Coveo Indexing Pipeline
Coveo Indexing Pipeline
The Coveo indexing pipeline is the process through which all content retrieved by a source goes before being indexed. The items get into the indexing pipeline either from Coveo source crawlers while the source is indexed (see Rebuild, Rescan, or Refresh operations), or when pushed by a custom process taking advantage of the Push API or Stream API.
For an administrator, a content manager, or a developer, knowing what the indexing pipeline does is useful in cases such as:
-
Troubleshooting item indexing issues while reviewing item logs from the Log Browser (platform-ca | platform-eu | platform-au) page.
-
Changing source mappings (see Manage source mappings).
-
Sending items to the Push API (see Push API usage).
See also About the Indexing Process.
The indexing pipeline consists of a series of sequential stages illustrated in the following diagram. As an administrator or developer, you can control the behavior of stages shown with a blue background, but can’t for the other stages.
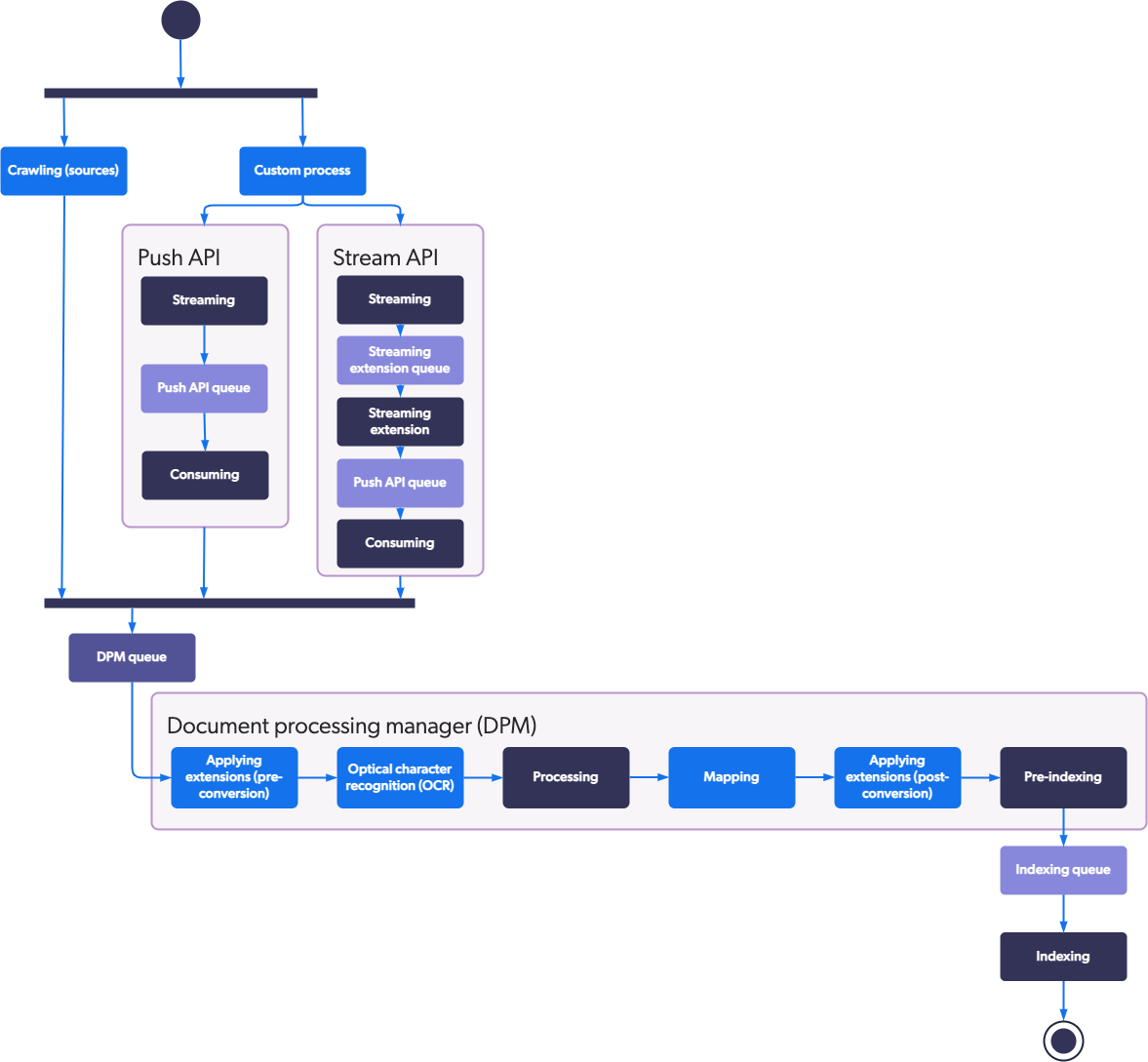
Each indexing pipeline stage is described in the rest of the article.
Crawling
A source crawls its target repository to fetch and push the content and metadata of each repository item.
As a member of the Administrators or Content Managers built-in groups, you can add sources from the Coveo Administration Console. Some item metadata is already made available by the connector, including the URI, modification date, and more depending on the source.
Streaming
The first Push API stage; reception of items to index from an external custom process.
As a developer, you fully control when and what items you send to the Push API, one by one or in batch (see Push API usage).
Streaming Extension Queue
The Streaming extension queue holds items ready to be processed by the Streaming extension stage.
Streaming Extension
The Streaming extension should be viewed as a way to enable specific ML features, such as Coveo Personalization-as-you-go, and is the only way to benefit from partial item updates.
Push API Queue
The Push API queue holds items ready to be processed by the Consuming stage.
Consuming
The last Push API stage transfers items to be processed from the Push API Push API Queue to the item processing manager DPM Queue one by one, or in batch, depending how they where pushed to the Streaming stage.
DPM Queue
The DPM queue holds the items ready to be processed by the item processing manager (DPM) set of stages.
Applying Extension (Pre-Conversion) (Optional)
Similar to Applying Extension (Post-Conversion).
Most indexing pipeline extensions are added in the post-conversion stage (see Pre-Conversion Versus Post-Conversion).
Optical Character Recognition (OCR)
At this stage, when Optical Character Recognition is enabled for a source, Coveo extracts text from images and PDF files (see Optical Character Recognition). The extracted text is then searchable in a Coveo-powered search interface and appears in the item Quick view (see Search result Quick view).
Processing
This stage essentially converts the content and properties of each item from its native format into a common format suitable for the Indexing stage using the appropriate Coveo converter for the supported file formats.
-
When the item is a PDF file, the PDF converter extracts the text and the properties from the PDF binary file.
-
When the item is an HTML file, the HTML converter extracts the text from the
bodyelement and metadata from themetaelements.
Mapping
This stage applies standard and custom source mappings to set Coveo field values with item metadata or literal text.
As an administrator:
-
When you create a source of a given type, a set of standard fields and mappings are automatically created. This source standard metadata is therefore automatically available in the index fields.
-
When you want to leverage custom metadata, you must create target Coveo index fields to host these metadata values and create mappings to set the Coveo index field values with the appropriate metadata or literal fix content (see Manage fields).
Applying Extension (Post-Conversion) (Optional)
By default, there are no post-conversion extensions.
As an administrator, maybe with the help of a developer, you can:
-
Create and add indexing pipeline extensions to your Coveo organization.
An extension script typically adds or modifies metadata, but can also read and modify item data streams as well as modify item permissions (see Use the Extensions API).
-
Assign one or more extensions to a specific source (see Apply an Extension to a Source).
-
Define a condition to execute the extension only when the item meets some criteria (see Indexing Pipeline Extension Condition Syntax Reference).
When assigned to a source, the script of an extension is executed for each source item.
When more than one pre-conversion extension is assigned to a source, they’re executed sequentially in the order in which they’re added to the source configuration.
When an extension script throws an error, the item keeps going through the next indexing pipeline stage.
Pre-Indexing
This stage further processes item fields and metadata to optimize index efficiency.
Indexing
This stage puts the item extracted content and properties into the Coveo unified index to make it available for user queries. Temporary files containing the extracted item content and properties are then deleted.
|
|
Note
Your Coveo index doesn’t store a copy of your original files. However, stored data include an excerpt of the item content to display in the search results. |
|
|
If your search page includes the Quickview component, users can use it to view the entire content of their search results (see Coveo Quickview Component). |