Create and manage Passage Retrieval (CPR) models
Create and manage Passage Retrieval (CPR) models
|
|
Passage Retrieval (CPR) is a paid product extension. Contact Coveo Sales or your Account Manager to add CPR to your organization license. |
A Passage Retrieval (CPR) model retrieves the most relevant passages that will be used by a generative application to generate output.
To implement CPR, you must first create a CPR model.
What does a CPR model do?
When a CPR model builds, it creates embeddings for the indexed items specified in the model settings and stores the embeddings in model memory.
|
|
Note
The model is preconfigured to rebuild and update the embeddings weekly based on when the model is created. Contact your Coveo Account Manager if a different build interval is required. |
|
|
By default, content retrieval is supported only for English content. However, Coveo offers beta support for content retrieval in languages other than English. Learn more about multilingual content retrieval and answer generation. |
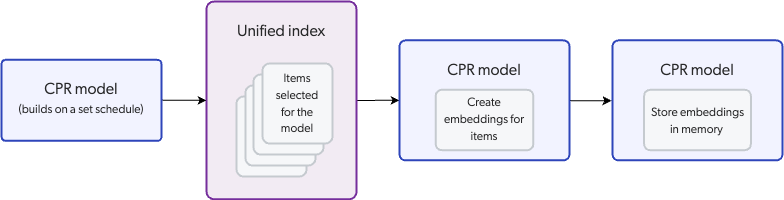
A CPR model uses a pre-trained sentence transformer language model to create the embeddings. The language model does this by capturing relationships between words, phrases, and sentences in the dataset.
A CPR model creates embeddings only for the content in an item's body, which is the content mapped to the body field in the Coveo index.
For more information, learn how CPR uses your content.
As shown in the following diagram, the model uses chunks to create the embeddings. Instead of creating a vector for each individual word, a vector is created for a segment of text (chunk) to increase relevance.
|
|
Note
You can choose the chunking strategy that the CPR model uses to create the chunks. |
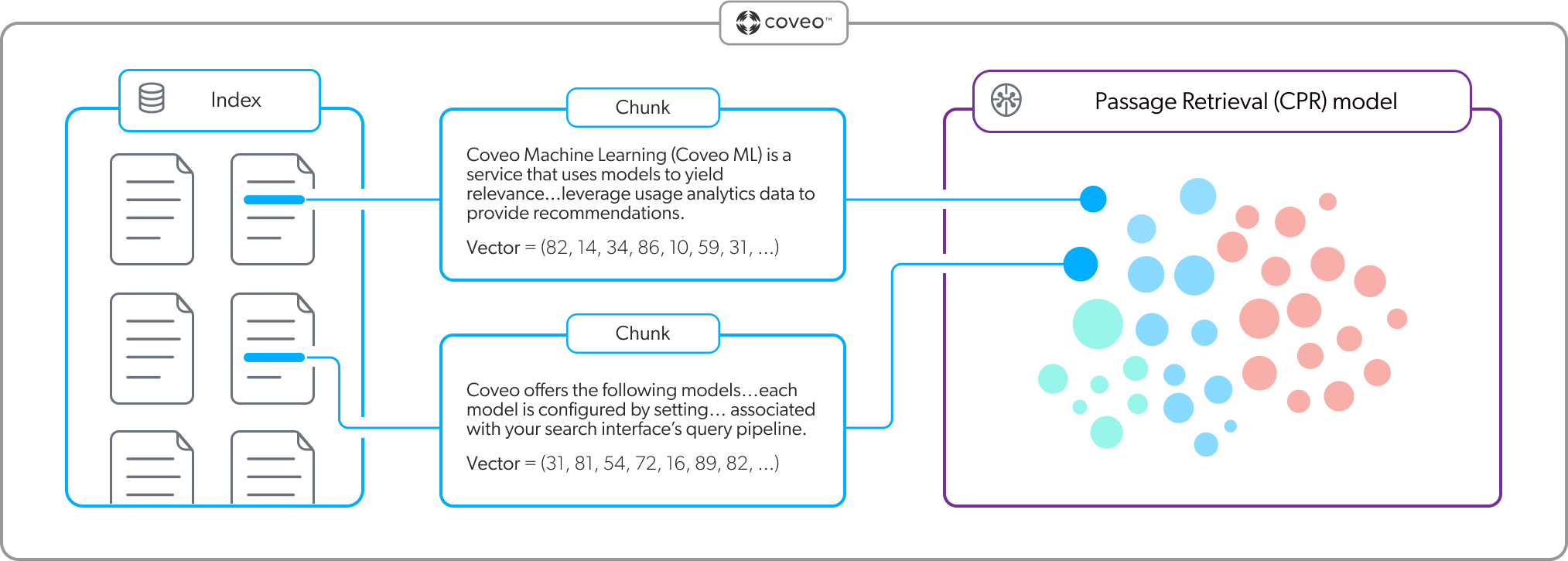
As shown in the following diagram, when a user enters a query in a LLM-powered application, the CPR model embeds the query in the embedding vector space in its memory to find the most relevant passages (chunks). In the context of the CPR passage retrieval flow, this is referred to as second-stage content retrieval. Only the passages corresponding to the most relevant items identified during first-stage content retrieval (items retrieved by the Coveo search engine) are considered. The most relevant passages are then exposed by the Passage Retrieval API to the LLM so it can generate an answer.

|
|
The embeddings that are created by the CPR model aren’t impacted by Coveo Analytics events. However, a CPR model leverages the most relevant items retrieved by your Coveo-powered search for a given user query. Therefore, by enabling an Automatic Relevance Tuning (ART) model, which learns from Coveo Analytics events, then the most relevant items, and by extension the generated output by your LLM, will be influenced by Coveo Analytics events. |
|
|
Note
You can set a custom value for the maximum number of items that the CPR model considers when retrieving the most relevant segments of text (passages). This is an advanced model query pipeline association configuration that should be used by experienced Coveo administrators only. For more information, see CPR model association advanced configuration. |
Prerequisites
-
You have the required privileges to create a CPR model.
-
The content you want to use for the model meets the item requirements and is optimized for CPR.
NoteA Passage Retrieval (CPR) implementation must include both a CPR model and a Semantic Encoder (SE) model. The same SE model can be used with multiple CPR models. Both the CPR and SE models must be configured to use the same content.
See CPR overview for information on how CPR and SE work together in the context of a user query to retrieve passages.
Keep the model embedding limits in mind when choosing the content for your model.
Create a CPR model
-
On the Models (platform-ca | platform-eu | platform-au) page of the Coveo Administration Console, click Add model, and then click the Passage Retrieval card.
-
Click Next.
-
In the Learn from section, select the content that the model will use. You can select the sources and apply additional filters using the Standard configuration, or use Advanced mode to define a custom filter expression.
You’ll lose the current mode settings when you switch between Standard and Advanced mode.
NoteA Passage Retrieval (CPR) implementation must include both a CPR model and a Semantic Encoder (SE) model. The same SE model can be used with multiple CPR models. Both the CPR and SE models must be configured to use the same content.
See CPR overview for information on how CPR and SE work together in the context of a user query to retrieve passages.
The Data volume preview section shows the impact of your settings on the data that’s available to the model.
-
In the Standard tab:
-
In the Sources dropdown menu, select the sources that contain the items from which you want the model to learn.
NoteIf your Coveo organization includes multiple indexes, the model can learn only from sources that are linked to the default index.
-
(Optional) In the Apply filters on dataset section, you can specify a condition to segment the content on which the model should base its training:
ExampleYou want the model to base its training only on items for which the collection field have the
FAQvalue.Therefore, you add a
collection is equal to FAQcondition.-
Click Add filter(s).
-
In the Field name input, enter the name of the field that you want to use to segment the dataset.
-
In the Select an operator dropdown menu, select the desired operator.
-
In the Value input, enter the value of the field on which you want to segment the dataset.
-
Click Apply.
-
-
-
In the Advanced tab:
-
Enter a custom filter expression using Coveo query syntax.
-
Click Apply.
-
-
-
Click Next.
-
In the Name your model input, enter a meaningful display name for the model.
-
(Optional) Use the Project selector to associate your model with one or more projects.
-
Click Start building.
-
Associate the model with a pipeline to use the model in a search interface.
-
If required, change the chunking strategy that’s used by the model.
Set the chunking strategy
To create the embeddings, a CPR model uses a process called chunking to break large pieces of text into smaller segments called chunks. The method that’s used to create the chunks is referred to as the chunking strategy.
The CPR model offers two chunking strategies to choose from:
|
|
Note
CPR models created after the release of structure-aware chunking (October 2025) use the structure-aware chunking strategy by default. CPR models created before October 2025 use the fixed-size chunking strategy by default. To view a CPR model's active chunking strategy, on the Models (platform-ca | platform-eu | platform-au) page, click the CPR model, and then click View JSON in the Action bar.
The chunking strategy appears in the |
|
|
Structure-aware chunking is specifically optimized for large language models (LLMs) and RAG systems, and is the recommended chunking strategy. You should use structure-aware chunking unless you have a specific use case that requires the use of fixed-size chunking. |
|
|
Note
You can configure each CPR model to use a different chunking strategy depending on your specific needs. |
To set the model chunking strategy
|
|
Modifying the chunking strategy initiates an automatic model rebuild. |
|
|
Note
Review the main considerations when choosing between chunking strategies. |
-
Access the Machine Learning section of the Swagger UI that’s associated with your Coveo organization region (US | CA | EU | AU).
-
Click Authorize and authenticate using your Coveo organization account credentials.
-
In the Swagger UI, expand the Machine Learning Models section.
-
Use the List all models
GETrequest to access your model’s JSON code: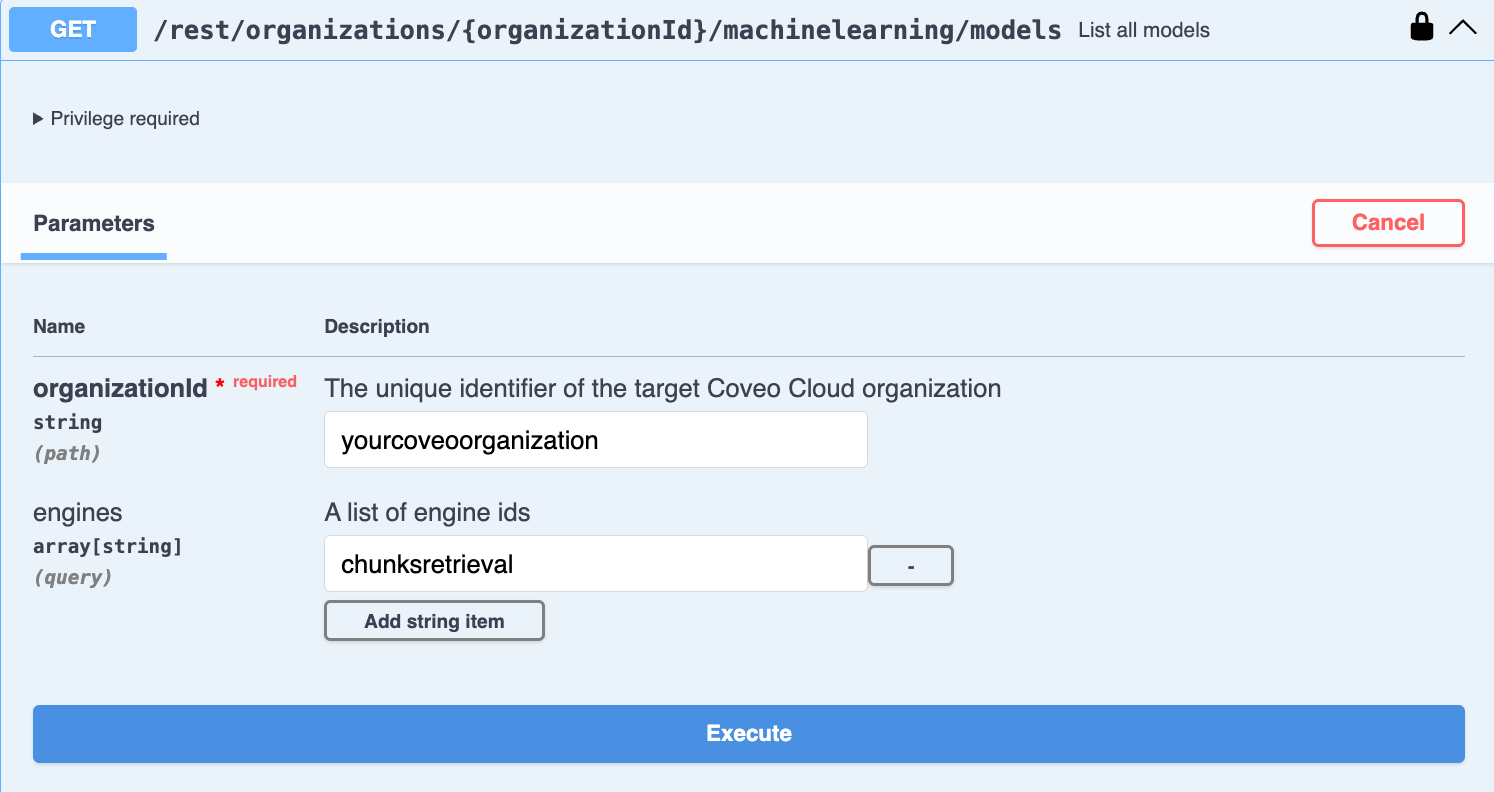
-
Enter your Coveo organization ID.
-
Enter the
chunksretrievalengine ID to filter the list to show only CPR models. -
Click Execute. The JSON code for all CPR models in your organization appears in the Response body.
-
In the Response body, copy the JSON code of the model that you want to configure. You’ll need it in the next step.
-
-
Use the Update the configuration of a model
PUTrequest to modify the model's JSON code: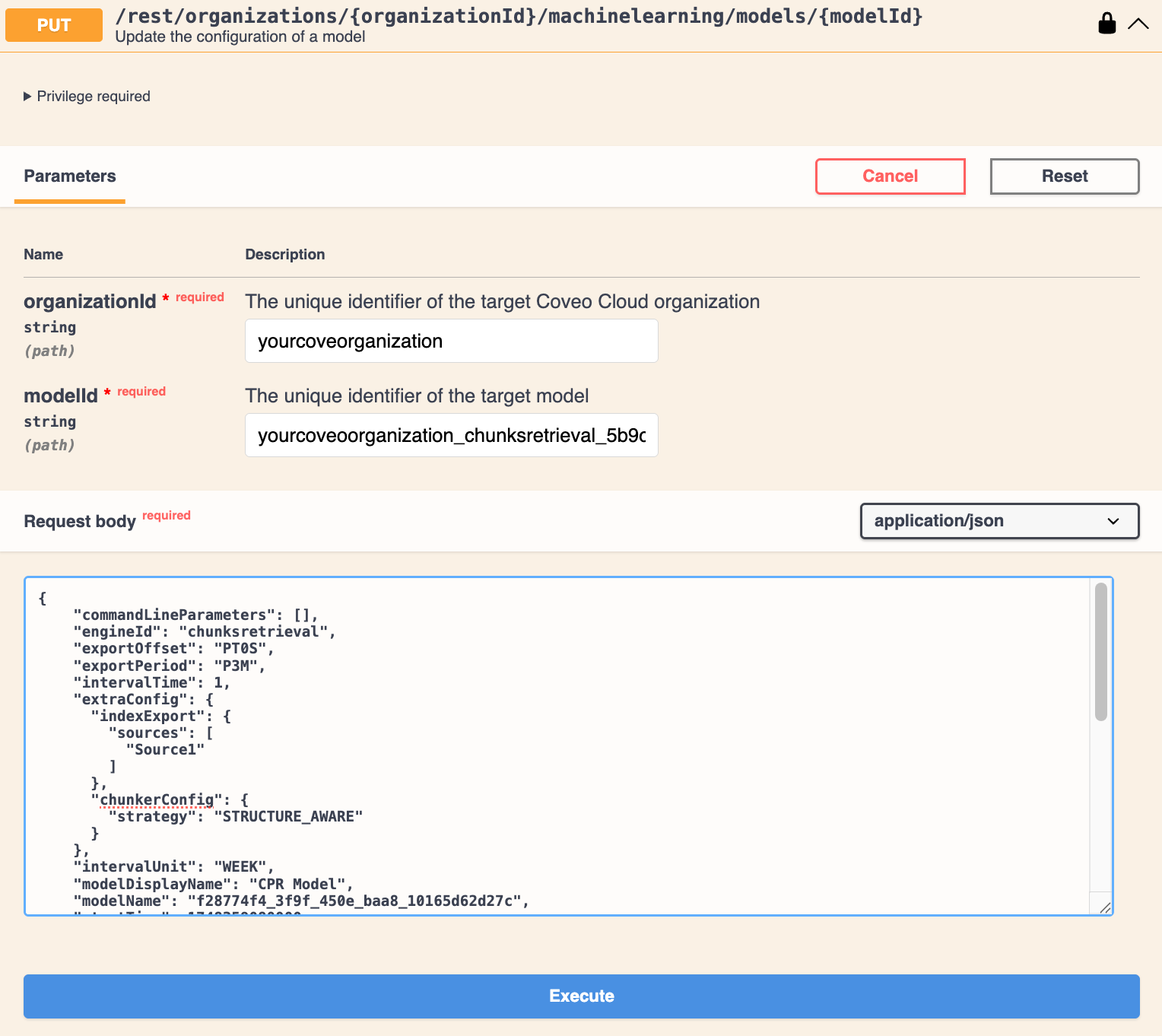
-
Paste the copied JSON code in the Request body.
-
Enter your Coveo organization ID.
-
Enter the ID of the model you want to modify.
If you don’t know the model ID, it appears in the model's JSON code in the
idfield. -
In the
extraConfigelement, add thechunkerConfigobject, and then add thestrategyparameter, and set it to eitherFIXED_SIZEorSTRUCTURE_AWARE.ExampleTo set the structure-aware chunking strategy, the JSON is as follows:
{ ... "extraConfig": { "chunkerConfig": { "strategy": "STRUCTURE_AWARE" }, } ... }
-
-
In the Swagger UI, click Execute to apply the changes to the model.
Edit a CPR model
-
On the Models (platform-ca | platform-eu | platform-au) page, click the model you want to edit, and then click Edit in the Action bar.
-
On the subpage that opens, select the Configuration tab.
-
Under Name, edit the model’s display name.
-
(Optional) Use the Project selector to associate your model with one or more projects.
-
In the Learn from section, select the content that the model will use. You can select the sources and apply additional filters using the Standard configuration or use Advanced mode to define a custom filter expression.
You’ll lose the current mode settings when you switch between Standard and Advanced mode.
NoteA Passage Retrieval (CPR) implementation must include both a CPR model and a Semantic Encoder (SE) model. The same SE model can be used with multiple CPR models. Both the CPR and SE models must be configured to use the same content.
See CPR overview for information on how CPR and SE work together in the context of a user query to retrieve passages.
The Data volume preview section shows the impact of your settings on the data that’s available to the model.
-
In the Standard tab:
-
In the Sources dropdown menu, select the sources that contain the items from which you want the model to learn.
NoteIf your Coveo organization includes multiple indexes, the model can learn only from sources that are linked to the default index.
-
(Optional) In the Apply filters on dataset section, you can specify a condition to segment the content on which the model should base its training:
ExampleYou want the model to base its training only on items for which the collection field have the
FAQvalue.Therefore, you add a
collection is equal to FAQcondition.-
Click Add filter(s).
-
In the Field name input, enter the name of the field that you want to use to segment the dataset.
-
In the Select an operator dropdown menu, select the desired operator.
-
In the Value input, enter the value of the field on which you want to segment the dataset.
-
Click Apply.
-
-
-
In the Advanced tab:
-
Enter a custom filter expression using Coveo query syntax.
-
Click Apply.
-
-
-
Click Save.
Delete a CPR model
|
|
Note
Models are automatically dissociated from all their associated query pipelines once they’re deleted. |
-
On the Models (platform-ca | platform-eu | platform-au) page, click the ML model that you want to delete, and then click More > Delete in the Action bar.
-
In the panel that appears, click Delete.
Review active model information
On the Models (platform-ca | platform-eu | platform-au) page, click the desired model (must be Active), and then click Open in the Action bar (see Reviewing model information).
Reference
Model embedding limits
The CPR model converts your content’s body text into numerical representations (vectors) in a process called embedding. It does this by breaking the text up into smaller segments called chunks, and each chunk is mapped as a distinct vector. For more information, see Embeddings.
Due to the amount of processing required for embeddings, the model is subject to the following embedding limits,depending on the chunking strategy.
|
|
Note
For a given model, the same chunking strategy is used for all sources and item types. |
| Limit | Structure-aware chunking | Fixed-size chunking | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
Chunk size |
Average of 300 tokens per chunk |
250 whitespace-delimited words per chunk |
||
Maximum number of items or chunks |
Up to 15 million items or 50 million chunks
|
|||
Maximum number of chunks per item |
1000
|
|||
"Status" column
On the Models (platform-ca | platform-eu | platform-au) page of the Administration Console, the Status column indicates the current state of your Coveo ML models.
The following table lists the possible model statuses and their definitions:
| Status | Definition | Status icon |
|---|---|---|
Active |
The model is active and available. |
|
Build in progress |
The model is currently building. |
|
Inactive |
The model isn’t ready to be queried, such as when a model was recently created or the organization is offline. |
|
Limited |
Build issues exist that may affect model performance. |
|
Soon to be archived |
The model will soon be archived because it hasn’t been queried for an extended period of time. |
|
Error |
An error prevented the model from being built successfully. |
|
Archived |
The model was archived because it hasn’t been queried for an extended period of time. |
|
Required privileges
By default, members with the required privileges can view and edit elements of the Models (platform-ca | platform-eu | platform-au) page.
The following table indicates the privileges required for members to manage Coveo Generic models (see Manage privileges and Privilege reference).
| Action | Service - Domain | Required access level |
|---|---|---|
View models |
Machine Learning - Models |
View |
Manage models |
Organization - Organization |
View |
Machine Learning - Models |
Edit |
|
Machine Learning - Allow content preview |
Enable |
|
Content - Sources |
View All |
|
Content - Fields |
View |