What’s attribution?
What’s attribution?
The Coveo for Commerce Advanced Reports rely on data attribution to provide insight on the key metrics that affect the performance of your ecommerce site. Attribution is the process of identifying the value of each touchpoint throughout the customer journey. This process is two-fold, as it first analyzes each touchpoint within the customer journey and determines how they led to a conversion. Afterward, it considers the entirety of the customer journey and determines which touchpoints should be credited for the total revenue.
In other words, conversion attribution identifies which events led to a transaction, while revenue attribution connects those events to determine how they impacted the total revenue of the transaction.
Attribution at Coveo
A conversion is typically the result of a series of events that map the customer journey. Therefore, it’s important to consider the entirety of the customer journey when analyzing the performance of your ecommerce site.
In the ecommerce industry, there are different types of attribution, such as last-touch and multi-touch attribution. While last-touch attribution bases the entirety of the conversion on the last click action on a product before being purchased, at Coveo, we rely on the more precise on-site multi-touch attribution to compute the metrics of the Advanced Reports.
On-site multi-touch attribution determines the value of each action that leads to a conversion, and is achieved by combining last-touch attribution with the product component. Available product components are search, recommendation, and listing.
Attribution example
A customer wants to purchase a laptop with a 12.4" display, as well as a 4k monitor, so they visit the store site for Acme Electronics:
-
They first type
laptop with 12.4 displayin the search bar. From the search results, they select a laptop priced at $500 and add it to their cart. -
Afterward, the customer views the products listed in the
Monitorslistings page until they find a 4k monitor priced at $250 and add it their cart. -
Lastly, when the customer is viewing their cart, they notice a product recommendation for a laptop bag priced at $50. They add the bag to the cart as well, and then proceed to the payment and complete the transaction.
If we analyze this customer journey through the on-site multi-touch attribution lens, the conversion is attributed to all three Coveo services:
-
1transaction is attributed to Coveo Search because of the event that occurred when the customer initially searched for the laptop. -
1transaction is attributed to Coveo Product Listings because of the event that occurred when the product listing in which the customer found the monitor was loaded. -
1transaction is attributed to Coveo Recommendations because of the event that occurred when the recommendation interface in which the customer found the laptop bag loaded.
|
|
Note
Transactions are only counted once on the Total transactions chart, even if they’re attributed to multiple Coveo services. |
While this transaction is attributed equally to each service, the revenue is attributed by the price of each item. The total of the transaction is $800, therefore:
-
$500 is attributed to the search event.
-
$250 is attributed to the product listing event.
-
$50 is attributed to the recommendation event.
For a more complex example involving multiple orders and items that aren’t attributed to Coveo, see Contribution to AOV.
|
|
If a transaction contains more than one product which is attributed to the same service, that transaction is counted only once on each service dashboard on the Advanced Reports (platform-ca | platform-eu | platform-au) page, regardless of how many items in the transaction are attributed to that same service. For example, a transaction contains four different products, each attributed to a specific Coveo service:
In this example, even though the Listing service is responsible for two products (Product 2 and Product 3), only one transaction is attributed to the Listing service. This means the transaction is split as follows:
|
About search attribution
If the visitor’s last action before adding the product to their cart was to click a search result that was returned after performing a query in the search box, Coveo attributes the purchase to the Coveo search service.
In this case, the visitor’s search query generates a unique ID called searchUid.
Sending the query causes a search page to load and provide search results that are related the query, which sends a search event to Coveo.
This search event contains in its payload a searchQueryUid property which is filled with the value of the searchUid returned by the visitor’s search query.
When the visitor clicks a product, the click event sent to Coveo includes the searchQueryUid property filled with the value of the searchUid generated by the search query.
By tracking the unique ID value used throughout the actions leading up to the purchase, Coveo can determine that the Coveo Search service was responsible for the purchase.
About product listings attribution
If the visitor’s last action before adding the product to their cart was to click a search result that was shown on a product listing page they accessed by selecting a product category, Coveo attributes the purchase to the Coveo product listings service.
In this case, selecting a product category sends a request to the Search API, which generates a unique ID called searchUid.
Sending this request causes the product listing page to load and display products that are relevant to the selected category, which sends a search event to Coveo UA.
This search event contains in its payload a searchQueryUid property which is filled with the value of the searchUid returned by the request to the Search API.
When the visitor clicks a product, the click event sent to Coveo includes the searchQueryUid property filled with the value of the searchUid generated by the search query.
By tracking the unique ID value used throughout the actions leading up to the purchase, Coveo can determine that the Coveo Listings service was responsible for the purchase.
About recommendation attribution
If the visitor’s last action before adding the product to their cart was to select a product from a recommendation interface, Coveo attributes the purchase to the Coveo recommendations service.

Recommendation interfaces can appear in different places in a Coveo-powered website. For example, they can appear on home pages, cart pages, product detail pages, etc.
When a page containing a recommendation interface loads, a request to the Search API is sent to query products that will fill the recommendation component.
The request generates a unique ID called searchUid.
Sending this request causes the recommendation interface to load and display the products returned by the request to the Search API, which sends a search event to Coveo UA.
This search event contains in its payload a searchQueryUid property which is filled with the value of the searchUid returned by the request to the Search API.
When the visitor clicks a product from the recommendation interface, the click event sent to Coveo includes the searchQueryUid property filled with the value of the searchUid generated by the search query.
By tracking the unique ID value used throughout the actions leading up to the purchase, Coveo can determine that the Coveo Recommendations service was responsible for the purchase.
On-site multi-touch attribution strategy
Coveo’s on-site multi-touch attribution strategy is further refined by the end result of the customer journey:
-
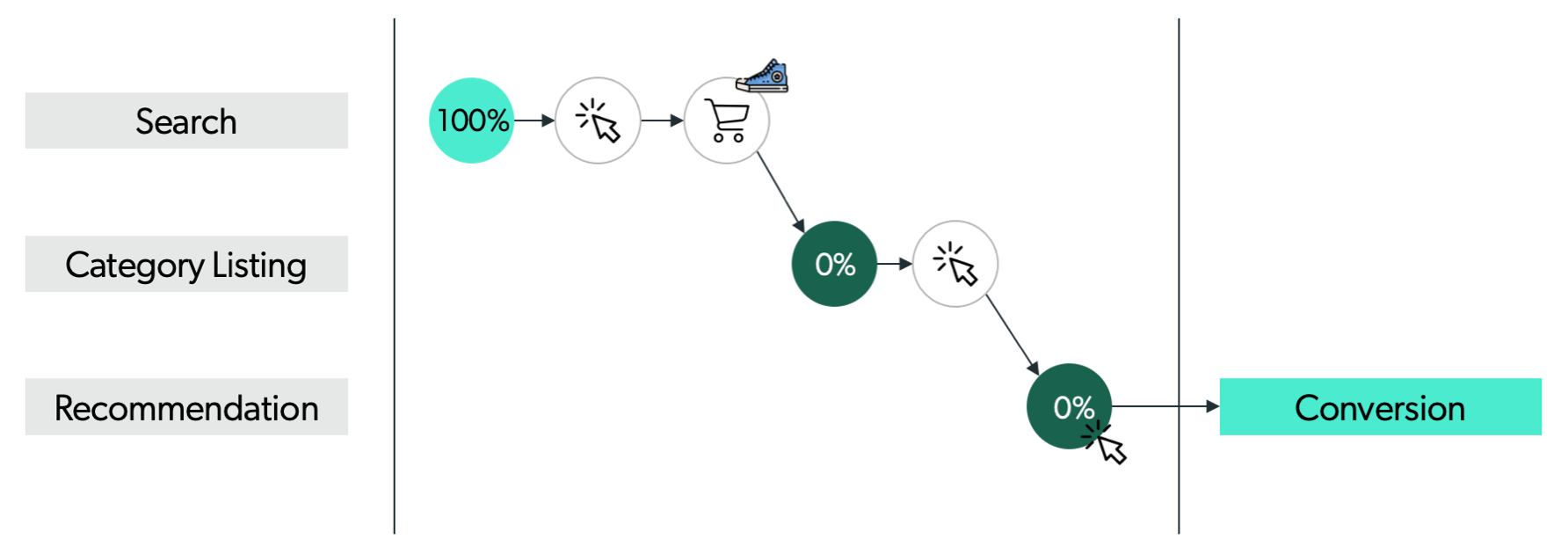
If a conversion with a purchase event including one product occurred, the last touchpoint before the add-to-cart defines the attribution.
ExampleIn the following customer journey where one product was purchased, the last touchpoint before the add-to-cart is a search on the search bar. Therefore, the entirety of the conversion is attributed to the search event triggered by the customer’s search action.
-
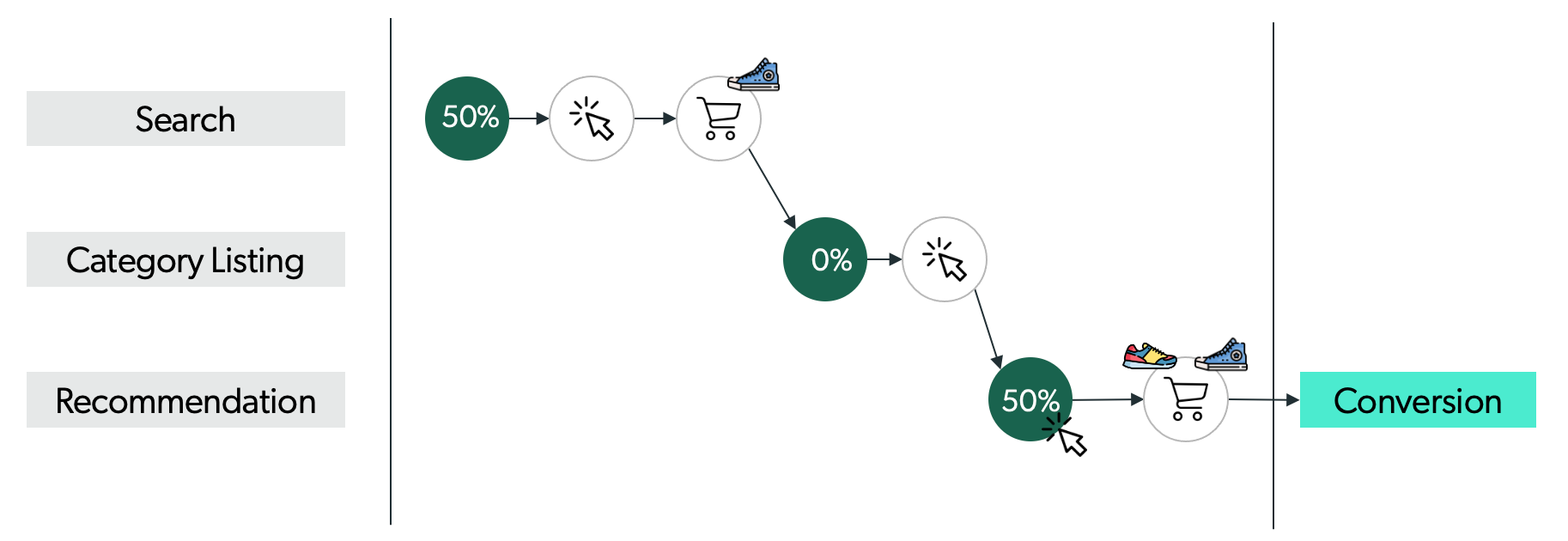
If a conversion with a purchase event of more than one product occurred, the last touchpoint before each add-to-cart defines the attribution. This means that each product is attributed to the last touchpoint before it was added to the cart.
ExampleIn the following customer journey where more than one product is purchased, the last touchpoints before each product is added to the cart are different. The first product’s touchpoint is a search on the search bar and the second product’s touchpoint is a click on a product recommendation. Therefore, the attribution is divided between the search events associated with the actions that displayed the purchased products (the search on the search bar and the generation of the recommended products).
-
If a conversion with a purchase event of more than one product occurred, and one of the purchased products was added from an external recommendation advert (other than Coveo), only the touchpoints associated with Coveo define the attribution.
ExampleA customer lands on a Coveo-powered site after a Google search. In the search bar, the customer enters “women sneaker” and clicks the first item (
product_id-1) that appears in the search results. They add the sneaker to their cart.At the bottom of that Product detail page (PDP), in the Coveo recommendation carousel, the customer clicks a recommended product (
product_id-2) and adds it to their cart as well.Without completing the purchase, but with the items still in the cart, the customer leaves the website.
Moments later, the customer finds and clicks a Google ad for another pair of shoes (
product_id-3) from the same site they were browsing previously. They add this product to their cart that previously contained the two other items.Their cart now contains three products (
product_id-1,product_id-2, andproduct_id-3), each one of them found through different services: a Coveo-powered search bar, a Coveo recommendation carousel, and a Google ad.If the customer completes the purchase for the three items in their cart, assuming the prices and quantity remain the same, 2/3 of the revenue will be attributed to Coveo. However, in regards to the transactions, 2 transactions are attributed to Coveo.