Capture cart events
Capture cart events
This article explains how to capture cart events and send the information to Coveo Usage Analytics (Coveo UA).
When to capture a cart event
Any time the content of a cart is modified by a user, the interface must log a cart event, together with the product information payload. Cart content modifications may include adding products, removing products, or changing the quantity of existing products in the cart. Depending on your site’s design, cart events can be triggered from different places, such as:
-
From a page which shows the current contents of a visitor's shopping cart
-
From an individual product detail page (PDP)
-
From a search results page
-
From a product listing page (PLP)
-
From a recommendation slot
|
|
cart events don’t count towards attribution. You must send an additional click event if the cart is modified directly from a search results page, PLP, or recommendation slot. |
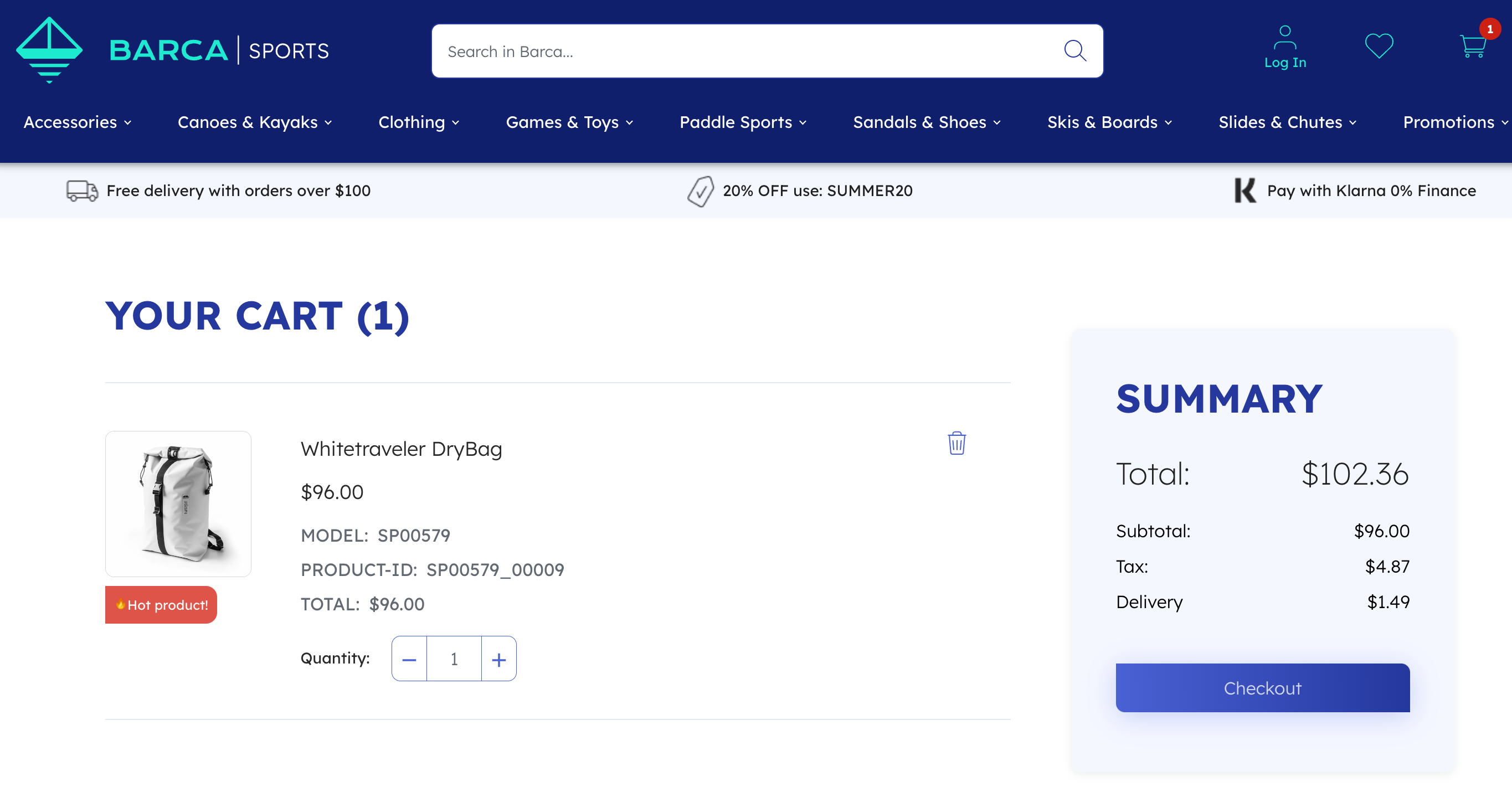
The following image is from the cart page view of the online sporting goods store Barca Sports, which provides visitors with the ability to modify the contents of their cart by increasing or decreasing the quantity of items.
At a minimum, log the product information and the quantity added or removed in the product data payload.
Coveo calculates quantity as the increase or decrease in value, not the new total amount.
For example, if a client changes the quantity of an item in the cart from 1 to 2, the quantity to pass in the cart event is 1.
Cart events and attribution
Coveo attributes transactions to product discovery solutions by tracking touchpoints along the user journey. In a Coveo-powered commerce implementation, click events are the main touchpoints used for attribution.
Cart events don’t count towards attribution. If your commerce implementation lets users modify the cart directly from the search results page, product listing pages (PLPs), or recommendation slots, you must send an additional click event along with the cart event. This lets Coveo attribute transactions to the correct solutions.
For more information, see Attribution at Coveo.
A user performs a query on a Coveo-powered commerce site. They click a product to open its product detail page (PDP), but they don’t make a purchase and navigate away from the site. Coveo tracks this touchpoint as part of the user’s journey.
Later, they revisit the site and see the same product in a recommendation slot. They click the product to open its PDP, creating another touchpoint tracked by Coveo. This time, the user adds the product to their cart and completes the purchase. This product is attributed to the recommendation solution.
How to capture a cart event
Capturing a cart event depends on your implementation approach.
-
If you’re using Headless, capture the event using the Headless controllers.
-
If you’re not using Headless, use the Relay library directly to capture the event.
Capture a cart event using Headless
With the Headless library, you can capture cart events using the Cart controller.
For more details, see Managing the cart.
Capture a cart event using Relay
If you’re using Relay library, when a user adds a product to cart, you can run the following code to capture the event and send the information to Coveo.
const relay = createRelay({...});  relay.emit('ec.cartAction', {
relay.emit('ec.cartAction', {  action: 'add',
action: 'add',  currency: 'USD',
quantity: 1,
product: {
productId: 'SP03929_00014',
name: 'Blue Bottle',
price: 16,
},
});
currency: 'USD',
quantity: 1,
product: {
productId: 'SP03929_00014',
name: 'Blue Bottle',
price: 16,
},
});| Initialize a Relay instance. | |
Use the emit function to send an event with Relay, specifying the event name.
In this example, the value is ec.cartAction since it’s capturing a cart event. |
|
| Include the necessary event data, as outlined in the reference documentation. Here a single product is being added to the cart. |
For a detailed description of the functions offered by the library, see the Relay documentation.
|
|
Note
When sending events with Relay, you don’t need to include the |
Send an additional click event
If your Coveo-powered commerce implementation lets users send cart events directly from the search results page, product listing pages (PLPs), or recommendation slots, you must send an additional click event along with the cart event.
Each query has a unique responseId associated with it, whether it generates search results, displays product listings, or showcases recommendations.
You must include this responseId in the click event sent along with the cart event so that Coveo can attribute transactions with direct cart events to the correct solutions.
const relay = createRelay({...});
relay.emit('ec.productClick', {  currency: 'USD',
position: 1,
responseId: '35009a79-1a05-49d7-b876-2b884d0f825b',
product: {
productId: 'SP03929_00014',
name: 'Blue Bottle',
price: 16,
},
});
relay.emit('ec.cartAction', {
currency: 'USD',
position: 1,
responseId: '35009a79-1a05-49d7-b876-2b884d0f825b',
product: {
productId: 'SP03929_00014',
name: 'Blue Bottle',
price: 16,
},
});
relay.emit('ec.cartAction', {  action: 'add',
currency: 'USD',
quantity: 1,
product: {
productId: 'SP03929_00014',
name: 'Blue Bottle',
price: 16,
},
});
action: 'add',
currency: 'USD',
quantity: 1,
product: {
productId: 'SP03929_00014',
name: 'Blue Bottle',
price: 16,
},
});| Log the click event, following the reference documentation. | |
| Log the cart event, following the reference documentation. |
Validating the cart event
It’s important to verify that your event is valid and contains the correct payload. Relay seamlessly integrates with Coveo Explorer, which can be used for event validation.
For more details on using Coveo Explorer to validate events, see Validating events.