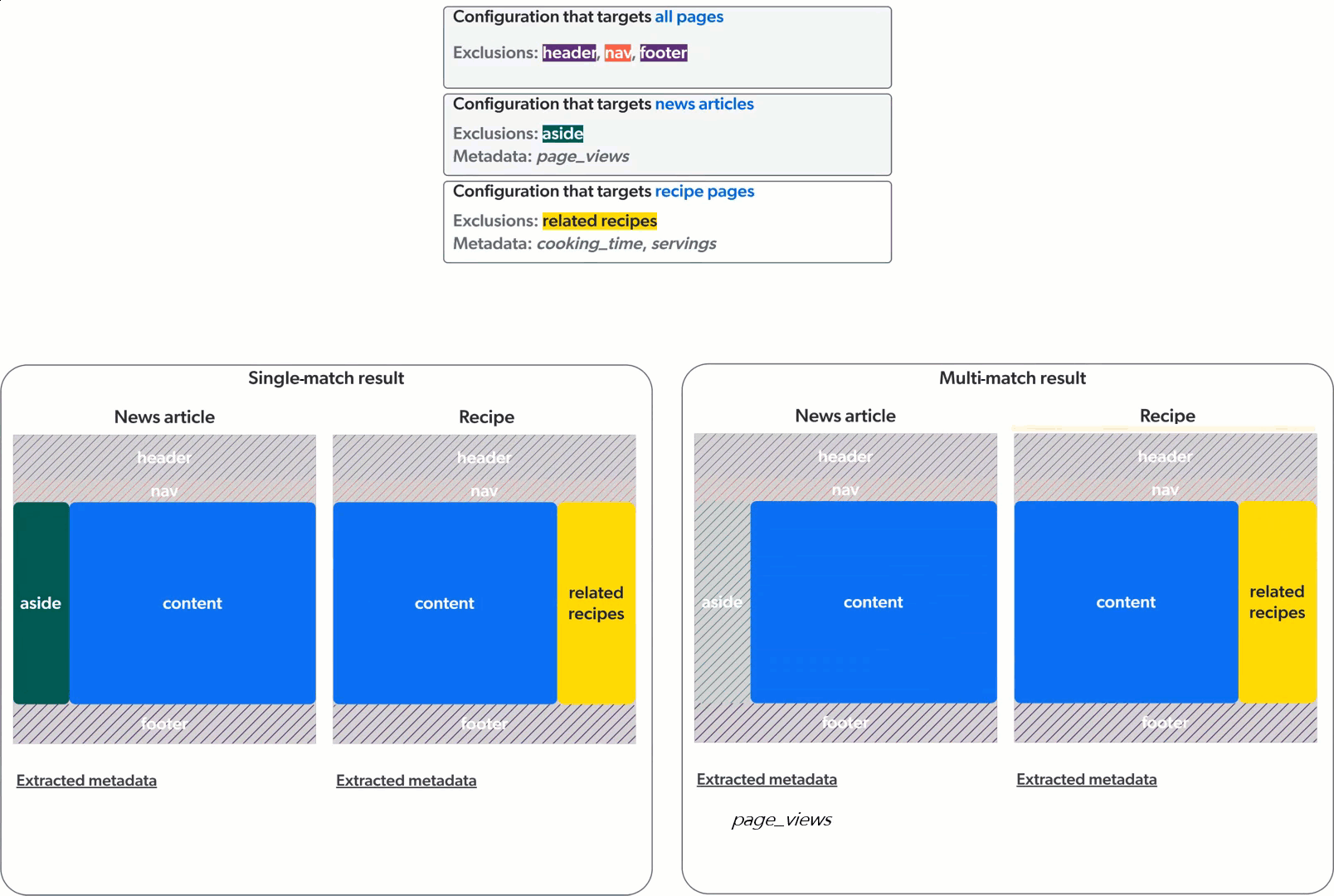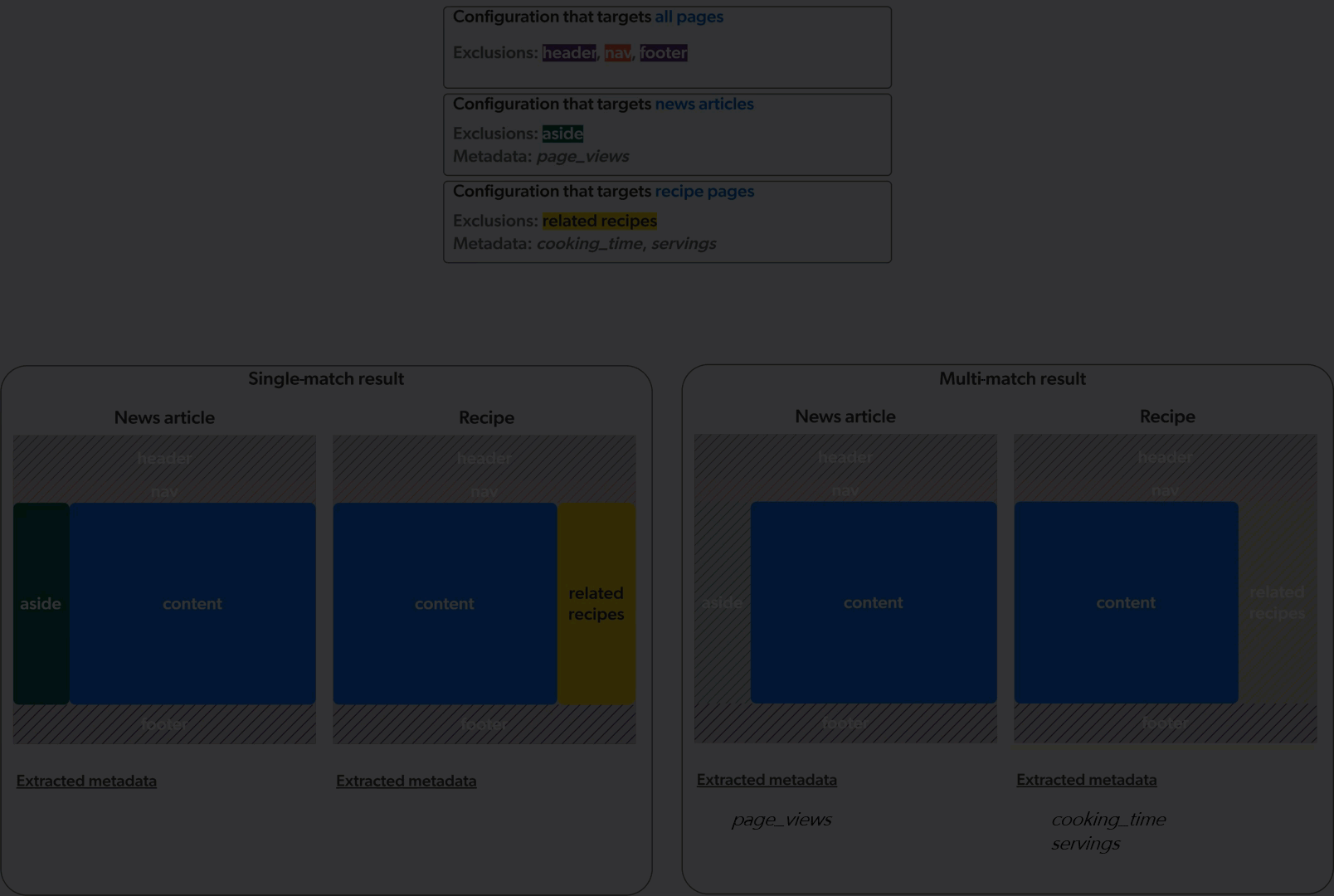
Sitemap sources created before mid-December 2023 were created in single-match mode. All new Sitemap sources are created in multi-match mode.
Coveo converted existing single-match sources containing zero or one web scraping configuration to multi-match mode. We recommend you convert any remaining single-match Sitemap source to multi-match mode.
If a Sitemap source is currently in single-match mode, the Web scraping subtab displays a banner prompting you to convert to multi-match mode.

To convert a Sitemap source to multi-match mode
-
In the Web scraping subtab, click Switch to multi-match mode.
-
Confirm you want to convert the source to multi-match mode.
A green You’re currently in multi-match mode banner then appears.
-
Click Save.
Once your source is fully converted, the Web scraping subtab no longer shows the green banner and the subtab description reflects the multi-match mode behavior.
"Advanced settings" subtab
The Advanced settings subtab lets you customize the Coveo crawler behavior. All advanced settings have default values, which are adequate in most use cases.
Content and images
If you want Coveo to extract text from image files or PDF files containing images, enable the appropriate option.
The extracted text is processed as item data, meaning that it’s fully searchable and will appear in the item Quick view. See Enable optical character recognition for details on this feature.
Execute JavaScript on pages
Only enable this option when some website content you want to consider for indexing is dynamically rendered by JavaScript. Enabling this option may significantly increase the time needed to crawl pages.
When Execute JavaScript on pages is enabled, specify the Add time for the crawler to wait before considering a page as fully rendered value.
When you set this value to 0 (default), the crawler doesn’t wait after the page is loaded.
If the JavaScript takes longer to execute than normal or makes asynchronous calls, consider increasing this value to ensure that the pages with the longest rendering time are indexed with all the dynamically rendered content.
Extract JSON-LD metadata
If you have JSON-LD metadata in your HTML pages that you want to index, enable the Extract JSON-LD metadata option.
When enabled, JSON-LD objects in the web page are extracted, flattened, and represented in jsonld.parent.child metadata format in your Coveo organization.
Given the following JSON-LD script tag in a web page:
<script id="jsonld" type="application/ld+json">
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "NewsArticle",
"url": "http://www.bbc.com/news/world-us-canada-39324587",
"publisher": {
"@type": "Organization",
"name": "BBC News",
"logo": "http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/special/2015/newsspec_10857/bbc_news_logo.png?cb=1"
},
"headline": "Canada Strikes Gold in Olympic Hockey Final"
}
</script>On an indexing action, the Sitemap connector would extract BBC News as the value for the jsonld.publisher.name metadata.
To index this metadata, you would therefore need to use %[jsonld.publisher.name] as the mapping rule for your field.
Time the crawler waits between requests to your server
Indicate the number of milliseconds between consecutive HTTP requests to the website server. The default value is 1000 milliseconds, which represents a crawling rate of one page per second.
"Authentication" subtab
The Authentication settings, used by the source crawler, emulate the behavior of a user authenticating to access restricted website content. If authentication is required, select the authentication type your website uses, whether Basic authentication or Form authentication. Then, provide the corresponding login details.
|
|
Whether you use Basic or Form authentication, limit your source crawling scope to one domain that you own. This reduces the risk of exposing your authentication credentials. |
|
|
Note
Manual form authentication is now only available on legacy sources. We recommend you migrate existing Manual form authentication sources to Form authentication. |
Basic authentication
When selecting Basic authentication, enter the credentials of an account on the website you’re making searchable. See Source credentials leading practices.
If your sitemap contains a link to a page of a different domain or subdomain that also requires basic authentication, the Sitemap source will provide the credentials you entered when challenged.
|
|
To prevent exposing your credentials, provide username and password information only when the site uses a communication protocol secured with TLS or SSL (HTTPS). You are responsible for ensuring that your Sitemap links requiring basic authentication credentials use HTTPS for increased security. The basic authentication credentials you enter will be provided, regardless of whether the link requiring these credentials uses HTTP or HTTPS. |
Form authentication
You can choose between two form authentication workflows:
Force authentication disabled (recommended)
With Force authentication disabled, the workflow typically goes as follows:
-
Coveo’s crawler requests a protected page.
-
The web server redirects the crawler to the Login page address.
-
Using the configured Validation method, the crawler determines it’s not authenticated. This automatically triggers the next step.
-
The crawler performs a standard login sequence using the provided Login details, or the Custom login sequence if one is configured.
-
After successful authentication, the web server responds by redirecting back to the requested protected page and returning cookies.
-
The crawler follows the server redirect to get the protected page and indexes that page.
-
The crawler requests the other pages using the cookies.
This is the default and recommended workflow as it emulates human behavior the best and ensures crawler re-authentication, when needed.
Force authentication enabled
With Force authentication enabled, the workflow typically goes as follows:
-
The crawler performs a standard login sequence using the provided Login details, or the Custom login sequence if one is configured.
-
After successful authentication, the web server responds with cookies that the crawler will use to request other pages.
-
The crawler requests the first URL from the web server using the cookies and indexes that page.
-
The crawler requests other pages using the cookies.
If the crawler loses authentication at some point (for example, if a cookie expires), it has no way of knowing it must re-authenticate unless you have a proper authentication status validation method. As a result, you may notice at some point that your source has indexed some, but not all, protected pages.
Only use Force authentication when no reliable authentication status validation method can be configured.
Username and password
Enter the credentials required to access the secured content. See Source credentials leading practices.
Login page address
Enter the URL of the website login page where the username and password are to be used.
Loading delay
Enter the maximum time the crawler should allow for JavaScript to execute and go through the login sequence before timing out.
Validation method
The crawler uses the validation method after requesting a page from the web server to know if it’s authenticated or not. When the validation method reveals that the crawler isn’t authenticated, the crawler immediately tries to re-authenticate.
To configure the validation method
-
In the dropdown menu, select your preferred authentication status validation method.
-
In the Value(s) field, specify the corresponding URL, regex or text.
-
For Redirection to URL:
Enter the URL where users trying to access protected content on the website are redirected to when they’re not authenticated. If the crawler is redirected to this URL, it will immediately authenticate (or re-authenticate).
Examplehttps://mycompany.com/login/failed.html -
For Text not found in page:
Enter the text that appears on the page after successful authentication. If this text isn’t found on the page, the crawler will immediately authenticate (or re-authenticate).
ExampleWhen a user successfully logs in, the page shows a "Hello, <USERNAME>!" greeting text. If the login username you specified was
jsmith@mycompany.com, the text to enter would be:Hello, jsmith@mycompany.com!ExampleLog out -
For Text found in page:
Enter the text that appears on the page when a user isn’t authenticated. If this text is found on the page, the crawler will immediately authenticate (or re-authenticate).
Examples-
An error has occurred. -
Your username or password is invalid.
-
-
For Cookie not found:
Enter the name of the cookie returned by the server after successful authentication. If this cookie isn’t found, the crawler will immediately authenticate (or re-authenticate).
ExampleASP.NET_SessionId -
For URL matches regex:
Enter a regex rule that matches the URL where users trying to access protected content are redirected to when they’re not authenticated. If the crawler is redirected to a URL that matches this regex, it will immediately authenticate (or re-authenticate).
Example.+Account\/Login.* -
For URL doesn’t match regex:
Enter a regex rule that matches the URL where users trying to access protected content are redirected to after successful authentication. If the crawler isn’t redirected to a URL that matches this regex, it will immediately authenticate (or re-authenticate).
-
Force authentication
Select this option if you want Coveo’s first request to be for authentication, regardless of whether it is actually required.
|
|
You should only force authentication if you have no reliable authentication status validation method. |
Custom login sequence
If the web page requires specific actions during the login process, you might have to configure a custom login sequence.
|
|
The standard source login sequence can handle various third-party login pages (for example, OneLogin, Google, Salesforce) and will try to automatically detect and login on first-party login forms. Make sure the standard source login sequence doesn’t work before configuring a custom login sequence. |
Custom login sequences have the following limitations:
-
They can have no more than five steps.
-
All steps must contain no more than ten actions.
-
There can only be one step to enter the password.
Contact the Coveo Support team if you need help.
"Crawling Module" subtab
If your source is a Crawling Module source, and if you have more than one Crawling Module linked to this organization, select the one with which you want to pair your source. If you change the Crawling Module instance paired with your source, a successful rebuild is required for your change to apply.
"Identification" subtab
The Identification subtab contains general information about the source.
Name
The source name. It can’t be modified once it’s saved.
"Content security" tab
Select who will be able to access the source items through a Coveo-powered search interface. For details on this parameter, see Content security.
"Access" tab
In the Access tab, set whether each group (and API key, if applicable) in your Coveo organization can view or edit the current source.
For example, when creating a new source, you could decide that members of Group A can edit its configuration while Group B can only view it.
See Custom access level for more information.
Completion
-
Finish adding or editing your source:
-
When you want to save your source configuration changes without starting a build/rebuild, such as when you know you want to do other changes soon, click Add source/Save.
-
When you’re done editing the source and want to make changes effective, click Add and build source/Save and rebuild source.
NoteOn the Sources (platform-ca | platform-eu | platform-au) page, you must click Launch build or Start required rebuild in the source Status column to add the source content or to make your changes effective, respectively.
Back on the Sources (platform-ca | platform-eu | platform-au) page, you can follow the progress of your source addition or modification.
Once the source is built or rebuilt, you can review its content in the Content Browser.
-
-
Once your source is done building or rebuilding, review the metadata Coveo is retrieving from your content.
-
On the Sources (platform-ca | platform-eu | platform-au) page, click your source, and then click More > View and map metadata in the Action bar.
-
If you want to use a currently not indexed metadata in a facet or result template, map it to a field.
-
Click the metadata and then, at the top right, click Add to Index.
-
In the Apply a mapping on all item types of a source panel, select the field you want to map the metadata to, or add a new field if none of the existing fields are appropriate.
Notes-
For details on configuring a new field, see Add or edit a field.
-
For advanced mapping configurations, like applying a mapping to a specific item type, see Manage mappings.
-
-
Click Apply mapping.
-
-
Depending on the source type you use, you may be able to extract additional metadata from your content. You can then map that metadata to a field, just like you did for the default metadata.
More on custom metadata extraction and indexing
Some source types let you define rules to extract metadata beyond the default metadata Coveo discovers during the initial source build.
For example:
Source type Custom metadata extraction methods Define metadata key-value pairs in the
addOrUpdatesection of thePUTrequest payload used to upload push operations to an Amazon S3 file container.REST API
and
GraphQL APIIn the JSON configuration (REST API | GraphQL API) of the source, define metadata names (REST API | GraphQL API) and specify where to locate the metadata values in the JSON API response Coveo receives.
Add
<CustomField>elements in the XML configuration. Each element defines a metadata name and the database field to use to populate the metadata with.-
Configure web scraping configurations that contain metadata extraction rules using CSS or XPath selectors.
-
Extract metadata from JSON-LD
<script>tags.
-
Configure web scraping configurations that contain metadata extraction rules using CSS or XPath selectors.
-
Extract JSON-LD
<script>tag metadata. -
Extract
<meta>tag content using theIndexHtmlMetadataJSON parameter.
Some source types automatically map metadata to default or user created fields, making the mapping process unnecessary. Some source types automatically create mappings and fields for you when you configure metadata extraction.
See your source type documentation for more details.
-
-
When you’re done reviewing and mapping metadata, return to the Sources (platform-ca | platform-eu | platform-au) page.
-
To reindex your source with your new mappings, click Launch rebuild in the source Status column.
-
Once the source is rebuilt, you can review its content in the Content Browser.
-
Troubleshooting
After a rebuild, you may notice that your source isn’t indexing as expected. For example, there may be missing or extra items, or the values of some fields may not meet your requirements.
To help you troubleshoot, refer to the list of common issues and solutions when using the Sitemap source.
Required privileges
You can assign privileges to allow access to specific tools in the Coveo Administration Console. The following table indicates the privileges required to view or edit elements of the Sources (platform-ca | platform-eu | platform-au) page and associated panels. See Manage privileges and Privilege reference for more information.
|
|
Note
The Edit all privilege isn’t required to create sources. When granting privileges for the Sources domain, you can grant a group or API key the View all or Custom access level, instead of Edit all, and then select the Can Create checkbox to allow users to create sources. See Can Create ability dependence for more information. |
| Actions | Service | Domain | Required access level |
|---|---|---|---|
View sources, view source update schedules, and subscribe to source notifications |
Content |
Fields |
View |
Sources |
|||
Organization |
Organization |
||
Edit sources, edit source update schedules, and view the View and map metadata subpage |
Content |
Fields |
Edit |
Sources |
|||
Content |
Source metadata |
View |
|
Organization |
Organization |
Migrate from manual form authentication
If you’re using manual form authentication, you’ll see a "Manual form authentication deprecation" warning when viewing the Authentication subtab. You’ll want to migrate to form authentication. To do so, we recommend you create a duplicate of your source and configure form authentication on the duplicate. When the duplicate is configured and fully tested, you can copy its configuration to the original source.
If you’re using a sandbox organization and a snapshot-based phased rollout, the alternative is to copy your original source and related resources configurations to your sandbox using the resource snapshots feature. Once your sandbox source authentication configurations updated and fully tested, you can use a snapshot to apply your changes to your production organization source.
Though the following procedure uses the source duplicate method, steps 3 to 8 inclusively are common to both methods.
To migrate from manual form authentication to form authentication
-
On the Sources (platform-ca | platform-eu | platform-au) page, click your source, and then click More > Duplicate in the Action bar.
-
Name your duplicate.
-
Click your duplicate source, and then click Edit in the Action bar.
-
Select the Authentication subtab.
-
Select the Form authentication radio button.
The following fields will be populated automatically using your existing manual form authentication settings: Username, Password, Login page address, Validation method and Value(s), Force authentication.
-
Rebuild your duplicate source.
-
Make sure that your duplicate source contains properly indexed content. Things you should check for:
-
Your duplicate source contains the same number of items as the original source.
-
For pages that are authentication protected in your website, make sure the Quick view of the corresponding items in your duplicate source shows the content of the actual website page. If form authentication fails, the item Quick view may display the content of your form authentication login page instead of the actual website page.
-
-
If form authentication is failing, consider making the following adjustments to your duplicate source form authentication configuration:
-
Changing the Validation method and associated Value(s) to a more reliable combination.
-
Increasing the Loading delay.
-
Setting up a custom login sequence.
Contact Coveo Support if you need help.
-
-
When you’re sure the authentication configuration on your duplicate source works, apply the changes to the original source.
-
On the Sources (platform-ca | platform-eu | platform-au) page, click your duplicate source, and then click More > Edit configuration with JSON in the Action bar.
-
Copy the
FormAuthenticationConfigurationJSON object. The object looks like the following:"FormAuthenticationConfiguration": { "sensitive": false, "value": "{\"authenticationFailed\":{\"method\":\"RedirectedToUrl\",\"values\":[\"https://something.com/Account/Login\"]},\"inputs\":[], \"formUrl\":\"https://something.com/Account/Login\",\"enableJavaScript\":true,\"forceLogin\":false,\"javaScriptLoadingDelayInMilliseconds\":2000,\"customLoginSequence\":{}}" } -
On the Sources (platform-ca | platform-eu | platform-au) page, click your original source, and then click More > Edit configuration with JSON in the Action bar.
-
Replace the
FormAuthenticationConfigurationobject with the one from your duplicate source. -
Click Save.
-
What’s next?
-
If you’re using the Crawling Module to retrieve your content, consider subscribing to deactivation notifications to receive an alert when a Crawling Module component becomes obsolete and stops the content crawling process.