Relevance Generative Answering (RGA) data security
Relevance Generative Answering (RGA) data security
Data is a valuable asset that drives growth and development in enterprises. Protecting your enterprise data, therefore, has always been of vital importance. Never more so than when dealing with generative AI technology.
A genAI model typically trains on a large corpus of data, and generates content based on that data. Generating new content from existing data is a powerful capability. However, it also raises new concerns about data privacy and security. Concerns such as "What data is the model using to train on, and is it retaining that data?", "Is my data being shared with others?", "What data is the model using to generate the new content?" , and "Will the generated content leak sensitive information to unintended audiences?".
For any enterprise to be able to use genAI technology ethically and safely, these concerns must be addressed. An enterprise must be able to control the content that’s used to train the model. The content that’s generated must be highly relevant but also take system permissions and access rights into account to prevent sensitive information from being leaked.
This article describes how Relevance Generative Answering (RGA) handles your enterprise content safely, and how RGA provides answers that are secure and always based solely on your most relevant and up-to-date content.
RGA data security can be broken down into these main features as shown in the following diagram:
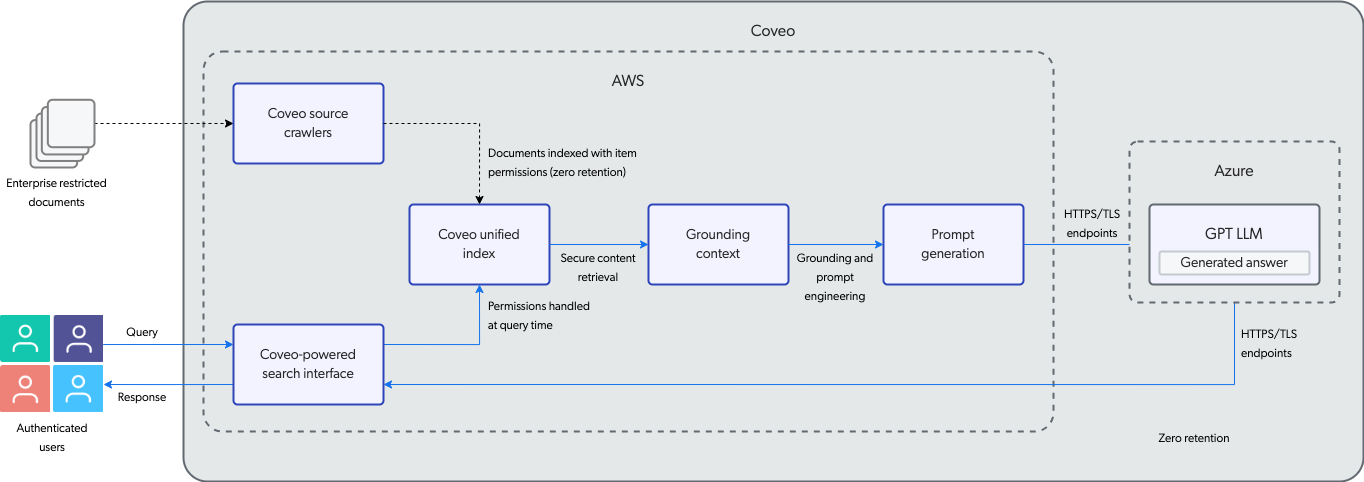
Secure content retrieval
Secure content retrieval is a feature of the Coveo Platform that allows for more efficient and secure searching and generation of enterprise content with Coveo security cache at its core.
|
|
Note
Existing Coveo Security protocols and data protection measures remain applicable throughout the RGA process and ensure that your enterprise documents and usage analytics data remain secure. |
Your enterprise data is stored in a secure Coveo unified index that’s only accessible to you and the people you authorize within your Coveo organization. Secure handling of your enterprise data applies not only at ingestion (crawling time) but also at query time.
-
At ingestion, the Coveo source crawlers retrieve the content from your enterprise data sources. The content is indexed with the item and user permissions from your repository’s permission system.
-
At query time, the Coveo security cache is used to handle the permissions for each authenticated user in your Coveo-powered search interface.
By indexing your enterprise restricted documents with item and user permissions, and then applying those user permissions at query time, Coveo ensures that sensitive information isn’t inadvertently exposed through search results or generated answers. Through a Coveo-powered search interface, authenticated users only see the items that they’re allowed to access within the indexed repository.
Grounding context
In the context of generative AI, grounding refers to the process of providing a generative LLM (GPT LLM) with specific and relevant information that’s not available to the model based on its training.
While generative LLMs come with a vast amount of knowledge, this knowledge is limited as it’s not use-case or industry specific. To obtain a relevant output to a query for your enterprise, we must provide the generative LLM with the necessary information. In other words, we need to "ground" the model in the context of a specific use case. Grounding is an important security feature in generative answering, as it helps to ensure that the generated output isn’t only relevant but secure. Grounding holds the model to factual data and relevant user context when generating an answer.
Coveo’s secure content retrieval makes grounding possible. The Relevance Generative Answering (RGA) model uses content retrieved from your Coveo index to create the grounding context that’s provided to the generative LLM. RGA’s two-stage content retrieval ensures that Coveo controls the data used to generate the text. The RGA model uses grounding and prompt engineering to construct a prompt for the generative LLM that includes a detailed instruction, the query, and the most relevant segments of text from the retrieved content. Confining the generative LLM to just the most relevant text from your secured content ensures that the generated answer is relevant and respects your enterprise content permissions.
By combining secure content retrieval and grounding context, RGA uses retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) to enhance the security, relevance, and reliability of content generated by an LLM.
HTTPS and TLS endpoints
RGA leverages GPT’s linguistic capabilities to generate the answer. The GPT LLM is hosted on Microsoft Azure’s servers. The RGA model sends the prompt to the Microsoft Azure OpenAI server, the GPT LLM generates the answer, and the answer is then sent back to Coveo.
HTTPS endpoints ensure that communication between Coveo and the Microsoft Azure OpenAI server is encrypted and secure. This prevents potential attacks such as eavesdropping, tampering, or data theft.
TLS endpoints use cryptographic protocols to provide authentication, confidentiality, integrity, and non-repudiation services. This allows secure web communication between Coveo and Microsoft Azure’s servers.
Zero retention
To maintain data privacy, enterprises must retain complete ownership of their data. With Coveo and RGA, you remain the sole owner of your data.
-
You control the content that’s indexed from your enterprise. This means that you control what content to index, when to update the content in the index, and how long your data is kept in the Coveo index. The index is only accessible to you and the people you authorize within your Coveo organization. Coveo doesn’t retain any of your enterprise content after it’s indexed.
-
The Coveo Machine Learning (Coveo ML) models, including the RGA and Semantic Encoder (SE) models that are used in the RGA answer-generation flow, are only available within your Coveo organization. The RGA and SE models use only the indexed content that you specify, and Coveo won’t fine-tune any other LLMs or share your data with other clients.
-
Coveo uses a GPT LLM that’s hosted on Microsoft Azure’s servers to generate the answer based on the content that’s controlled and provided by the RGA model (see Grounding context). The Azure OpenAI GPT LLM is a stateless model that’s shared for all Coveo customers. The GPT LLM is used solely for the purpose of generating answers. The model isn’t trained on your enterprise data, and it doesn’t retain any of your data for future learning. Microsoft Azure will process your data, but such data won’t be stored by Microsoft Azure.
Logged analytics data
Coveo logs usage analytics data related to RGA, and retains the data for a period of time as specified in Data retention.
You can create reports on the RGA custom UA events. To access data that’s not available through the RGA UA events, such as the user query and generated answer, contact your Coveo Customer Success Manager (CSM).