Capture cart events (Coveo UA)
Capture cart events (Coveo UA)
|
|
We strongly recommend that all new Commerce implementations use the Event Protocol to log events. |
This article explains how to capture cart update events and send the information to Coveo along with the product information using the Coveo UA library.
When to send a cart event
Any time the content of a cart is modified by a user, the interface must log a cart modification event, together with the product information payload. Cart content modifications may include adding products, removing products, or changing the quantity of existing products in the cart. Depending on your site’s design, cart modification events can be triggered from different places, such as:
-
From a page which shows the current contents of a visitor’s shopping cart
-
From an individual product detail page (PDP)
-
From a search results page
-
From a product listing page (PLP)
-
From a recommendation slot
|
|
WARNING
cart modification events don’t count towards attribution. You must send an additional click event if the cart is modified directly from a search results page, PLP, or recommendation slot. |
The following image is from the cart page view of the online sporting goods store Barca Sports, which provides visitors with the ability to modify the contents of their cart by increasing or decreasing the quantity of items.
At a minimum, log the product information and the quantity added or removed in the product data payload.
Coveo calculates quantity as the increase or decrease in value, not the new total amount.
For example, if a client changes the quantity of an item in the cart from 1 to 2, the quantity to pass in the cart modification event is 1.

Cart events and attribution
Coveo attributes transactions to product discovery solutions by tracking touchpoints along the user journey. In a Coveo-powered commerce implementation, click events are the main touchpoints used for attribution.
Cart events don’t count towards attribution. If your commerce implementation lets users modify the cart directly from the search results page, product listing pages (PLPs), or recommendation slots, you must send an additional click event along with the cart event. This lets Coveo attribute transactions to the correct solutions.
For more information, see Attribution at Coveo.
A user performs a query on a Coveo-powered commerce site. They click a product to open its product detail page (PDP), but they don’t make a purchase and navigate away from the site. Coveo tracks this touchpoint as part of the user’s journey.
Later, they revisit the site and see the same product in a recommendation slot. They click the product to open its PDP, creating another touchpoint tracked by Coveo. This time, the user adds the product to their cart and completes the purchase. This product is attributed to the recommendation solution.
Capture a cart modification event using Coveo UA library commands
When the content of a cart is modified, you must run the following JavaScript code which contains Coveo UA library commands.
coveoua('ec:addProduct', {
'id': 'SP00579_00009',  'name': 'Whitetraveler DryBag',
'category': 'Accessories/Bags/Drybags',
'price': 96,
'name': 'Whitetraveler DryBag',
'category': 'Accessories/Bags/Drybags',
'price': 96,  'quantity': 1,
'quantity': 1,  });
coveoua('ec:setAction', '<ACTION_TYPE>');
});
coveoua('ec:setAction', '<ACTION_TYPE>');  coveoua('send', 'event');
coveoua('send', 'event'); 
| Add product data payload | |
The currencyCode for the item’s price is set as a global field when initializing the Coveo UA library |
|
| The number of units added by this event | |
| Set the action type | |
| Send the event |
Add product data payload
The ec:addProduct command includes the relevant product data in the event you’re about to send.
In this case the product dataset contains the product id, name, category, price and quantity.
Cart product dataset requirements
The following table lists the fields sent along with the event and the solutions that use these fields. Search, Listings, and Recs columns refer to whether the ML that powers those solutions needs those data points. The Reporting column is for general reporting purposes that encompasses all solutions. For more information on these fields, including other recommended and optional fields that can be sent, refer to the Product fields reference.
| Field | Priority | Search | Listings | Recs | Reporting |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Required |
|||||
Required |
|||||
Required |
|||||
Required |
|||||
Required |
|||||
Recommended |
|||||
Recommended |
|||||
Recommended |
-
Only needed when you must setup ML to recommend at the group level.
|
|
Note
When you structure your items with product grouping, ensure that you add the Using the recommended approach for product data, you would find, for example, |
Refer to Product data fields reference for more information.
Set the action type
The ec:setAction command is used to specify which <ACTION_TYPE> is to be performed on this data.
In the case above, we want to add the product data payload.
To capture when there’s a decrease in cart items, you would use remove.
Send the event
Finally, the send command sends an event with a given payload to the Coveo analytics endpoint.
Send an additional click event
If your Coveo-powered commerce implementation lets users send cart modification events directly from the search results page, product listing pages (PLPs), or recommendation slots, you must send an additional click event along with the cart event.
Each query has a unique searchUid associated with it, whether it generates search results, displays product listings, or showcases recommendations.
You must include this searchUid in the click event sent along with the cart event so that Coveo can attribute transactions with direct cart modification events to the correct solutions.
Headless or Atomic (recommended)
When you send click events using Headless or Atomic, you don’t need to worry about including the searchUid in the event.
This process is handled automatically for you.
Coveo UA library
However, if you’re using the Coveo UA library to log click events, you’ll need to pass the searchUid value in the payload of the click event.
For information on extracting the searchUid, see Extract the searchUid.
The following example showcases a function that sends a click event using the Coveo UA library, followed by a cart modification event:
const logClickAndAddToCart = (result) => {
coveoua('send', 'click',{  actionCause: 'documentOpen',
anonymous: true,
documentPosition: 1,
documentTitle: result.title,
documentUrl: result.clickUri,
originLevel1: 'Search',
searchQueryUid: engine.state.search.response.searchUid,
actionCause: 'documentOpen',
anonymous: true,
documentPosition: 1,
documentTitle: result.title,
documentUrl: result.clickUri,
originLevel1: 'Search',
searchQueryUid: engine.state.search.response.searchUid,  sourceName: result.raw.source,
customData: {
contentIDKey: 'permanentid',
contentIDValue: result.raw.ec_productid,
},
});
coveoua('ec:addProduct', {
sourceName: result.raw.source,
customData: {
contentIDKey: 'permanentid',
contentIDValue: result.raw.ec_productid,
},
});
coveoua('ec:addProduct', {  'id': result.raw.ec_productid,
'name': result.raw.ec_name,
'brand': result.raw.ec_brand,
'category': result.raw.ec_category,
'price': result.raw.ec_price,
'quantity': 1,
});
coveoua('ec:setAction', 'add');
coveoua('send', 'event');
}
'id': result.raw.ec_productid,
'name': result.raw.ec_name,
'brand': result.raw.ec_brand,
'category': result.raw.ec_category,
'price': result.raw.ec_price,
'quantity': 1,
});
coveoua('ec:setAction', 'add');
coveoua('send', 'event');
}| Send a click event using the Coveo UA library, specifying the required payload fields. | |
Extract the value of the searchUid field from the Headless engine to ensure correct attribution. |
|
| Capture a cart modification event by adding the product payload, setting the action type, and sending the event. |
|
|
Note
If you’re currently pairing the The added advantage of this method is two-fold. First, it provides a more exact representation of clickthrough rates, especially for stores that have 'add to cart' buttons on their listing pages. Second, it bolsters the efficacy of our machine learning models, as these models leverage click events as valuable data points. We will continue to support pairing the
For information on how to extract the |
Set the action type
The ec:setAction command is used to specify which <ACTION_TYPE> is to be performed on this data.
In the case above, we want to add the product data payload.
To capture when there’s a decrease in cart items, you would use remove.
Send the event
Finally, the send command sends an event with a given payload to the Coveo analytics endpoint.
Cart event validation
When the cart event is logged, use the developer tools for client-side request verification to inspect your visit to ensure everything done using the UI is captured as a set of consistent and coherent events properly mapped to their Coveo UA parameters. This must occur after the implementation is applied.
Inspect the cart event through the network browser and ensure it satisfies the following:
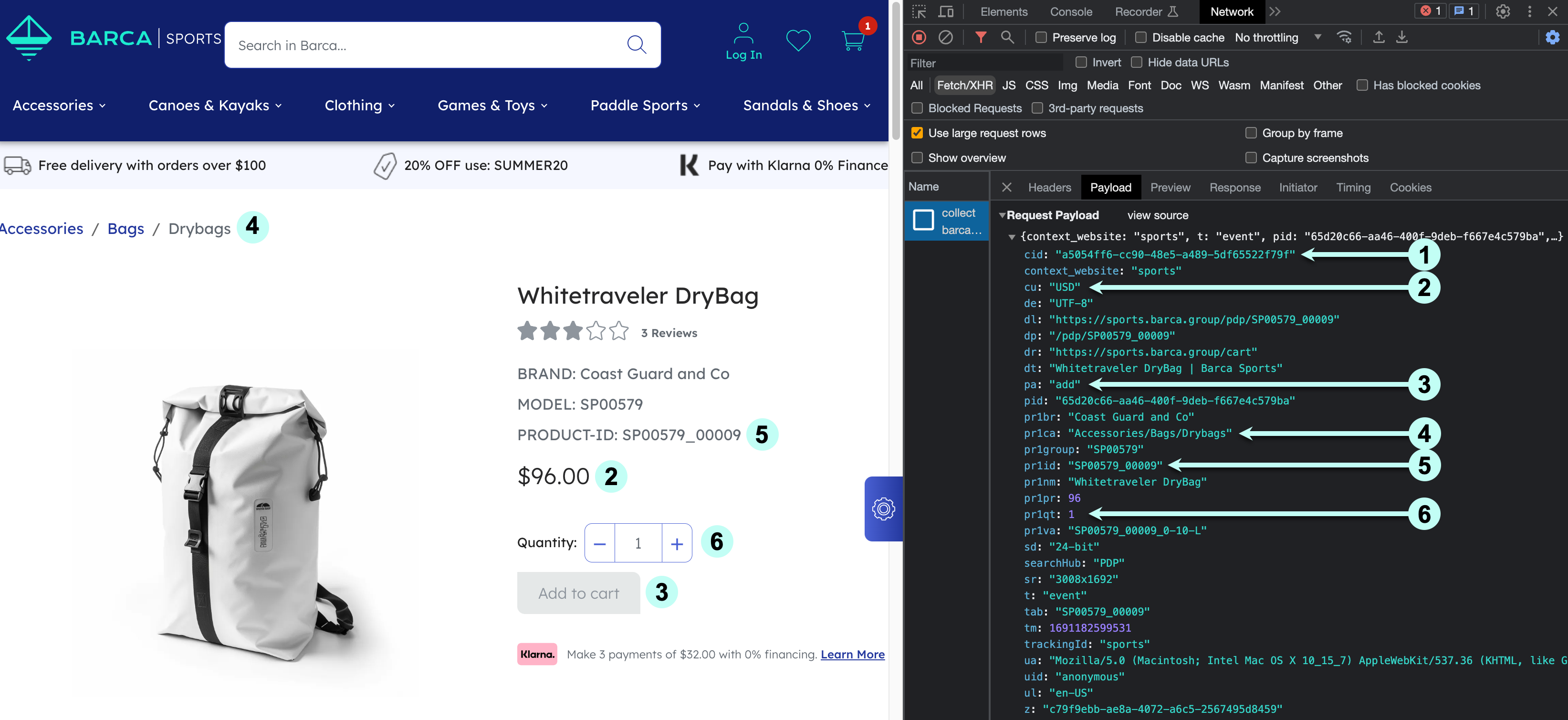
1 The client ID (cid) is consistent with other events sent on the page.
2 The currency matches what’s being displayed to the visitor.
3 Confirm the event is an addition (add) or removal (remove) from cart.
4 Category values should use / to represent hierarchies and use | to represent multiple values.
5 The product ID matches what’s set in the catalog entity (same is true if sending group and variant).
6 The quantity reflects the change in cart items (for example, if a visitor already has a product in their cart and they add another 2 identical items, this will take the total amount in the cart to 3, so quantity in the event is set to 2).
|
|
Note
Adding to cart directly from a search results page, listings or recommendation carousel should also send an additional click event with a search ID that matches that of the corresponding search. |
Event field data mapping
The following table shows how the client-side fields are mapped to parameters in the analytics request sent to Coveo UA. Ensure this information is properly passed in the payload.
| Field name | Description | Parameter |
|---|---|---|
The currency of the product being purchased |
||
Identifier for the base product |
||
The product category |
||
The price shown to the user (including discounts) |
||
The product brand |
||
The product name |
||
The product group ID |
||
The unique identifier of the variant selected |
||
Quantity added or removed |
For a complete list of parameters that can be sent in the event, see Log Collect events.
|
|
Note
Parameters such as |