Document Object Python API Reference
Document Object Python API Reference
Creating an indexing pipeline extension (IPE) implies writing Python code that uses the document object to manipulate item properties (see Creating an Indexing Pipeline Extension With the API and Coveo Indexing Pipeline).
This article provides reference information describing the object methods and their parameters. You may also want to read about the versions of the Indexing Pipeline Extensions API, especially if your organization has dictionary fields.
Log
This method displays a message and its severity in the current Log Browser (platform-ca | platform-eu | platform-au) entry. It’s useful when debugging.
|
|
Leading practice
Always use the |
Syntax:
log(message, severity)
log Parameters
The following table shows the log method parameters:
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Required: string |
The message that you want to log when applying an extension script. |
|
string |
Optionally used to indicate the message severity type. Default value is The allowed case insensitive severity values are:
|
log Examples
log("Hello world!", "Notification")fulltitle = document.get_meta_data_value('titleselection', 'crawler', True)
try:  # modifying fulltitle variable
fulltitle = fulltitle[0]
# logging a meaningful success message
log('added metadata value to title: ' + fulltitle)
# catching all exceptions and logging them as a string for debugging purposes
except Exception as e:
# modifying fulltitle variable
fulltitle = fulltitle[0]
# logging a meaningful success message
log('added metadata value to title: ' + fulltitle)
# catching all exceptions and logging them as a string for debugging purposes
except Exception as e:  log(str(e), 'Error')
log(str(e), 'Error')This script example uses the log method in two different ways.
-
First, the
tryblock modifies the metadata and logs a success message only when the script runs without raising an error. In this particular case, the second argument is missing as the default valueNormaldefines the log message severity. -
When the
tryblock fails, theexceptblock catches the exception and sends a log containing the error message:
|
|
Note
Applying an extension populates the For example, when a very long string exceeds the 4K limit, even if it represents the one and only log that applies to your extension, the whole string is replaced with the 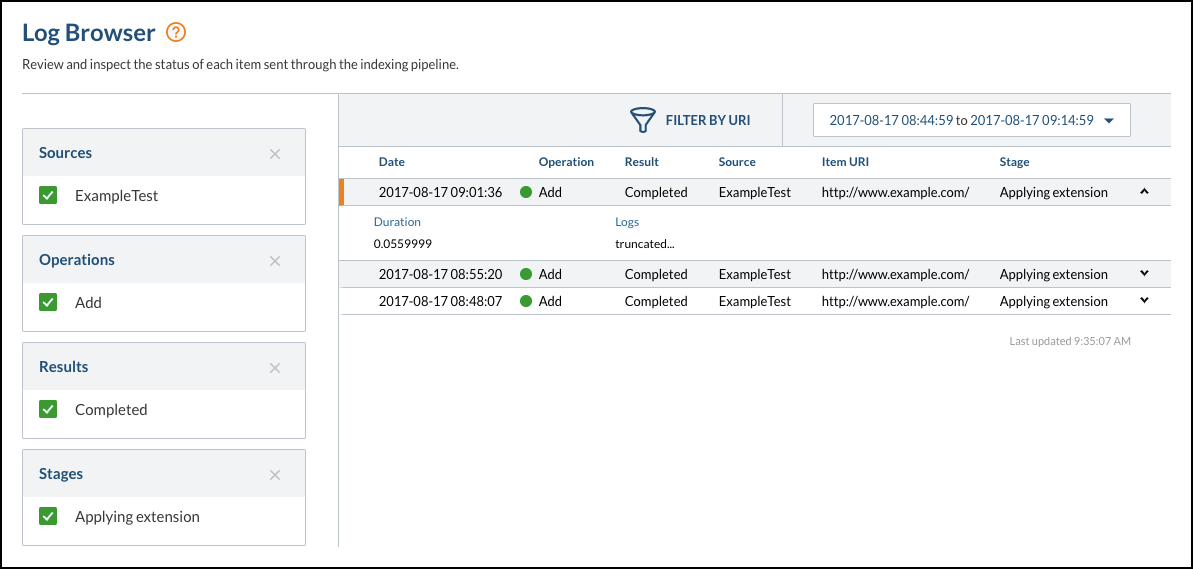
|
Get URI
You use this method to get the item URI.
Syntax:
document.uriYou can easily output an item uri in the Log Browser by adding those lines in your extension:
my_variable = document.uri
log(my_variable)Get All Metadata
You use this method to get all item metadata.
It returns a list of MetaDataValue objects (see Document Object JSON Schema).
Syntax:
document.get_meta_data()Because unmapped metadata isn’t indexed, using this method makes all metadata available before the final indexing step. The following extension script makes it possible to consult a list of all custom metadata:
import json
document.add_meta_data({'allmetadatavalues': json.dumps(document.get_meta_data())})|
|
You must map the |
Get a Metadata Value
You use this method to get a metadata value for a given metadata name and origin.
|
|
Note
This method returns a list of values. If there’s only one metadata value, this list will contain a single element. |
Syntax:
document.get_meta_data_value(name, origin, reverse)
get_meta_data_value Parameters
The following table shows the get_meta_data_value method parameters:
| Parameter | Type | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Required: string |
The name of the metadata to retrieve. |
||
|
string |
The unique identifier of the Coveo indexing pipeline step from which to retrieve a metadata value. The allowed
|
||
|
Boolean |
Whether to scan the metadata origin in reverse order or not.
The default value is |
get_meta_data_value Example
# Get original title from the crawling module in a log message
original_title = document.get_meta_data_value('title', 'crawler') # Remember, this method returns a list
log(original_title[0], 'Normal')Add Metadata
You use this method to add an item metadata key and its associated value. You can also use it to unset or override item metadata.
|
|
For all sources except push sources, if you add metadata before the mapping stage, you must map the metadata to a field for it to be indexed. For example, if you add metadata in a post-conversion extension script, the metadata is only indexed when the index contains a field whose name matches the metadata key. |
Syntax:
document.add_meta_data({metadataKey: metadataValue})Use an array to specify values for a multi-value field:
document.add_meta_data({"language": ["en", "fr"]})Because unmapped metadata isn’t indexed, using this method makes all metadata available before the final indexing step. The following extension script makes it possible to consult a list of all custom metadata:
import json
document.add_meta_data({'allmetadatavalues': json.dumps(document.get_meta_data())})|
|
You must map the |
add_meta_data Example
# Unsetting the author metadata value
document.add_meta_data({'Author': ''})Get All Permissions
You use this method to get all item permissions.
It returns a list of PermissionLevel objects:
{
"PermissionSets": [
{
"AllowAnonymous": false,
"DeniedPermissions": [],
"Name": "",
"AllowedPermissions": []
}
],
"Name": ""
},
{
"PermissionSets": [
{
"AllowAnonymous": false,
"DeniedPermissions": [],
"Name": "View All Data Members",
"AllowedPermissions": [
{
"SecurityProvider": "SALESFORCE-00Df40000000SAbEAM",
"IdentityType": "virtualgroup",
"Identity": "ViewAll:Irrelevant:",
"AdditionalInfo": {}
},
{
"SecurityProvider": "SALESFORCE-00Df40000000SAbEAM",
"IdentityType": "virtualgroup",
"Identity": "ObjectAccess:ViewAllRecordsProfiles:Solution",
"AdditionalInfo": {}
},
{
"SecurityProvider": "SALESFORCE-00Df40000000SAbEAM",
"IdentityType": "virtualgroup",
"Identity": "ObjectAccess:ViewAllRecordsPermissionSets:Solution",
"AdditionalInfo": {}
}
]
}
],
"Name": "View All Data"
},
{
"PermissionSets": [
{
"AllowAnonymous": false,
"DeniedPermissions": [],
"Name":"Read access members",
"AllowedPermissions": [
{
"SecurityProvider": "SALESFORCE-00Df40000000SAbEAM",
"IdentityType": "virtualgroup",
"Identity": "ObjectAccess:ReadRecordsProfiles:Solution",
"AdditionalInfo": {}
},
{
"SecurityProvider": "SALESFORCE-00Df40000000SAbEAM",
"IdentityType": "virtualgroup",
"Identity": "ObjectAccess:ReadRecordsPermissionSets:Solution",
"AdditionalInfo": {}
}
]
}
],
"Name": "Read Access & Sharing"
}Syntax:
document.get_permissions()
get_permissions Example
# Get item permissions in a log message
import json
my_permissions = json.dumps(document.get_permissions())
log(str(my_permissions))Clear All Permissions
You use this method to clear all item permissions.
|
|
Be careful when using the |
Syntax:
document.clear_permissions()Add Allowed Permission
You use this method to add an allowed security identity.
Syntax:
document.add_allowed(identity, identity_type, security_provider, {additional_info})
add_allowed Parameters
The following table shows the add_allowed method parameters:
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Required: string |
The allowed security identity name to add. |
|
Required: string |
Allowed values are:
|
|
Required: string |
The name of the security identity provider. Sample value: |
|
dictionary of string |
A collection of key value pairs that can be used to uniquely identify the security identity. |
add_allowed Example
# Allowing access to all users logging in with Coveo account
document.add_allowed('*@coveo.com', 'user', 'Email Security Provider', {})Add Denied Permission
You use this method to add a denied security identity.
Syntax:
document.add_denied(identity, identity_type, security_provider, {additional_info})
add_denied Parameters
The following table shows the add_denied method parameters:
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Required: string |
The denied security identity name to add. |
|
Required: string |
Allowed values are:
|
|
Required: string |
The name of the security identity provider. Sample value: |
|
dictionary of string |
A collection of key value pairs that can be used to uniquely identify the security identity. |
add_denied Example
# Denying access to all users logging in with hotmail account
document.add_denied('*@hotmail.com', 'user', 'Email Security Provider', {})Set Permissions
You use this method to set item permissions. To set permissions, define at least one permission level, one permission set, and one permission.
Syntax:
document.set_permissions([PermissionLevel])PermissionLevel
The following table shows the permission level parameters:
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
String |
The name of the permission level. |
|
Array of PermissionSet |
Array of permission sets |
PermissionSet
The following table shows the permission set parameters:
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Required: String |
The name of the permission set. |
|
Required: Boolean |
Whether to allow anonymous access. |
|
Array of Permission |
Array of allowed permissions |
|
Array of Permission |
Array of denied permissions |
Permission
The following table shows the permission parameters:
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Required: string |
The name of the security identity. Sample value: |
|
Required: string |
Allowed values are:
|
|
Required: string |
The name of the security identity provider. Sample value: |
|
dictionary of string |
A collection of key value pairs that can be used to uniquely identify the security identity. |
set_permissions Example
The complexity of the permission model can range from allowing full anonymous access to requiring the resolution of permissions for several permission levels, each containing one or more permissions sets.
import json
# defining security levels
# top_level allows ceo@coveo.com and denies Accountants
top_level = document.PermissionLevel('CEO', [document.PermissionSet('TopSet', False,
[document.Permission('ceo@coveo.com', 'user', 'Email Security Provider')],
[document.Permission('Accountants', 'group', 'Email Security Provider')])])
# lower_level allows myGroup1 and denies myGroup2 and myGroup3
lower_level = document.PermissionLevel('Employees', [document.PermissionSet('LowerSet', False,
[document.Permission('myGroup1', 'group', 'Email Security Provider')],
[document.Permission('myGroup2', 'group', 'Email Security Provider'),
document.Permission('myGroup3', 'group', 'Email Security Provider')])])
# Set item permission levels
document.set_permissions([top_level, lower_level])
# Get item permissions in a log message
my_permissions = json.dumps(document.get_permissions())
log(str(my_permissions))Get All Data Streams
You can use this method to get access to item data streams when you must read or modify these streams.
This method returns a list of ReadOnlyDataStream objects.
Each of these is a BytesIO value, which is a stream of in-memory bytes (see Python Buffered Streams).
[
<extension_runner.ApiV1.ReadOnlyDataStream object at 0x7f88fc0665d0>,
<extension_runner.ApiV1.ReadOnlyDataStream object at 0x7f88fc0662d0>,
<extension_runner.ApiV1.ReadOnlyDataStream object at 0x7f88fc066590>
]Syntax:
document.get_data_streams()
get_data_streams Example
-
In the Edit an extension window, select at least one of the checkbox associated with each item data in order for the
get_data_streams()method to return something. Note
NoteA user must specify that their extension requires access to an item binary data in order for the data to be downloaded and passed along to the extension runner.
To optimize indexing performance, you should only access a data stream when necessary.
-
Use the
get_data_streams()method in your Python extension script.body = document.get_data_streams() # body is now a list of `ReadOnlyDataStream` objects which are accessible data streams # body[1] is the `ReadOnlyDataStream` object corresponding to `body_html` log(body[1].read())The preceding code has visible effects in the Log Browser:
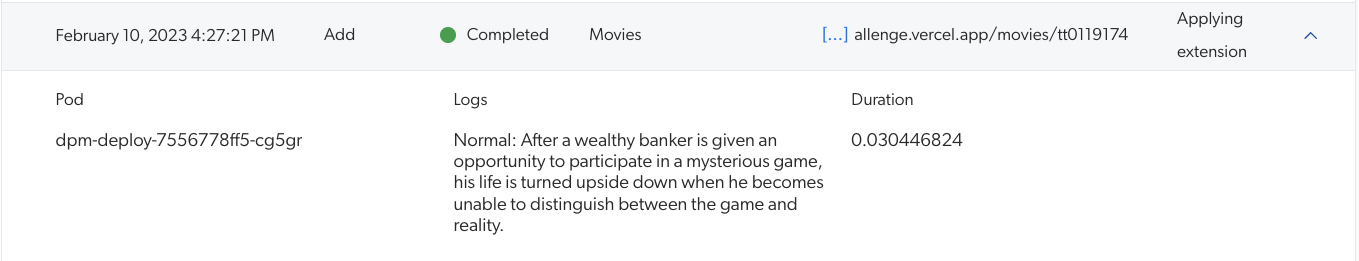
Get a Data Stream
You use this method to get a data stream for a given name and origin.
This method returns a single ReadOnlyDataStream object.
This is a BytesIO value, which is a stream of in-memory bytes (see Python Buffered Streams).
|
|
Note
For Web and Sitemap type sources, use the web scraping feature rather than extensions to do common HTML content processing such as excluding sections and extracting metadata (see Web scraping configuration). |
Syntax:
document.get_data_stream(name, origin, reverse)
get_data_stream Parameters
The following table shows the get_data_stream method parameters:
| Parameter | Type | Description | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Required: string |
The available item data streams are:
|
||||||||||
|
string |
The unique identifier of the Coveo indexing pipeline step from which to retrieve a data stream. The allowed
|
||||||||||
|
Boolean |
Whether to scan the metadata origin in reverse order or not.
The default value is |
get_data_stream Examples
# Get document body text data stream to appear in a log message
# You must select the Body text checkbox because this indexing pipeline extension script needs to access it
my_data_stream = document.get_data_stream('body_text').read()
log(my_data_stream)# Get decoded documentdata stream to appear in a log message
# You must select the Original file checkbox because this indexing pipeline extension script needs to access it
my_data_stream = document.get_data_stream('documentdata').read().decode()
log(my_data_stream)DataStream Attribute Setter
You use this method to access and set a DataStream object for a given name and origin.
This method returns a single modifiable DataStream object.
This is a BytesIO value, which is a stream of in-memory bytes (see Python Buffered Streams).
When applicable, the extension runner is responsible for writing the item binary data back after executing the script.
Syntax:
document.DataStream(name, origin, reverse)The parameters are the same as those listed above for the get_meta_data method.
DataStream Example
# Override the item body text
text = document.DataStream('body_text')
text.write('This is a test')
document.add_data_stream(text)Add Data Stream
You use this method to add or override an item data stream.
Syntax:
document.add_data_stream(stream)
add_data_stream Example
# Import the requests library to perform API calls
import requests
extracted_text = [x.strip('\r\n\t') for x in document.get_data_stream('body_text', 'converter').readlines() if x.strip('\r\n\t')]
# Override item html with perdu.com
html = document.DataStream('Body_HTML')
html.write(requests.get('http://perdu.com').text)
# Override the text with part of the original item
text = document.DataStream('body_text')
text.write('This is a test.')
text.write(extracted_text[0])
# Override the thumbnail of the item with Coveo logo
thumbnail = document.DataStream('$thumbnail$')
thumbnail.write(requests.get('https://careers.coveo.com/assets/images/opengraph.png').content)
document.add_data_stream(html)
document.add_data_stream(text)
document.add_data_stream(thumbnail)Reject Item
You use this method to set the item state as rejected.
Syntax:
document.reject()Document Object JSON Schema
The Document object can be represented with the following JSON schema:
{
"$schema": "http://json-schema.org/draft-04/schema#",
"definitions": {
"MetaDataValue": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"origin": {
"type": "string"
},
"values": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"key": {
"type": "string"
},
"value": {
"type": "array",
"items": {
"type": "string"
}
}
}
}
}
},
"Permission": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"identity": {
"type": "string"
},
"identity_type": {
"type": "string"
},
"security_provider": {
"type": "string",
"enum": ["user", "group", "virtualgroup", "unknown"]
},
"additional_info": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"key": {
"type": "string"
},
"value": {
"type": "string"
}
}
}
}
},
"PermissionSet": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"name": {
"type": "string"
},
"allow_anonymous": {
"type": "boolean"
},
"allowed_permissions": {
"type": "array",
"items": {
"$ref": "#/definitions/Permission"
}
},
"denied_permissions": {
"type": "array",
"items": {
"$ref": "#/definitions/Permission"
}
}
}
},
"PermissionLevel": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"name": {
"type": "string"
},
"permission_sets": {
"type": "array",
"items": {
"$ref": "#/definitions/PermissionSet"
}
}
}
},
"DataStream": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"name": {
"type": "string"
},
"origin": {
"type": "string"
}
}
},
"Document": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"uri": {
"type": "string"
},
"meta_data": {
"type": "array",
"items": {
"$ref": "#/definitions/MetaDataValue"
}
},
"permissions": {
"type": "array",
"items": {
"$ref": "#/definitions/PermissionLevel"
}
},
"data_streams": {
"type": "array",
"items": {
"$ref": "#/definitions/DataStream"
}
}
}
}
}
}To consult a single item document object just before indexing time, using this script as the last executed post-conversion script populates a documentobject metadata.
import json
# Get document object JSON into a metadata
document_object = json.dumps(document)
document.add_meta_data({'documentobject': document_object})|
|
Note
You must map |
The preceding extension script returns the document object JSON:
{
"DataStream": [
{
"Origin": "converter",
"Name": "body_html"
},
{
"Origin": "mypostconversionextension",
"Name": "body_html"
},
{
"Origin": "converter",
"Name": "body_text"
},
{
"Origin": "mypostconversionextension",
"Name": "body_text"
},
{
"Origin": "mypostconversionextension",
"Name": "$thumbnail$"
},
{
"Origin": "crawler",
"Name": "documentdata"
}
],
"Permissions": [
{
"PermissionSets": [
{
"AllowAnonymous": false,
"DeniedPermissions": [],
"Name": "",
"AllowedPermissions": [
{
"SecurityProvider": "Email Security Provider",
"IdentityType": "user",
"Identity": "*@coveo.com",
"AdditionalInfo": {}
}
]
}
],
"Name": ""
}
],
"URI": "http://www.example.com/",
"MetaData": [
{
"Origin": "crawler",
"Values": {
"originaluri": [
"http://www.example.com/"
],
[ ... ]
"permanentid": [
"f1777111f5d0f1c81ffa04de75112889e6a0649e06d83370cdf2cbfb05f3"
],
"content-type": [
"text/html; charset=utf-8"
]
}
},
{
"Origin": "mypreconversionextension",
"Values": {
"title": [
"Brand New Title"
]
}
},
{
"Origin": "converter",
"Values": {
"conversionstate": [
0
],
"detectedtitle": [
"Example Domain"
],
"language": [
"English"
],
[ ... ]
"originalhtmlcharset": [
65001
],
"extractedsize": [
420
]
}
},
{
"Origin": "mapping",
"Values": {
"sourcetype": [
"Web"
],
"language": [
"English"
],
"title": [
"Example Domain"
],
[ ... ]
"date": [
1376092475
],
"permanentid": [
"f1777111f5d0f1c81ffa04de75112889e6a0649e06d83370cdf2cbfb05f3"
],
"size": [
1270
]
}
},
{
"Origin": "mypostconversionextension",
"Values": {
"author": [
"Coveo Documentation Team"
]
}
}
]
}