Coveo indexing pipeline extensions
Coveo indexing pipeline extensions
Items crawled in Sitecore are then sent to the Coveo Platform document processing manager (DPM) to be processed and indexed.
The DPM provides two indexing pipeline extension (IPE) stages during which you can modify your items, using Python code, before they’re indexed. The choice of stage depends on your use case.

|
|
Note
Don’t use indexing pipeline extensions for tasks that the connector itself is designed to handle. For example, when using the Web or Sitemap connector, you shouldn’t use an IPE to remove unwanted sections of web pages. These connectors support web scraping configurations for that very purpose. |
Choosing between a pre-conversion and a post-conversion extension
An important stage of the Coveo indexing pipeline is the Processing stage. During this stage, incoming items are converted to an index-ready format. Coveo provides indexing pipeline extension stages prior to this conversion stage and after it.
Examples of use cases for pre-conversion extensions:
-
Rejecting a web page using advanced rules.
-
Formatting values.
Examples of use cases for post-conversion extensions:
-
Modifying the body of a page.
-
Adding or modifying metadata.
If you’re unsure about the stage to choose, see our decision table.
Once you’ve chosen the appropriate stage, you can create your indexing pipeline extension.
Example: Removing unwanted HTML sections
Using the CleanHtml Coveo for Sitecore processor is a simple way to remove webpage content that you don’t want to index. However, it may require that you add exclusion tags in many layouts that your Sitecore items are linked to. An alternative is to use an indexing pipeline extension, which leverages the powerful and full-featured BeautifulSoup library.
This example shows how to create an indexing pipeline extension that removes the following from your webpages:
-
tags whose
classattribute value iscoveo-no-index -
<footer>tags.
Create the extension
-
In the Extensions (platform-ca | platform-eu | platform-au) section of the Coveo Administration Console, click Add extension.
-
In the Add an Extension panel, give your extension a name and a description.
-
For this example, you need the extension to access the Original file data of your items.
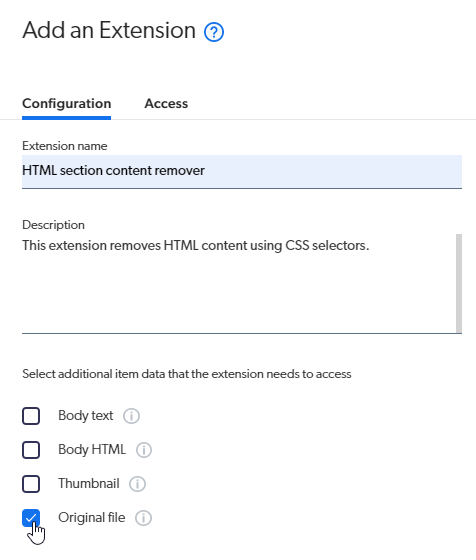
-
In the Extension script field, paste the following code:
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup read_only_stream = document.get_data_stream('documentdata') if read_only_stream is not None: modified_data = BeautifulSoup(read_only_stream.read().decode(), 'html.parser') # Remove matching nodes for element in modified_data.select('.coveo-no-index, footer'): element.decompose() modified_stream = document.DataStream('documentdata') modified_stream.write(str(modified_data)) document.add_data_stream(modified_stream) -
Click Add extension.
|
|
Note
For the list of CSS selectors BeautifulSoup supports, see Quick Start - Soup Sieve. |
Associate the extension with your source
To link your extension to a source, you can proceed as follows:
-
Under Content in the Administration Console left menu, select Sources.
-
Click the source you want to run your indexing pipeline extension on, and then click More > Add extensions in the Action bar.
-
In the Add extensions panel, with the Common tab selected, click Add > Extension.
-
In the Apply an Extension on Source Items panel, select your extension in the dropdown menu.
-
Select the PRE-CONVERSION stage.
-
Select the SKIP EXTENSION action on error.
-
In the Conditions to apply field, type
%[haslayout] == "1". Since thehaslayoutfield is Sitecore-specific, this condition ensures the extension is only applied to Sitecore items that have a layout. -
Click Apply extension.
-
Back in the Add extensions panel, click Save.
-
Rebuild your source from your Sitecore instance, so the extension executes and removes the targeted content.