Add a Google Drive for Work source
Add a Google Drive for Work source
You can add the content of your domain’s Google Drives to a Coveo organization by creating a Google Drive for Work source.
You can configure a Google Drive for Work source to index only My Drive content, both My Drive and Shared drives content, or only content from Shared drives. See how to index content from shared drives.
Google Drive can store large volumes of content. We recommend following our leading practices to optimize indexing speed and enhance the relevance of search results.
|
|
Note
When using the Coveo quickview component in search results, users won’t be able to preview files over 50 MB that aren’t native to Google Drive, such as |
Source key characteristics
The following table presents the main characteristics of a Google Drive for Work source.
| Features | Supported | Additional information | |
|---|---|---|---|
Google Drive for Work version |
Latest cloud version |
Following available Google Drive for Work releases |
|
Indexable content |
Files and folders |
||
Content security options |
The findability of files shared by link depends on the file link-sharing settings specified in Google Drive. |
||
metadata indexing for search |
Automapping of metadata to a field with a matching name |
Disabled by default and not recommended for this source type. |
|
Automatically indexed metadata |
Sample of autopopulated fields (no user-defined metadata required):
After a content update operation, inspect your item field values in the Content Browser. |
||
Collected indexable metadata |
The Google Drive source collects some of the metadata that the Google Drive API makes available. After a rebuild, review the View and map metadata subpage for the list of indexed metadata and to index additional metadata from those available. |
||
Custom metadata collection |
Use the Google Drive API to add custom file properties and enable the Custom properties option. Then, your Google Drive source will automatically collect the properties as metadata during content update operations. |
||
Prerequisites
Before you create a Google Drive for Work source, you must:
-
Ensure you have a Google account with administrator credentials. Administrator privileges are required to create a Google Cloud Console project and service account, and to set up domain-wide delegation of authority to the service account.[1]
Add a Google Drive for Work source
Before you start, make sure you’ve authorized your Coveo organization to access your users' Google Drive.
Follow the instructions below to add a Google Drive for Work source.
-
On the Sources (platform-ca | platform-eu | platform-au) page, click Add source.
-
In the Add a source of content panel, click the Google Drive for Work source tile.
-
Configure your source.
|
|
Leading practice
It’s best to create or edit your source in your sandbox organization first. Once you’ve confirmed that it indexes the desired content, you can copy your source configuration to your production organization, either with a snapshot or manually. See About non-production organizations for more information and best practices regarding sandbox organizations. |
"Configuration" tab
In the Add a Google Drive source panel, the Configuration tab is selected by default. It contains your source’s general and authentication information, as well as other parameters.
"Identification" subtab
The Identification subtab contains general information about the source.
Name
Enter a name for your source.
|
|
Leading practice
A source name can’t be modified once it’s saved, therefore be sure to use a short and descriptive name, using letters, numbers, hyphens ( |
Project
Use the Project selector to associate your source with one or more Coveo projects.
"Content to index" subtab
The Content to index subtab lets you define the content that you want to make available as search results.
Content
Select All users or specify the users whose content you want to target. Then, choose the types of drives to index for these users—whether individual user drives, shared drives, or both.
|
|
When indexing content from shared drives only, consider using a dedicated user account and share the relevant shared drives with this account. |
Exclusions and inclusions
Add exclusion and inclusion rules to crawl only specific items based on their URL.
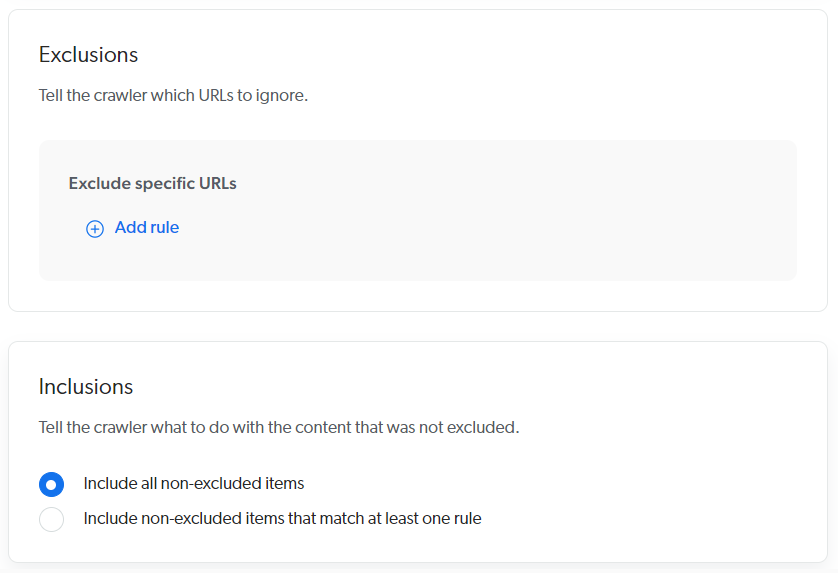
The URLs to specify in exclusion and inclusion rules are unique to Coveo.
They aren’t the ones you see in Google Drive.
The Coveo URL (that is, the Item URI) begins with googledrive:// and follows a pattern that includes references to:
-
The user’s email address (for My Drive content)
-
The Google shared drive ID (for Shared drives content)
-
The Google file ID.
The following are examples of Coveo URLs:
-
googledrive://source_17345/Root:GoogleDrive/User:msaunders@gd.abc.com/File:1xQ5E-mHczB-q2YHJU7cD-iDS2KWe5rU -
googledrive://source_17345/Root:GoogleDrive/SharedDrive:0AIzbK3jw1UPpUk9PVA/File:1jKgYruqAZqEsmHSGqk0Wml3M3wS3NSY1dMv5L9Es4vs
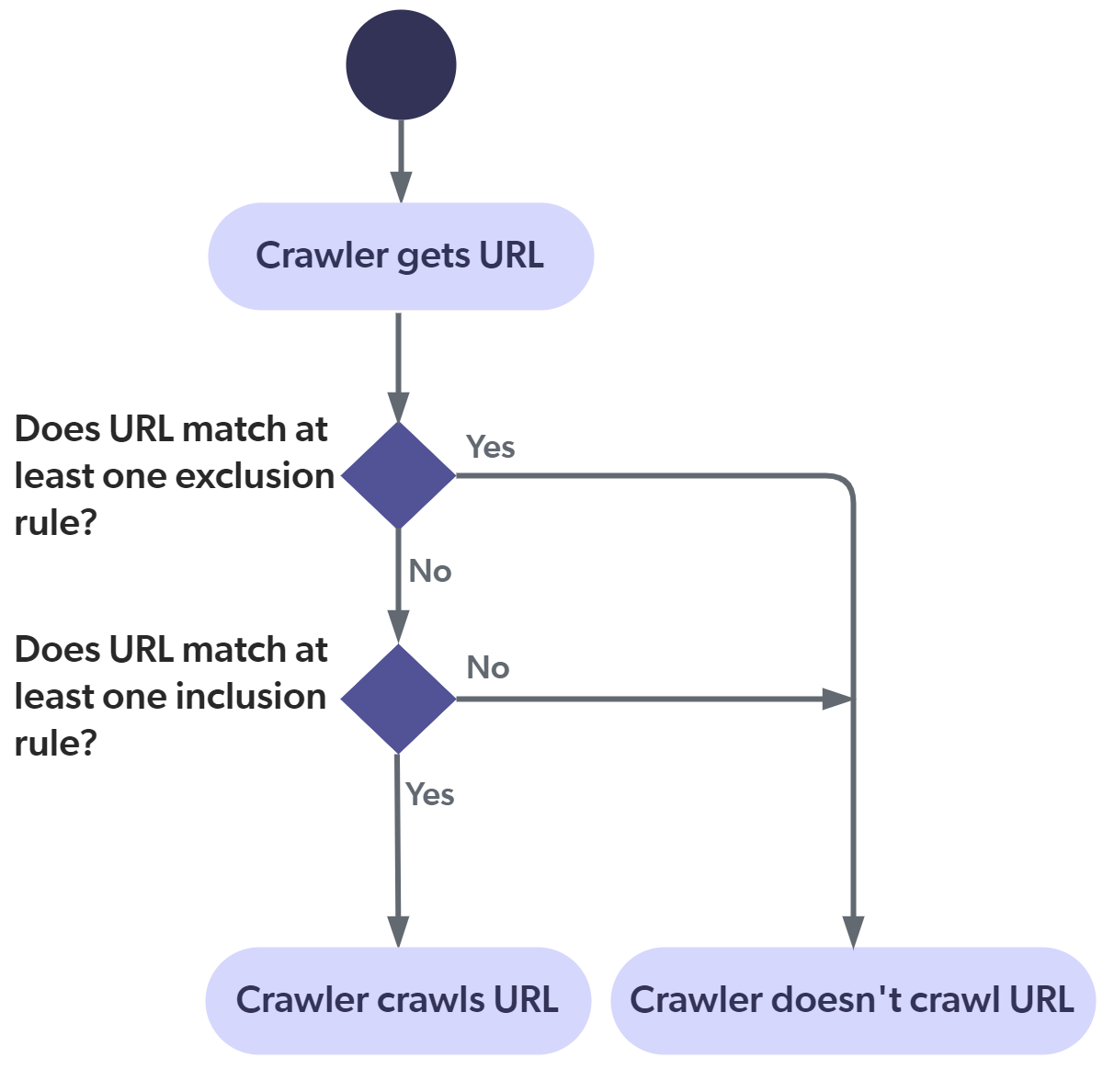
The following diagram illustrates how the Google Drive crawler applies the exclusion and inclusion rules. This flow applies to all items, including the starting URLs. You must therefore pay attention to not filter out your starting URLs.
|
|
About the "Include all non-excluded items" option
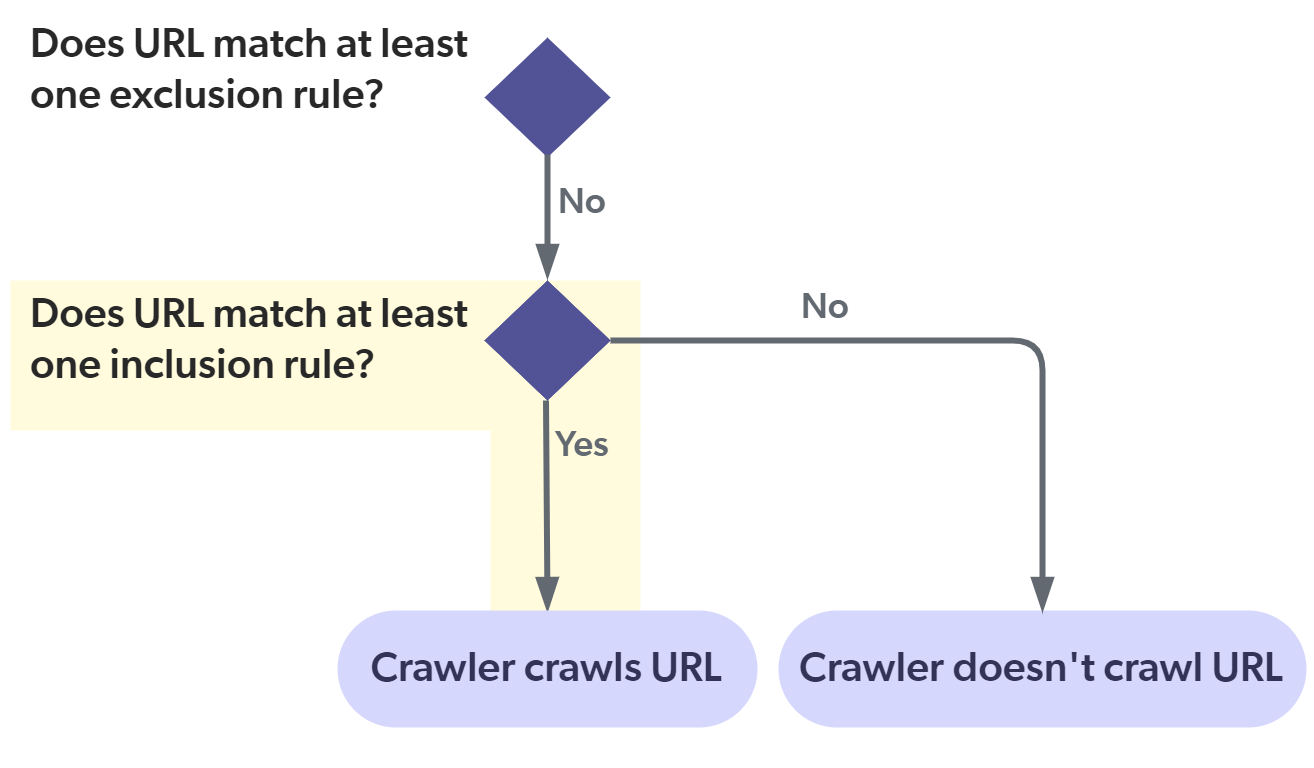
The Include all non-excluded items option automatically adds an "include all" inclusion rule in the background.
This ensures that all starting URLs meet the The following are common Google Drive for Work source configuration patterns:
|
You can use any of the six types of rules:
-
is and a URL that includes the protocol. For example,
https://myfood.com/. -
contains and a string found in the URL. For example,
recipes. -
begins with and a string found at the beginning of the URL and which includes the protocol. For example,
https://myfood. -
ends with and a string found at the end of the URL. For example,
.pdf. -
matches wilcard rule and a wildcard expression that matches the whole URL. For example,
https://myfood.com/recipes*. -
matches regex rule and a regex rule that matches the whole URL. For example,
^.*(company-(dev|staging)).*html.?$.When using regex rules, make sure they match the desired URLs with a testing tool such as Regex101.
Exclusion and inclusion configuration examples
The following examples illustrate how to configure exclusion and inclusion rules for your source.
Example 1: Excluding a specific shared drive
You’re indexing shared drives but you want to exclude a specific one (for example, the https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/0AIzbK3jw1UPpUk9PVA shared drive).
Possible solution
-
Exclusions:
SharedDrive:0AIzbK3jw1UPpUk9PVA(type:contains) -
Inclusions: Include all non-excluded items
Example 2: Excluding the My Drive content of a specific user
You’re indexing the My Drive content of all users but you want to exclude user `msaunders@gd.abc.com’s drive.
Possible solution
-
Exclusions:
User:msaunders@gd.abc.com(type:contains) -
Inclusions: Include all non-excluded items
Example 3: Excluding a specific file
You want to prevent a specific file from being indexed.
For example, the file you would share via the https://docs.google.com/document/d/1jKgYruqAZqEsmHSGqk0Wml3M0wS3NSP1dMv5L9Es4vs/edit?usp=drive_link link.
Possible solution
-
Exclusions:
File:1jKgYruqAZqEsmHSGqk0Wml3M0wS3NSP1dMv5L9Es4vs(type:contains) -
Inclusions: Include all non-excluded items
Additional exclusions
Crawl folders as individual items
Select the Exclude folders option to index the files in folders but not the folders themselves. If you don’t exclude folders, your index will contain items that represent Google Drive folders. If you don’t select the Exclude folders option, your index will contain items that represent Google Drive folders.
Exclude MIME types
(Recommended) In the drop-down menu, select the Google Drive supported MIME types you want to exclude from indexing.
You can also add your own MIME types to the exclusion list.
Exclude older content
(Recommended) You can specify a time frame within which a file must have been created or modified to be indexed. Use the two controls to specify the number of units and the time period respectively.
|
|
Note
During a content update operation, existing items that no longer meet the specified criteria are removed from the index. |
"Advanced settings" subtab
The Advanced settings subtab lets you customize the crawler behavior. All advanced settings have default values that are adequate in most use cases.
Content and images
If you want Coveo to extract text from image files or PDF files containing images, enable the appropriate option.
The extracted text is processed as item data, meaning that it’s fully searchable and will appear in the item Quick view. See Enable optical character recognition for details on this feature.
Additional content
You can choose to index trashed items and custom properties.
|
|
Note
Including custom properties significantly increases communication traffic between the source and the Google Drive. This, in turn, significantly increases indexing time. |
"Authentication" subtab
Your Google Drive for Work source must authenticate to retrieve your Google Drive content.
Google Apps domain
Enter the Google Drive domain that you want to index.
Google Apps administrator account email
Enter the email of a Google Apps administrator account in the user@company.com format.
Google Service account email
Enter the Google service account email address that you obtained when you authorized your Coveo organization to access your users' Google Drive.
Private key file (.p12)
Click Upload private key file, and then select the private key file that you created when you authorized your Coveo organization to access your users' Google Drive.
"Content security" tab
Select who will be able to access the source items through a Coveo-powered search interface. For details on this parameter, see Content security.
|
|
When using the Everyone content security option, see Safely apply content filtering for information on how to ensure that your source content is safely filtered and only accessible by intended users. |
"Access" tab
In the Access tab, specify whether each group (and API key, if applicable) in your Coveo organization can view or edit the current source.
For example, when creating a new source, you could decide that members of Group A can edit its configuration, while Group B can only view it.
For more information, see Custom access level.
Completion
-
Finish adding or editing your source:
-
When you want to save your source configuration changes without starting a build/rebuild, such as when you know you want to do other changes soon, click Add source/Save.
-
When you’re done editing the source and want to make changes effective, click Add and build source/Save and rebuild source.
NoteOn the Sources (platform-ca | platform-eu | platform-au) page, you must click Launch build or Start required rebuild in the source Status column to add the source content or to make your changes effective, respectively.
Back on the Sources (platform-ca | platform-eu | platform-au) page, you can follow the progress of your source addition or modification.
Once the source is built or rebuilt, you can review its content in the Content Browser.
-
-
Once your source is done building or rebuilding, review the metadata Coveo is retrieving from your content.
-
On the Sources (platform-ca | platform-eu | platform-au) page, click your source, and then click More > View and map metadata in the Action bar.
-
If you want to use a currently not indexed metadata in a facet or result template, map it to a field.
-
Click the metadata and then, at the top right, click Add to Index.
-
In the Apply a mapping on all item types of a source panel, select the field you want to map the metadata to, or add a new field if none of the existing fields are appropriate.
Notes-
For details on configuring a new field, see Add or edit a field.
-
For advanced mapping configurations, like applying a mapping to a specific item type, see Manage mappings.
-
-
Click Apply mapping.
-
-
Depending on the source type you use, you may be able to extract additional metadata from your content. You can then map that metadata to a field, just like you did for the default metadata.
More on custom metadata extraction and indexing
Some source types let you define rules to extract metadata beyond the default metadata Coveo discovers during the initial source build.
For example:
Source type Custom metadata extraction methods Define metadata key-value pairs in the
addOrUpdatesection of thePUTrequest payload used to upload push operations to an Amazon S3 file container.REST API
and
GraphQL APIIn the JSON configuration (REST API | GraphQL API) of the source, define metadata names (REST API | GraphQL API) and specify where to locate the metadata values in the JSON API response Coveo receives.
Add
<CustomField>elements in the XML configuration. Each element defines a metadata name and the database field to use to populate the metadata with.-
Configure web scraping configurations that contain metadata extraction rules using CSS or XPath selectors.
-
Extract metadata from JSON-LD
<script>tags.
-
Configure web scraping configurations that contain metadata extraction rules using CSS or XPath selectors.
-
Extract JSON-LD
<script>tag metadata. -
Extract
<meta>tag content using theIndexHtmlMetadataJSON parameter.
Some source types automatically map metadata to default or user created fields, making the mapping process unnecessary. Some source types automatically create mappings and fields for you when you configure metadata extraction.
See your source type documentation for more details.
-
-
When you’re done reviewing and mapping metadata, return to the Sources (platform-ca | platform-eu | platform-au) page.
-
To reindex your source with your new mappings, click Launch rebuild in the source Status column.
-
Once the source is rebuilt, you can review its content in the Content Browser.
-
Index content of shared drives
The Google Drive for Work source’s basic content configurations allow you to index content from Shared drives managed by your organization or domain users.
If you need to index content from multiple shared drives that aren’t managed by the same user, configuring your source and maintaining control over the indexed content can become challenging. A better approach is to create a dedicated user account in your Google Workspace domain and share the desired shared drives with this account. The Index handpicked shared drives only article contains instructions on how to set this up.
File link sharing and findability
A file is always indexed under its Google Drive owner with the permissions that the owner has set.
If your source content security setting is set to Same users and groups as in your content system, a user will only see a Google Drive file in their Coveo search results if they’re authorized to search for the file in Google Drive. This visibility is determined by the file’s link-sharing settings.
Depending on the file’s link-sharing settings in Google Drive, general access can be:
-
Restricted to only people with access
A user with this access can search for the file in Google Drive and will see it in Coveo search results.
-
Granted to Anyone in this group… (that is, the group that the owner belongs to)
When this access is granted, the file will be set to one of the following:
-
Can find in search results
A user in the same group as the owner with this access can search for the file in Google Drive and will see the file in Coveo search results.
-
Must have link to access
A user in the same group as the owner with this access can’t search for the file in Google Drive and won’t see the file in Coveo search results.
-
-
Anyone with the link
A user with with this access can’t search for the file in Google Drive and, therefore, won’t see the file in Coveo search results.
|
|
Using the Everyone content security option isn’t recommended for Google Drive sources. This option effectively overrides the link-sharing settings in Google Drive, notably files that can only be accessed with its link. As a result, all files indexed in the source become searchable via free-text search by anyone who accesses a Coveo-powered search interface that targets this source. |
|
|
Note
When you set the link-sharing options for a folder in Google Drive, all files in the folder automatically inherit the folder’s link-sharing settings. This means that if you set the link-sharing options for a specific file, and then set the options for the file’s folder, the file’s link-sharing settings change to match its folder settings. |
Restrict access to searchable content only
If the link-sharing options for a Google Drive file is set to allow access to everyone in your organization, you can use the OnlyIndexFilesSharedToDomainAndSearchable source parameter in conjunction with the Anyone in this group… > Can find in search results link setting in Google Drive to index the file only if it’s set as searchable in Google Drive.
You can use this parameter, for instance, if you want to exclude a file from Coveo search results but make the file accessible in Google Drive.
By default, the OnlyIndexFilesSharedToDomainAndSearchable parameter value is set to false, which means that all shared files are indexed and appear in Coveo search results for everyone in your organization.
To restrict file access in Coveo search results only to files that are set as searchable in Google Drive
-
In Google Drive, for each file that you want your organization members to see in Coveo search results, set the file to Can find in search results.
-
Right-click the file, and then select Share > Share.
-
In the General access section, select your group.
-
Next to the group, click the role (for example,
Viewer), and then select Can find in search results. -
Click Done.
-
-
On the Sources (platform-ca | platform-eu | platform-au) page, click the Google Drive for Work source, and then click More > Edit configuration with JSON in the Action bar.
-
In the Edit configuration with JSON panel, set the
OnlyIndexFilesSharedToDomainAndSearchableparameter value totrue. -
Click Save or Save and Rebuild.
Safely apply content filtering
The best way to ensure that your indexed content is seen only by the intended users is to enforce content security by selecting the Same users and groups as in your content system option. Should this option be unavailable, select Specific users and groups instead.
However, if you need to configure your source so that the indexed source content is accessible to Everyone, you should adhere to the following leading practices. These practices ensure that your source content is safely filtered and only accessible by the appropriate users:
-
Configure query filters: Apply filter rules on a query pipeline to filter the source content that appears in search results when a query goes through that pipeline.
-
Use condition-based query pipeline routing: Apply a condition on a query pipeline to make sure that every query originating from a specific search hub is routed to the right query pipeline.
-
Configure the search token: Authenticate user queries via a search token that’s generated server side that enforces a specific search hub.
Following the above leading practices results in a workflow whereby the user query is authenticated server side via a search token that enforces the search hub from which the query originates. Therefore, the query can’t be modified by users or client-side code. The query then passes through a specific query pipeline based on a search hub condition, and the query results are filtered using the filter rules.
Configure query filters
Filter rules allow you to enter hidden query expressions to be added to all queries going through a given query pipeline.
They’re typically used to add a field-based expression to the constant query expression (cq).
You apply the @objectType=="Solution" query filter to the pipeline to which the traffic of your public support portal is directed.
As a result, the @objectType=="Solution" query expression is added to any query sent via this support portal.
Therefore, if a user types Speedbit watch wristband in the search box, the items returned are those that match these keywords and whose objectType has the Solution value.
Items matching these keywords but having a different objectType value aren’t returned in the user’s search results.
To learn how to configure query pipeline filter rules, see Manage filter rules.
|
|
Note
You can also enforce a filter expression directly in the search token. |
Use condition-based query pipeline routing
The most recommended and flexible query pipeline routing mechanism is condition-based routing.
When using this routing mechanism, you ensure that search requests are routed to a specific query pipeline according to the search interface from which they originate, and the authentication is done server side.
To accomplish this:
-
Apply a condition to a query pipeline based on a search hub value, such as Search Hub is Community Search or Search Hub is Agent Panel. This condition ensures that all queries that originate from a specific search hub go through that query pipeline.
-
Authenticate user queries via a search token that’s generated server side and that contains the search hub parameter that you specified in the query pipeline.
Configure the search token
When using query filters to secure content, the safest way to enforce content security is to authenticate user queries using a search token that’s generated server side. For instance, when using this approach, you can enforce a search hub value in the search token. This makes every authenticated request that originates from a component use the specified search hub, and therefore be routed to the proper query pipeline. Because this configuration is stored server side and encrypted in the search token, it can’t be modified by users or client-side code.
Implementing search token authentication requires you to add server side logic to your web site or application. Therefore, the actual implementation details will vary from one project to another.
The following procedure provides general guidelines:
|
|
Note
If you’re using the Coveo In-Product Experience (IPX) feature, see Implement advanced search token authentication. |
-
Authenticate the user.
-
Call a service exposed through Coveo to request a search token for the authenticated user.
-
Specify the
userIDsfor the search token, and enforce asearchHubparameter in the search token.
|
|
Note
You can specify other parameters in the search token, such as a query |
For more information and examples, see Search token authentication.
Required privileges
You can assign privileges to allow access to specific tools in the Coveo Administration Console. The following table indicates the privileges required to view or edit elements of the Sources (platform-ca | platform-eu | platform-au) page and associated panels. See Manage privileges and Privilege reference for more information.
|
|
Note
The Edit all privilege isn’t required to create sources. When granting privileges for the Sources domain, you can grant a group or API key the View all or Custom access level, instead of Edit all, and then select the Can Create checkbox to allow users to create sources. See Can Create ability dependence for more information. |
| Actions | Service | Domain | Required access level |
|---|---|---|---|
View sources, view source update schedules, and subscribe to source notifications |
Content |
Fields |
View |
Sources |
|||
Organization |
Organization |
||
Edit sources, edit source update schedules, and edit source mappings |
Organization |
Organization |
View |
Content |
Fields |
Edit |
|
Sources |
|||
View and map metadata |
Content |
Source metadata |
View |
Fields |
|||
Organization |
Organization |
||
Content |
Sources |
Edit |