Revenue per visitor (RPV)
Revenue per visitor (RPV)
The revenue per visitor (RPV) is calculated by summing the total revenue (earned in a specific time range) and dividing it by the total number of visitors (that converted or not).
This article contains SQL queries to create Snowflake dashboard tiles to report on the following metrics:
To learn how you can create custom dashboards in Snowflake and use the queries listed in this section, see Create Snowflake dashboards.
RPV per service
The following query creates a Snowflake dashboard tile that displays the RPV earned by each Coveo service (that is, Searches, Product listings, and Recommendations). This metric includes taxes, shipping costs, and discounts.
|
|
Updates to the computation methods for this metric have been implemented. As a result, executing this SQL query may yield slightly different results from those shown in the Advanced Reports (platform-ca | platform-eu | platform-au) page of the Coveo Administration Console. A new version of this query, which aligns with the outcomes of the reports of the Advanced Reports page, will soon be available. |
with transaction_base as (
select distinct
date(ins.start_time) as date,
v.client_xid,
ins.insight_id,
ins.insight_type,
tr.transaction_id,
c.item_id,
c.price*c.quantity as item_revenue
from COVEO_CORE_MODEL_V001.COMMON.INSIGHTS ins
join COVEO_CORE_MODEL_V001.COMMON.VISITS v on v.visit_id = ins.visit_id
left join COVEO_CORE_MODEL_V001.COMMERCE.CART_ITEMS c on c.insight_id = ins.insight_id
left join COVEO_CORE_MODEL_V001.COMMERCE.TRANSACTIONS tr on tr.cart_id = c.cart_id
where date = :daterange
)
select distinct
insight_type,
sum(item_revenue) / count(distinct client_xid) as revenue_per_visitors
from transaction_base
group by insight_type
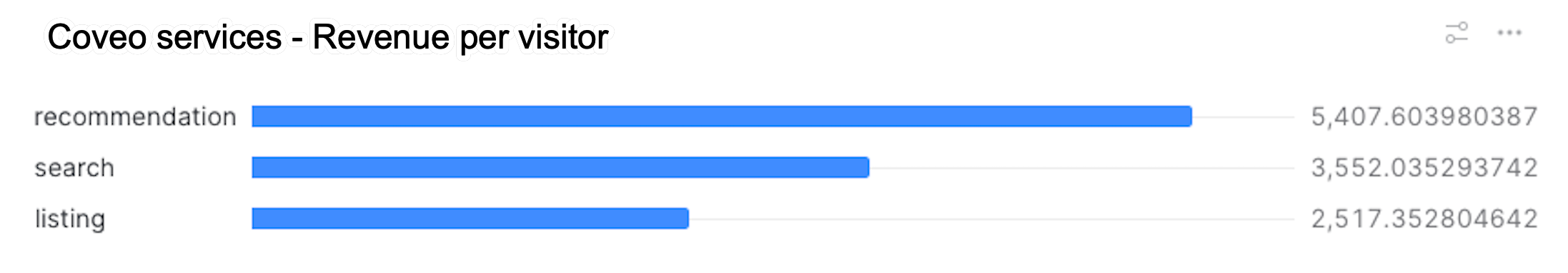
order by revenue_per_visitors descWhen using the default query, your dashboard should look like the following:
The Chart type, Data, and Appearance sections should look like the following. See Using charts for more information.

RPV per service on a daily basis
The following query creates a Snowflake dashboard tile that displays the RPV earned by each Coveo service (that is, Searches, Product listings, and Recommendations) on a daily basis. This metric includes taxes, shipping costs, and discounts.
|
|
Updates to the computation methods for this metric have been implemented. As a result, executing this SQL query may yield slightly different results from those shown in the Advanced Reports (platform-ca | platform-eu | platform-au) page of the Coveo Administration Console. A new version of this query, which aligns with the outcomes of the reports of the Advanced Reports page, will soon be available. |
with transaction_base as (
select distinct
date(ins.start_time) as date,
v.client_xid,
ins.insight_id,
ins.insight_type,
tr.transaction_id,
c.item_id,
c.price*c.quantity as item_revenue
from COVEO_CORE_MODEL_V001.COMMON.INSIGHTS ins
join COVEO_CORE_MODEL_V001.COMMON.VISITS v on v.visit_id = ins.visit_id
left join COVEO_CORE_MODEL_V001.COMMERCE.CART_ITEMS c on c.insight_id = ins.insight_id
left join COVEO_CORE_MODEL_V001.COMMERCE.TRANSACTIONS tr on tr.cart_id = c.cart_id
where date = :daterange
)
select distinct
date,
insight_type,
sum(item_revenue) / count(distinct client_xid) as revenue_per_visitors
from transaction_base
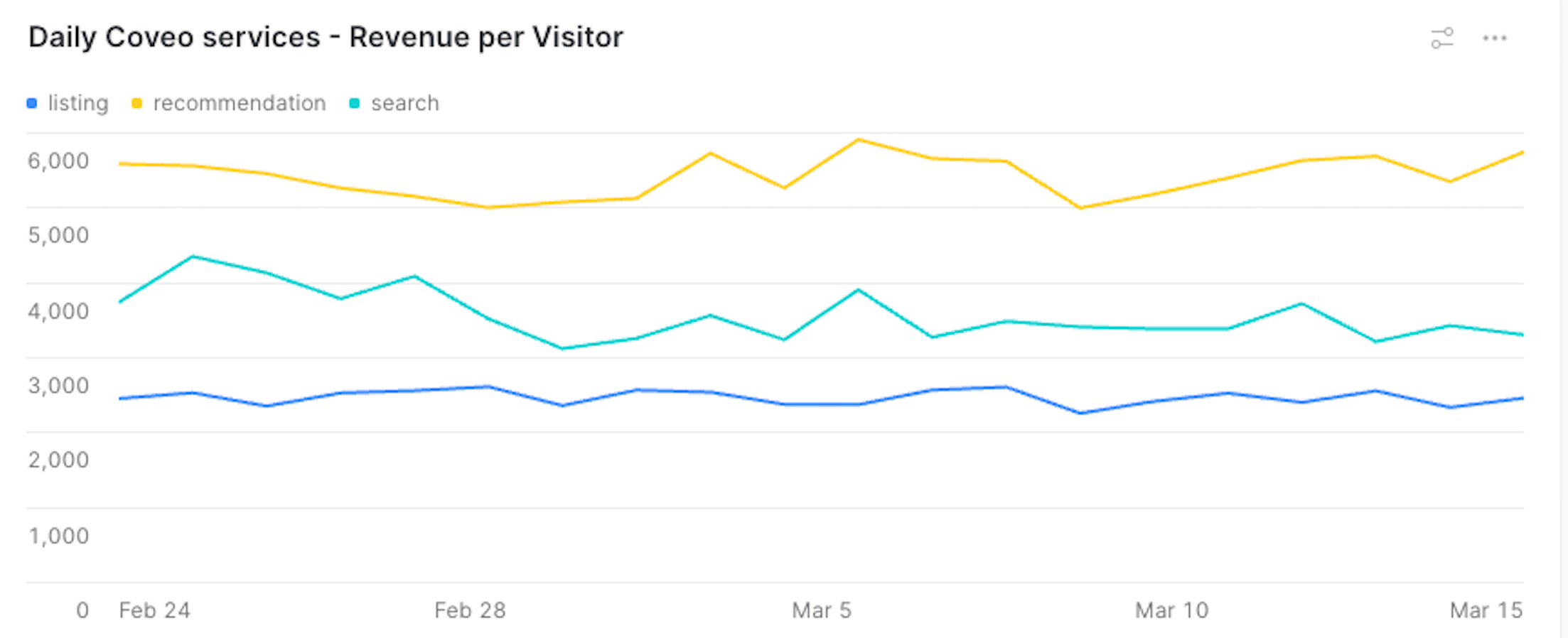
group by date, insight_typeWhen using the default query, your dashboard should look like the following:
The Chart type, Data, and Appearance sections should look like the following. See Using charts for more information.
RPV per component
The query in this section creates a Snowflake dashboard tile that reports on different Coveo service components.
|
|
Note
A Coveo service component refers to a specific instance exploited by a Coveo service. For example, you can have many components that leverage the Recommendation service:
In this case, the dashboard will report on these three different components. |
The following code sample serves as a base to get the RPV metric for different Coveo components. You can add the required information to this generic version, according to the Coveo service component that you want to report on. However, the required information has been added to the sample queries in the following sections, so we recommend that you try one of them:
|
|
Updates to the computation methods for this metric have been implemented. As a result, executing this SQL query may yield slightly different results from those shown in the Advanced Reports (platform-ca | platform-eu | platform-au) page of the Coveo Administration Console. A new version of this query, which aligns with the outcomes of the reports of the Advanced Reports page, will soon be available. |
with transaction_base as (
select distinct
date(ins.start_time) as date,
v.client_xid,
{COMPONENT},
c.insight_id,
ins.insight_type,
tr.transaction_id,
c.item_id,
c.price*c.quantity as item_revenue
from COVEO_CORE_MODEL_V001.COMMON.INSIGHTS ins
join COVEO_CORE_MODEL_V001.COMMON.VISITS v on v.visit_id = ins.visit_id
left join COVEO_CORE_MODEL_V001.COMMERCE.CART_ITEMS c on c.insight_id = ins.insight_id
left join COVEO_CORE_MODEL_V001.COMMERCE.TRANSACTIONS tr on tr.cart_id = c.cart_id
where date = :daterange
and ins.insight_type = '{INSIGHT-TYPE}' -- add on of the follwing between the quotes ('search', 'listing' or 'recommendation')
)
select distinct
{ALIAS OF COMPONENT},
sum(item_revenue)/count(distinct client_xid) as revenue_per_visitors
from transaction_base
group by {ALIAS OF COMPONENT}
order by revenue_per_visitors desc
limit 10Where you replace:
-
{INSIGHT-TYPE}with the Coveo service on which you want to report (that is,search,listing, orrecommendation). -
{COMPONENT}depending on the service you selected in step 1:Service selected in step 1 Value to replace {COMPONENT}withsearchquery_expressionlistingec_listingrecommendationorigin as recommendation_component -
Occurrences of
{ALIAS_OF_COMPONENT}, depending on the Coveo service you selected in step 1:Service selected in step 1 Value to replace {ALIAS_OF_COMPONENT}withsearchquery_expressionlistingec_listingrecommendationrecommendation_component
Top 10 query expressions
The following query creates a Snowflake dashboard tile that displays the top 10 query expressions that generated the highest RPV.
|
|
Updates to the computation methods for this metric have been implemented. As a result, executing this SQL query may yield slightly different results from those shown in the Advanced Reports (platform-ca | platform-eu | platform-au) page of the Coveo Administration Console. A new version of this query, which aligns with the outcomes of the reports of the Advanced Reports page, will soon be available. |
with transaction_base as (
select distinct
date(ins.start_time) as date,
v.client_xid,
query_expression,
c.insight_id,
ins.insight_type,
tr.transaction_id,
c.item_id,
c.price*c.quantity as item_revenue
from COVEO_CORE_MODEL_V001.COMMON.INSIGHTS ins
join COVEO_CORE_MODEL_V001.COMMON.VISITS v on v.visit_id = ins.visit_id
left join COVEO_CORE_MODEL_V001.COMMERCE.CART_ITEMS c on c.insight_id = ins.insight_id
left join COVEO_CORE_MODEL_V001.COMMERCE.TRANSACTIONS tr on tr.cart_id = c.cart_id
where date = :daterange
and ins.insight_type = 'search'
)
select distinct
query_expression,
sum(item_revenue)/count(distinct client_xid) as revenue_per_visitors
from transaction_base
group by query_expression
having revenue_per_visitors is not null
order by revenue_per_visitors desc
limit 10When using the default query, your dashboard should look like the following:
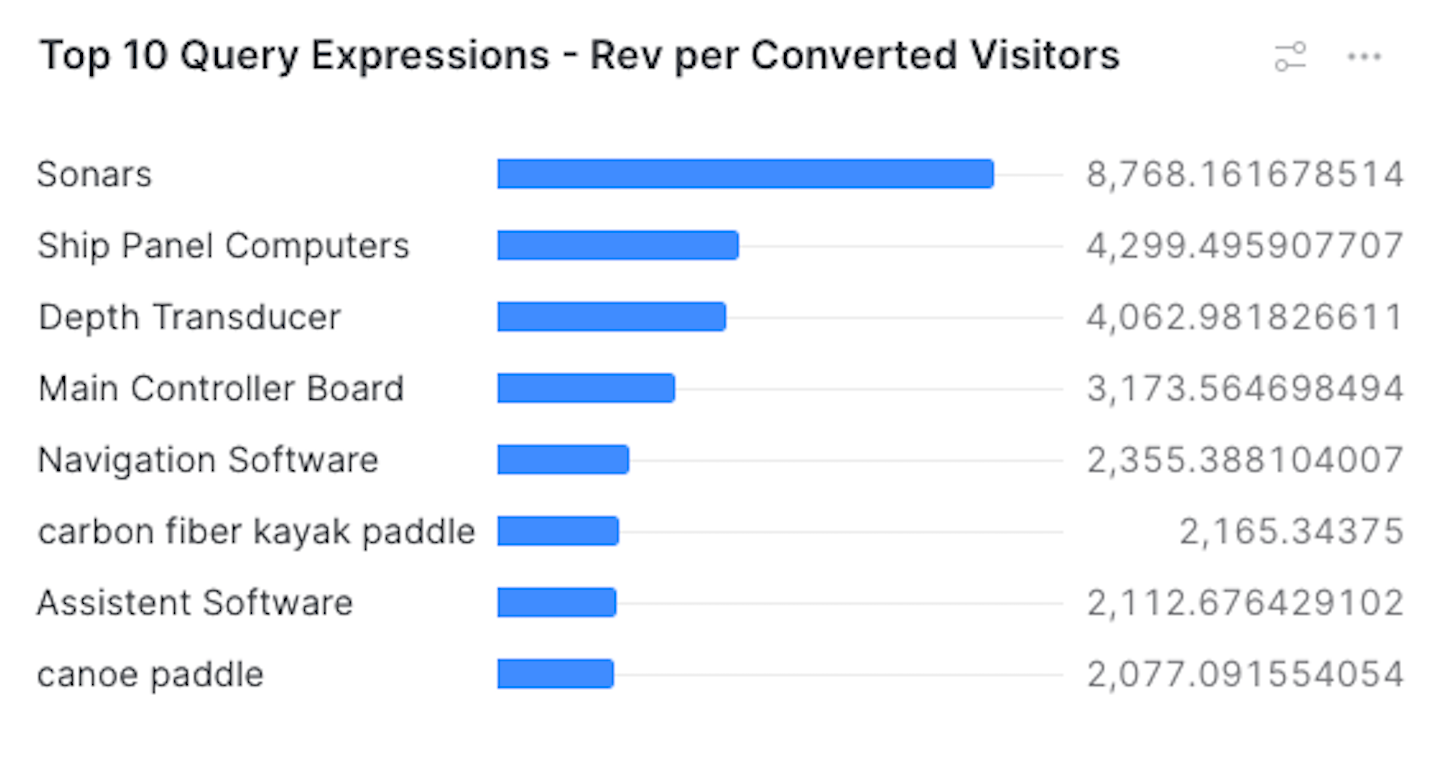
The Chart type, Data, and Appearance sections should look like the following. See Using charts for more information.
Top 10 product listing pages
The following query creates a Snowflake dashboard tile that displays the paths of the top 10 product listing pages that generated the highest RPV.
|
|
Updates to the computation methods for this metric have been implemented. As a result, executing this SQL query may yield slightly different results from those shown in the Advanced Reports (platform-ca | platform-eu | platform-au) page of the Coveo Administration Console. A new version of this query, which aligns with the outcomes of the reports of the Advanced Reports page, will soon be available. |
with transaction_base as (
select distinct
date(ins.start_time) as date,
v.client_xid,
ec_listing,
c.insight_id,
ins.insight_type,
tr.transaction_id,
c.item_id,
c.price*c.quantity as item_revenue
from COVEO_CORE_MODEL_V001.COMMON.INSIGHTS ins
join COVEO_CORE_MODEL_V001.COMMON.VISITS v on v.visit_id = ins.visit_id
left join COVEO_CORE_MODEL_V001.COMMERCE.CART_ITEMS c on c.insight_id = ins.insight_id
left join COVEO_CORE_MODEL_V001.COMMERCE.TRANSACTIONS tr on tr.cart_id = c.cart_id
where date = :daterange
and ins.insight_type = 'listing'
)
select distinct
ec_listing,
sum(item_revenue)/count(distinct client_xid) as revenue_per_visitors
from transaction_base
group by ec_listing
having revenue_per_visitors is not null
order by revenue_per_visitors desc
limit 10When using the default query, your dashboard should look like the following:
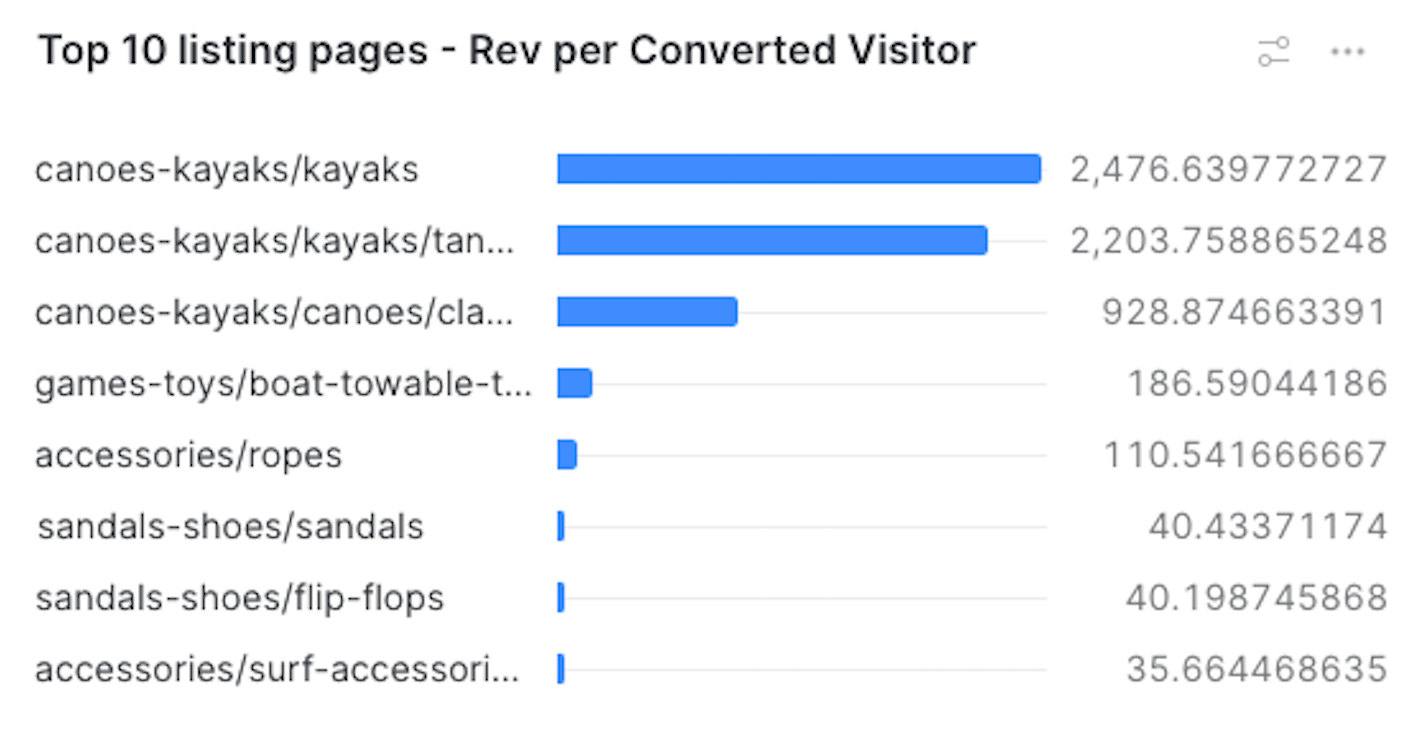
The Chart type, Data, and Appearance sections should look like the following. See Using charts for more information.
Top 10 recommendation components
The following query creates a Snowflake dashboard tile that displays the recommendation components that generated the highest RPV.
|
|
Updates to the computation methods for this metric have been implemented. As a result, executing this SQL query may yield slightly different results from those shown in the Advanced Reports (platform-ca | platform-eu | platform-au) page of the Coveo Administration Console. A new version of this query, which aligns with the outcomes of the reports of the Advanced Reports page, will soon be available. |
with transaction_base as (
select distinct
date(ins.start_time) as date,
v.client_xid,
origin as recommendation_component,
c.insight_id,
ins.insight_type,
tr.transaction_id,
c.item_id,
c.price*c.quantity as item_revenue
from COVEO_CORE_MODEL_V001.COMMON.INSIGHTS ins
join COVEO_CORE_MODEL_V001.COMMON.VISITS v on v.visit_id = ins.visit_id
left join COVEO_CORE_MODEL_V001.COMMERCE.CART_ITEMS c on c.insight_id = ins.insight_id
left join COVEO_CORE_MODEL_V001.COMMERCE.TRANSACTIONS tr on tr.cart_id = c.cart_id
where date = :daterange
and ins.insight_type = 'recommendation'
)
select distinct
recommendation_component,
sum(item_revenue)/count(distinct client_xid) as revenue_per_visitors
from transaction_base
group by recommendation_component
having revenue_per_visitors is not null
order by revenue_per_visitors desc
limit 10When using the default query, your dashboard should look like the following:
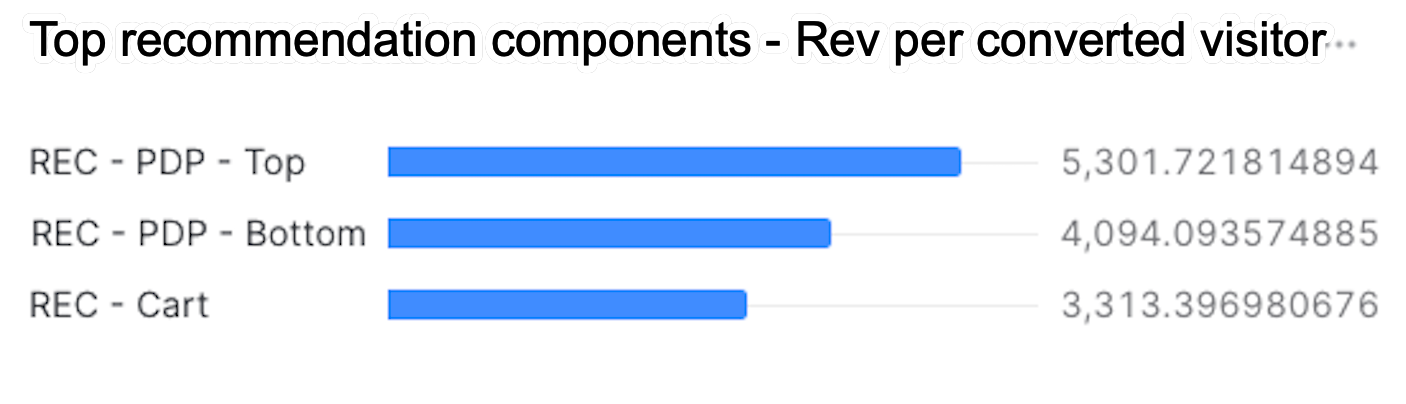
The Chart type, Data, and Appearance sections should look like the following. See Using charts for more information.