Multilingual content retrieval and answer generation
Multilingual content retrieval and answer generation
A Coveo Machine Learning (Coveo ML) model that uses a text encoder to process language can be configured to support multiple languages. Currently, this applies to the following Coveo Machine Learning (Coveo ML) models:
By default, these models use an English-only text encoder, and therefore support processing and retrieving only English content. However, Coveo offers beta support for all the other index-supported languages.
|
|
Coveo offers beta support for languages other than English. This means that languages other than English aren’t fully tested or supported by Coveo and performance may vary. |
This article describes how to configure these models to process and retrieve content, and generate content in the case of RGA, in any of the index-supported languages.
Multilingual configuration overview
If you have content in any of the index-supported languages, multilingual configuration allows the Passage Retrieval (CPR), Relevance Generative Answering (RGA), Semantic Encoder (SE), and Smart Snippet models to create the embeddings that the model then uses to retrieve content based on semantic similarity.
For the RGA model, the configuration also includes setting the language for the generated answers. Typically, you would set it to match the language of the content that the RGA model retrieves, but you can set it to a different language using the generative LLM’s translation capabilities.
Specifically, multilingual configuration allows each of the models to do the following in the chosen language:
-
CPR: Retrieve the most relevant passages.
-
RGA: Generate answers.
-
SE: Retrieve the most relevant content for CPR and RGA during first-stage content retrieval.
NoteWhen using CPR or RGA, you must also configure the SE model to support multilingual content.
-
Smart Snippets: Retrieve the most relevant item and display a snippet of that item in the search results.
To configure multilingual support
-
For CPR, SE, and Smart Snippets, configure the model to use a multilingual text encoder for content retrieval.
-
For RGA, configure the model to use a multilingual text encoder for content retrieval, and set the language that you want for the generated answers.
NoteTo generate answers in a language other than English, you must use a custom search interface that was created using the Coveo Atomic library, Coveo Headless library, or Coveo Quantic library.
Generating answers in a language other than English isn’t supported if you created your RGA-enabled search interface using one of the Coveo hosted search interface builders (Hosted search page builder, Hosted Insight Panel builder, or In-Product Experience builder).
Configure multilingual content retrieval
This configuration applies to CPR, RGA, SE, and Smart Snippets, and consists of setting the model to use a multilingual text encoder, and specifying the dataset and dataset languages.
CPR, RGA, SE, and Smart Snippets use a pre-trained text encoder to create the embeddings that the model then uses to retrieve content based on semantic similarity. By default, these models use an English-only text encoder. Configuring a model to use a multilingual text encoder allows the model to effectively create the embeddings for content in different languages, and then retrieve content in the desired language based on those embeddings.
|
|
Associate your model with a search interface and query pipeline that are configured to handle multiple languages. If the associated query pipeline doesn’t filter content based on the desired language, the model’s multilingual encoder retrieves content from all available items in its training set based on semantic similarity, regardless of language. |
To configure multilingual content retrieval
-
If you haven’t yet created the model, create the model using the Administration Console.
-
Access the Machine Learning section of the Swagger UI that’s associated with your Coveo organization region (US | CA | EU | AU).
-
Click Authorize and authenticate using your Coveo organization account credentials.
-
In the Swagger UI, expand the Machine Learning Models section.
-
Use the List all models
GETrequest to access your model’s JSON code: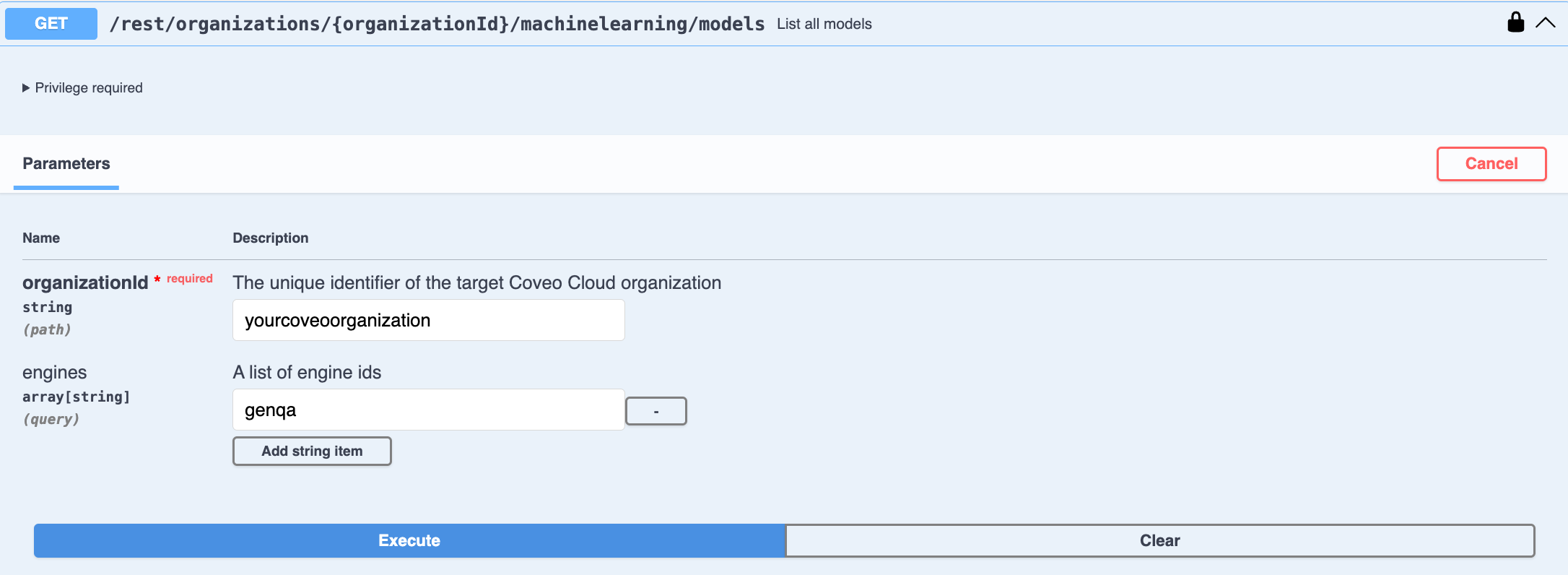
-
Enter your Coveo organization ID.
-
Filter the list by entering the engine ID of the model type you want to configure. Use
chunksretrievalfor CPR,genqafor RGA,embeddingsfor SE, andmlquestionansweringfor Smart Snippets. -
Click Execute. The JSON code for all the models of the chosen type in your organization appears in the Response body.
-
In the Response body, copy the JSON code of the model that you want to configure. You’ll need it in the next step.
-
-
Use the Update the configuration of a model
PUTrequest to modify the model's JSON code: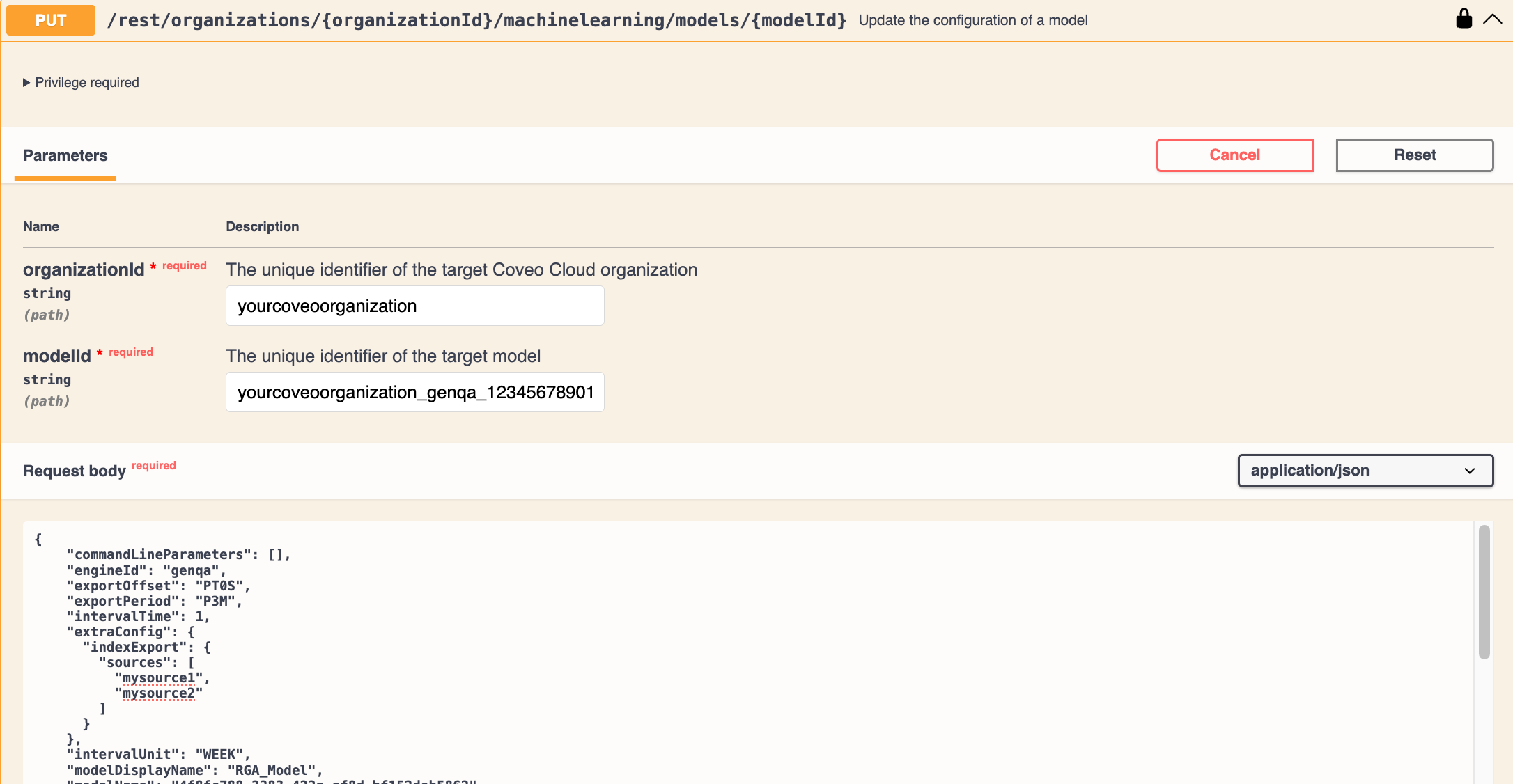
-
Paste the copied JSON code in the Request body.
-
Enter your Coveo organization ID.
-
Enter the ID of the model you want to modify.
If you don’t know the model ID, it appears in the model's JSON code in the
idfield. -
Modify the JSON code to set the model to use a multilingual text encoder, and specify the dataset and dataset languages:
-
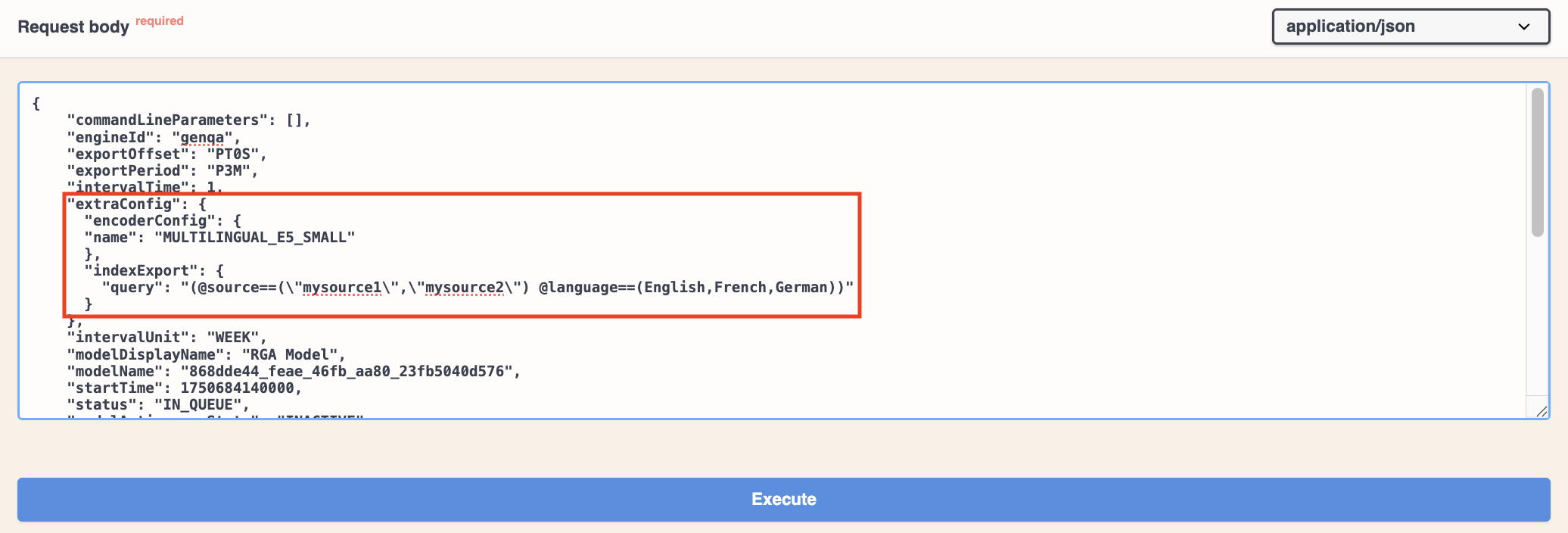
In the
extraConfigelement of the JSON, add theencoderConfigparameter to set the multilingual text encoder toMULTILINGUAL_E5_SMALL.{ ... "extraConfig": { "encoderConfig": { "name": "MULTILINGUAL_E5_SMALL" }, } ... } -
In the
indexExportelement of the JSON, use thequeryparameter to specify the sources that contain the datasets that you want the model to use, as well as the content languages.You can set a model to use dataset content in different languages, and then configure the query pipeline to filter the content the model retrieves based on the required language.
ExampleYou want your RGA model to use the datasets from two sources:
mysource1andmysource2. The two sources contain content in English, French, and German, and the languages are specified using thelanguagefield in the source items.The
queryparameter would be:{ ... "extraConfig": { "indexExport": { "query": "(@source==(\"mysource1\",\"mysource2\") @language==(English,French,German))" }, } ... }If you remove
Germanfrom the list of languages, the RGA model will use only the English and French content from those sources. The German content won’t be embedded, retrieved, or used for answer generation. -
In the
indexExportelement, delete thesourcesparameter from the JSON, if it exists. The sources are now specified in thequeryparameter, so thesourcesparameter is no longer needed.
-
-
-
In the Swagger UI, click Execute to apply the changes to the model. You can review the model information in the Administration Console to see if your changes were applied successfully.
Set the language for generated answers
This configuration applies only for RGA. If you’ve configured your RGA model to retrieve content in multiple languages, you can apply additional configuration to set the language of the generated answers. Typically, you would set it to match the language of the content that the RGA model retrieves, but you can set it to a different language. If set to a different language than the content, the generative LLM translates the generated answer.
To determine the language of the generated answer, the RGA model relies on a locale setting that specifies the language and region.
For example, en-US is the locale for English in the United States, and fr-FR is the locale for French in France.
Depending on how you choose to configure your RGA implementation, the locale that’s used for the generated answer can come from the search interface, the query pipeline, or the RGA model configuration itself. Once a locale is established, the RGA model includes that locale in the prompt that’s sent to the LLM for answer generation. The generative LLM then generates the answer in that language.
No matter how you configure your RGA implementation, RGA ultimately relies on two parameters to establish the locale: targetLocaleFromRequest and targetLocale.
These parameters are typically set in the RGA model configuration, but they can also be set in the RGA model association in the query pipeline.
How and where you set these parameters is based on your chosen strategy for setting the locale.
To set the language used by RGA for generated answers
-
Configure multilingual content retrieval for the RGA model.
NoteBecause the SE model is used by RGA to retrieve relevant content, the SE model must also be configured to retrieve multilingual content.
-
Determine your locale strategy to know where and how to set the locale that’s used for generated answers. This is based on your implementation needs and RGA’s locale workflow, and may require you to do one or both of the following:
-
Set the locale in the search interface to send the locale along with the query request.
-
Create query parameter rules in the query pipeline to set the locale value.
-
-
Set the RGA locale parameters (
targetLocaleFromRequestandtargetLocale) that RGA will use to determine the language for generated answers.
Determine your locale strategy
Before we get into specifics on how to configure the locale for your RGA implementation, let’s first look at where the locale can be set in the RGA workflow. For maximum flexibility, the locale that’s used for generated answers can come from the search interface, the query pipeline that’s used by the RGA model, or from the RGA model configuration itself.
The following diagram illustrates the path a locale setting takes in an RGA workflow, beginning with the recommended locale setting in the search interface. This isn’t to say that the locale setting must absolutely be set in the search interface. It can be set at any of the indicated points along the path, with each subsequent step having the potential to override the locale set in a previous step. You can use this diagram to help you determine the optimal implementation method for your specific needs.
|
|
Associate your model with a search interface and query pipeline that are configured to handle multiple languages. If the associated query pipeline doesn’t filter content based on the desired language, the model’s multilingual encoder retrieves content from all available items in its training set based on semantic similarity, regardless of language. |
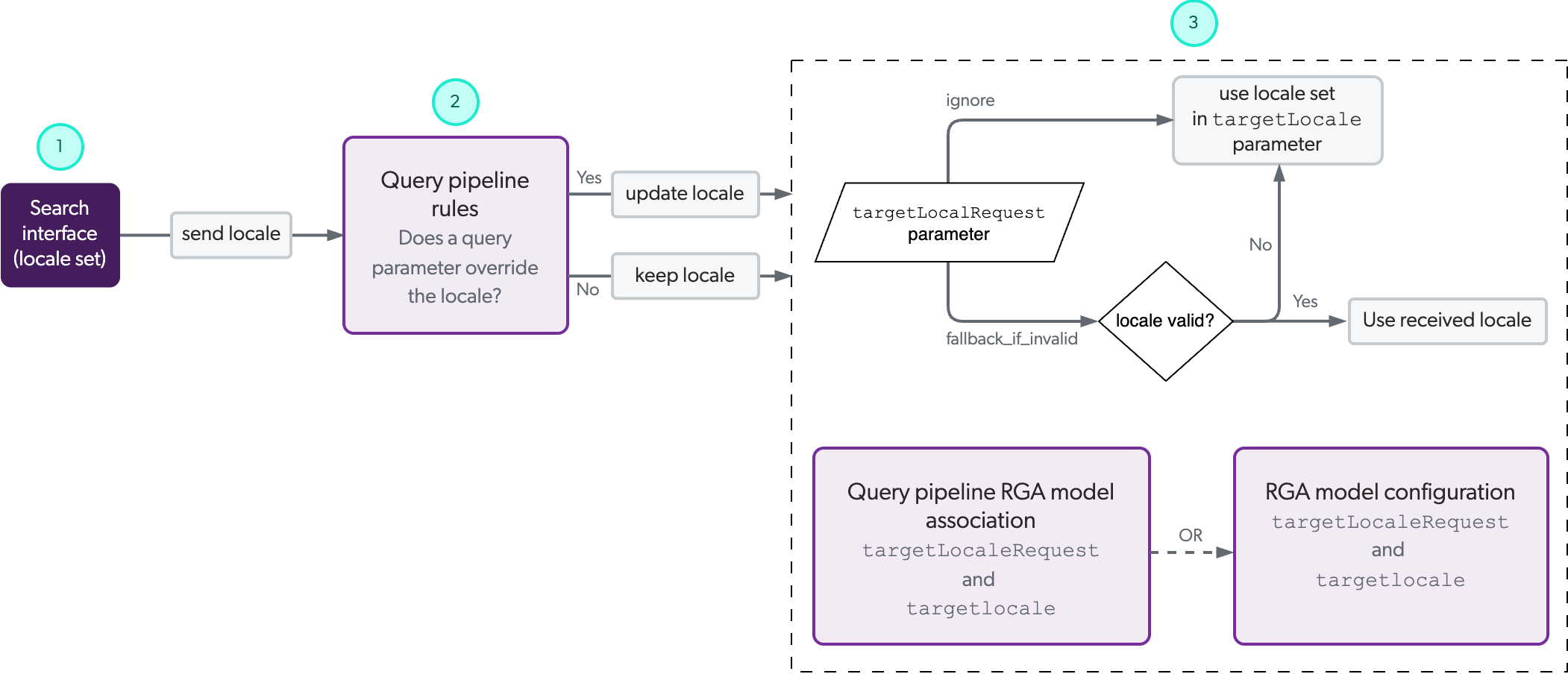
1 |
(Optional) If the locale is set in your RGA-enabled search interface, the locale value is sent as part of the query request to the query pipeline that’s used by the RGA model.
|
||
2 |
(Optional) You can create a query parameter rule in the query pipeline to override the locale value from the search interface, or to set the locale value. If you don’t set a query parameter rule for the locale, the locale that’s received from the search interface is kept. |
||
3 |
(Required) The
|
|
|
See example configurations of how to configure your locale settings based on different scenarios. |
Set the locale in the search interface
While setting the locale in your RGA-enabled search interface is optional, it’s the recommended way to set the locale for generated answers.
|
|
Note
Even if you set the locale in the search interface, you must still set the RGA locale parameters. |
Enterprises typically build their websites and search interfaces to serve specific business logic and audiences. It’s for this reason that Coveo recommends that you set the locale in the search interface to take advantage of the same business logic when it comes to the language of generated answers. Allowing the search interface to dictate the language for generated answers is the most reliable way to provide a consistent customer experience without introducing unnecessary complexity in your RGA implementation.
|
|
Even if you configure a locale for all your search interfaces, you can still override the locale later in the RGA workflow to accommodate for specific use cases and flows. In other words, you could use the search interface locale for the majority of use cases, but override it when needed. |
Set the locale for your RGA-enabled search interface based on the library or framework that you used to build your search interface:
|
|
The locale used for RGA must be a valid tag that includes a language code, or language and region codes, according to the IETF BCP 47 standard.
For example, use |
Set the locale using a query parameter rule
There may be instances where you want to use a query parameter rule in the query pipeline to set or override the locale value that the RGA model receives. This is especially useful if you’re using the same query pipeline for multiple search interfaces, or setting the locale based on a specific condition.
|
|
Note
Even if you set the locale using a query parameter rule, you must still set the RGA locale parameters. |
To create a query parameter rule for the locale
Add a query parameter rule using the Locale parameter in the query pipeline that’s used by your RGA-enabled search interface.
|
|
The locale used for RGA must be a valid tag that includes a language code, or language and region codes, according to the IETF BCP 47 standard.
For example, use |
Set the RGA locale parameters
The RGA model references the targetLocaleFromRequest and targetLocale parameter settings to determine what locale to use for the generated answer.
|
|
These parameters are required to generate answers in a language other than English. If the parameters aren’t set, the generated answers will always default to English. |
-
targetLocaleFromRequest: Sets whether to ignore or use the locale that the RGA model receives with the query request. It can be set to one of the following values:-
ignore: Instructs the RGA model to ignore any locale that it receives, and instead use the locale that’s specified in thetargetLocaleparameter. -
fallback_if_invalid: Instructs the RGA model to use the locale that it receives. In the case of an invalid locale, the RGA model will use the locale that’s specified in thetargetLocaleparameter.
-
-
targetLocale: Sets the locale to use iftargetLocaleFromRequestis set toignore, or if it’s set tofallback_if_invalidand the locale is invalid.The locale used for RGA must be a valid tag that includes a language code, or language and region codes, according to the IETF BCP 47 standard. For example, use
fr-FRfor French in France ordefor international German. See Supported locale tags for details.
|
|
See example configurations of how to configure your locale settings based on different scenarios. |
To set the RGA locale parameters
You can set the targetLocaleFromRequest and targetLocale parameters in the RGA model association in the query pipeline, or in the RGA model configuration.
For more information, see Model association versus model configuration.
Set the RGA locale parameters in the model configuration
Set the RGA locale parameters in the model configuration
-
Access the Machine Learning section of the Swagger UI that’s associated with your Coveo organization region (US | CA | EU | AU).
-
Click Authorize and authenticate using your Coveo organization account credentials.
-
In the Swagger UI, expand the Machine Learning Models section.
-
Use the List all models
GETrequest to access your model’s JSON code:-
Enter the organizationId of your Coveo organization.
-
Filter the list to show only RGA models by entering
genqafor the engine Id. -
Click Execute. The JSON code for all your RGA models appears in the Response body.
-
In the Response body, copy the JSON code of the model that you want to configure. You’ll need it in the next step.
-
-
Use the Update the configuration of a model
PUTrequest to modify the model’s JSON code:-
Paste the copied JSON code in the Request body.
-
Enter the organizationId of your Coveo organization.
-
Enter the modelId of the model you want to modify.
If you don’t know the model ID, it appears in the model’s JSON code in the
idfield. -
In the
extraConfigelement of the JSON, add thetargetLocaleFromRequestandtargetLocalelocale parameters with your chosen settings.The locale used for RGA must be a valid tag that includes a language code, or language and region codes, according to the IETF BCP 47 standard. For example, use
fr-FRfor French in France ordefor international German. See Supported locale tags for details.ExampleYou want your RGA model to use the locale that it receives from the search interface, and use English as the fallback language if the locale is invalid.
The
targetLocaleFromRequestandtargetLocaleparameter settings would be:{ ... "extraConfig": { "encoderConfig": { "name": "MULTILINGUAL_E5_SMALL" }, "indexExport": { "query": "(@source==(\"mysource1\",\"mysource2\") @language==(EN,FR,DE))" }, "targetLocaleFromRequest": "fallback_if_invalid", "targetLocale": "en-US" }, ... }
-
-
In the Swagger UI, click Execute to apply the changes to the model. You can review the model information in the Administration Console to see if your changes were applied successfully.
Set the RGA locale parameters in the model association in the query pipeline
Set the RGA locale parameters in the model association
-
On the Query Pipelines (platform-ca | platform-eu | platform-au) page, click the query pipeline that’s used by your RGA-enabled search interface, and then click Edit components in the Action bar.
-
Select the Machine Learning tab.
-
Double-click the RGA model association that you want to edit.
-
If the Edit a Model Association subpage opens in JSON view, proceed to the next step. Otherwise, in the upper-right corner, click
, click Switch to JSON view.
-
In the
customQueryParameterselement of the JSON, add thetargetLocaleFromRequestandtargetLocalelocale parameters with your chosen settings.The locale used for RGA must be a valid tag that includes a language code, or language and region codes, according to the IETF BCP 47 standard. For example, use
fr-FRfor French in France ordefor international German. See Supported locale tags for details.ExampleYou want your RGA model to ignore the locale that it receives, and use French for generated answers.
The
targetLocaleFromRequestandtargetLocaleparameter settings would be:{ ... "customQueryParameter": { ... "targetLocaleFromRequest": "ignore", "targetLocale": "fr-FR" }, ... }
Model association versus model configuration
You can set the targetLocaleFromRequest and targetLocale parameters in the RGA model association in the query pipeline, or in the RGA model configuration itself.
|
|
Note
Depending on your implementation needs, you can also set the parameters in both the RGA model association and RGA model configuration. If the parameters are set in both, the settings in the model association take precedence and the ones in the model configuration are ignored. |
Depending on your implementation needs, you can set the parameters as follows:
-
Both parameters set in the model association only.
-
Both parameters set in the RGA model configuration only.
-
One parameter setting in the model association and another in the model configuration. This is an advanced configuration, but it’s useful in situations where you use the same RGA model across multiple query pipelines, or if you use the same RGA model more than once in the same query pipeline. In this case, a parameter setting in the model association takes precedence over the setting in the model configuration. If a parameter is set in the model association, the corresponding setting in the model configuration is ignored.
ExampleYou want to use the same RGA model in three different query pipelines. One query pipeline is used for English content, and the other two are used for French and German content respectively. In each case, you want the RGA model to ignore the locale it receives, and use a different locale for each query pipeline.
You can set the parameters as follows:
-
In the RGA model configuration, set the
targetLocaleFromRequestparameter toignore. -
In the RGA model association in the query pipeline, set the
targetLocaleparameter toen-US,fr-FR, orde-DEdepending on the query pipeline.
Given this configuration, since the
targetLocaleFromRequestparameter is not set in the model association, it uses the setting in the RGA model configuration, and thetargetLocalesetting in each of the model associations is used. If the model configuration had atargetLocalesetting, it would be ignored in favor of the setting in the model association since that setting takes precedence. -
Leverage the LLM translation capabilities
It’s possible to generate answers in a language that’s different from the language of the content that the RGA model retrieves.
RGA leverages GPT’s linguistic capabilities to generate the answer. This includes the LLM’s ability to translate text.
During answer generation, the RGA model sends a prompt that includes the retrieved chunks and the desired locale to the GPT LLM that’s used to generate the answer. If the language of the chunks is different from the requested locale language, the GPT LLM generates the answer using the original content and then translates the answer before streaming it back to the search interface.
When the generated answer is in a different language than the content that was used to generate it, the citations for the generated answer appear in the original language.
If the RGA model retrieves content in English and the locale for answer generation is set to Japanese (ja-JP), the answer appears in Japanese, but the citations are for the English content.
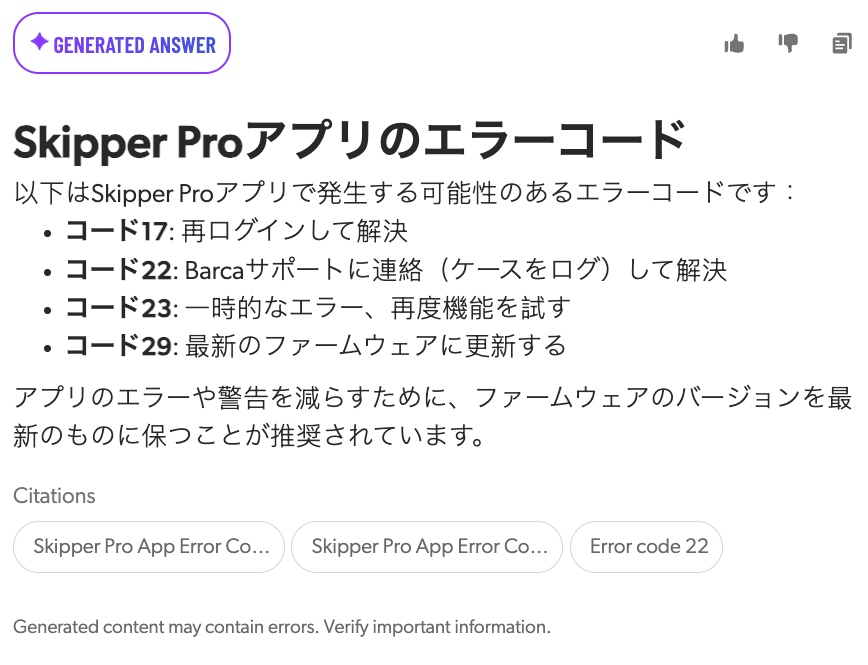
|
|
RGA doesn’t control the quality of the translation. The GPT LLM translates the answer on-the-fly, and the translated chunks are not stored in the Coveo index. While the GPT LLM’s translation capabilities may be useful to bridge content gaps in certain languages, you should use caution for content that requires high-quality translations, such as legal or technical documents. |
Example configurations
The following examples show how to configure the locale for generated answers in different scenarios.
Generate answers in a single language that is not English
| Unilingual workflow - Locale set in the RGA model configuration |
|---|
Scenario:
Configuration:
Result: This sets the RGA model to ignore any locale it receives and always use |
Generate answers using the language of my search interface
| Multilingual workflow with separate query pipelines - Locale set in the RGA model configuration |
|---|
Scenario:
Configuration
Result:
|
| Multilingual workflow with one query pipeline - Locale set in the RGA model associations | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
Scenario:
Configuration:
Result:
|
Generate answers in the language of my search interface with content that might be in a different language
| Multilingual workflow using generative LLM translation capabilities | ||
|---|---|---|
Scenario:
Configuration:
Result:
|
Supported locale tags
The locale that’s used by RGA for answer generation must be a valid tag that includes the language, or language and region, as per the IETF BCP 47 standard (language code or language code-region code).
The language code must follow the ISO 639-1 standard, which provides two-letter codes for languages, such as en for English and fr for French.
The region code must follow the ISO 3166-1 standard, such as FR for France and US for United States.
The following table lists the most common locale tags that you can use for multilingual content retrieval and answer generation:
| Language | Region | Locale |
|---|---|---|
Arabic |
International |
ar |
Algeria |
ar-DZ |
|
Egypt |
ar-EG |
|
Morocco |
ar-MA |
|
Saudi Arabia |
ar-SA |
|
Chinese |
International |
zh |
Mainland China, simplified characters |
zh-CN |
|
Hong Kong, traditional characters |
zh-HK |
|
Singapore |
zh-SG |
|
Taiwan, traditional characters |
zh-TW |
|
Croatian |
International |
hr |
Croatia |
hr-HR |
|
Czech |
International |
cs |
Czechia |
cs-CZ |
|
Danish |
International |
da |
Denmark |
da-DK |
|
Dutch |
International |
nl |
Belgium |
nl-BE |
|
Netherlands |
nl-NL |
|
English |
International |
en |
Australia |
en-AU |
|
Canada |
en-CA |
|
United Kingdom |
en-GB |
|
New Zealand |
en-NZ |
|
United States |
en-US |
|
Estonian |
International |
et |
Estonia |
et-EE |
|
Finnish |
International |
fi |
Finland |
fi-FI |
|
French |
International |
fr |
Belgium |
fr-BE |
|
Canada |
fr-CA |
|
Switzerland |
fr-CH |
|
Algeria |
fr-DZ |
|
France |
fr-FR |
|
German |
International |
de |
Austria |
de-AT |
|
Switzerland |
de-CH |
|
Germany |
de-DE |
|
Luxembourg |
de-LU |
|
Greek |
International |
el |
Cyprus |
el-CY |
|
Greece |
el-GR |
|
Hebrew |
International |
he |
Israel |
he-IL |
|
Hungarian |
International |
hu |
Hungary |
hu-HU |
|
Italian |
International |
it |
Switzerland |
it-CH |
|
Italy |
it-IT |
|
Japanese |
International |
ja |
Japan |
ja-JP |
|
Korean |
International |
ko |
South Korea |
ko-KR |
|
Norwegian |
International |
no |
Norway |
no-NO |
|
Polish |
International |
pl |
Poland |
pl-PL |
|
Portuguese |
International |
pt |
Angola |
pt-AO |
|
Brazil |
pt-BR |
|
Portugal |
pt-PT |
|
Romanian |
International |
ro |
Moldova |
ro-MD |
|
Romania |
ro-RO |
|
Russian |
International |
ru |
Belarus |
ru-BY |
|
Kazakhstan |
ru-KZ |
|
Russia |
ru-RU |
|
Serbian |
International |
sr |
Cyrillic, Serbia |
sr-Cyrl-RS |
|
Slovak |
International |
sk |
Slovakia |
sk-SK |
|
Slovenian |
International |
sl |
Slovenia |
sl-SI |
|
Spanish |
International |
es |
Argentina |
es-AR |
|
Colombia |
es-CO |
|
Spain |
es-ES |
|
Mexico |
es-MX |
|
Peru |
es-PE |
|
Swedish |
International |
sv |
Sweden |
sv-SE |
|
Turkish |
International |
tr |
Cyprus |
tr-CY |
|
Turkey |
tr-TR |
|
Ukrainian |
International |
uk |
Ukraine |
uk-UA |