Monitor search consumption
Monitor search consumption
Each Coveo customer license agreement defines a set of usage limits and quotas. Administrators and other members with the required privileges can review these limits and their current statuses from the Settings (platform-ca | platform-eu | platform-au) page in the Coveo Administration Console (see Review organization settings and limits).
Search entitlement metrics measure actual search resources consumed by the end users of a solution. As such, those metrics deserve particular attention and can be visualized in their own dedicated consumption dashboard.
This article provides information to help administrators use the consumption dashboard to accurately monitor search entitlement metrics for their Coveo organization.
Introduction to license entitlements
Usage of the Coveo Platform by end users is licensed in two different ways, depending on the type of deployment:
-
Public facing or anonymous search interfaces generally use an entitlement based on query quotas that are reset on the first day of each month.
-
Authenticated search interfaces (private and public facing) can use one of several kinds of per-user entitlements, with no limit on the actual number of queries performed.
Refer to your customer agreement for more details on the entitlements that apply to your contract.
Get started with the consumption dashboard
Access the Consumption (platform-ca | platform-eu | platform-au) dashboard from the Settings page in the Coveo Administration Console, under License > Consumption.
If your license agreement includes search entitlements based on metrics other than queries, select the most appropriate entitlement metric for each search hub. For search hubs that shouldn’t use a per-user entitlement metric, leave the default value Queries.
Once you’re done, the Consumption dashboard header should display accurate totals.
Consumption dashboard particularities
-
The AdminConsole search hub represents the search interfaces in the Coveo Administration Console. Queries originating from this search hub therefore come from the Content Browser (platform-ca | platform-eu | platform-au) page, for example.
-
Queries with Unassigned in the Search Hub column didn’t originate from a specific search hub. These queries were however valid, yielded valid results, and counted against your entitlements. These queries are typically made by developers testing Coveo’s search API without specifying the
searchHubparameter. A couple of them is acceptable. However, if you have a large number of unassigned queries, use your usage analytics reports to understand where they come from. Fix the issue as soon as possible to avoid further impact on machine learning and reporting.
Query types
There are several types of queries other than the normal ones: recommendation and persistent. Each type counts against its monthly quota. For search interfaces where end users aren’t individually identifiable, search entitlements are usually based on query quotas that are reset on the first day of each month.
Queries
Queries refer to the number of times the Coveo Search API was used to retrieve results in search hubs.
Technically speaking, a query is a Coveo Search API request that retrieves query results. Other uses of the Search API such as requesting field-based or Coveo Machine Learning (Coveo ML) query suggestions, generating search tokens, retrieving Quick view data, etc. aren’t counted as queries.
As a rule of thumb, most actions impacting the results or facets being displayed in a search interface count as queries.
The following actions count as queries:
-
Loading a search interface.
-
Switching to a different tab.
-
Submitting a search request from a search box.
-
Selecting a displayed query suggestion.
-
Changing the sort criterion or sort direction of search results.
-
Switching to a different page of search results.
-
Changing the number of results per page.
-
Selecting, deselecting, or excluding a facet value.
-
Changing the sort order or matching mode of a facet.
-
Using the search box at the bottom of a facet.
-
Navigating through search page states using browser history.
-
Expanding the result of a threaded conversation (for example, Chatter).
-
Any custom code that triggers a search request.
The following actions aren’t counted as queries:
-
Retrieving query suggestions while typing keywords in a search box.
-
Opening a Quick view for a search result.
|
|
Note
Customer Queries allocation is based on the information shared by customers, depending on the use case and the customer’s search page’s current traffic. |
Recommendation queries
Recommendation queries originate from search interfaces that leverage the Coveo ML Content Recommendation (CR) and Product Recommendation (PR) features.
Recommendation queries count against the recommendations per month (RPM) quota (that is, they don’t count against the queries quota). The Recommendation queries column appears in the table when at least one search hub received such queries.
-
For more information on Coveo ML CR models, see Deploy Content Recommendations (CR).
-
For more information on Coveo ML PR models, see Leveraging Machine Learning Product Recommendations.
Persistent queries
|
|
Persistent queries are no longer part of product entitlements and have been deprecated. |
Persistent queries are typically used to render relatively static, search-based content in a web page or application (see Render static content using persistent queries).
Persistent queries count against the persistent queries per month quota (that is, they don’t count against the queries quota).
Coveo tracks the number of unique persistent queries executed each month (see Determine persistent query uniqueness). In essence, this means that even if a given unique persistent query is executed a thousand times during a month, it still only counts once against the PQPM quota. The Recommendation queries column appears in the table when at least one search hub received such queries.
Usage analytics search event count discrepancies
Query counts displayed in the Consumption dashboard measure actual search resource usage at the API level. In contrast, the search event count Coveo Analytics metric measures end user behavior (see Search Event Count). An action reported as a single search event in a usage analytics report may therefore in fact have required several queries to be performed. As such, there may be discrepancies between the counts you see in usage analytics reports and those you see in the Consumption dashboard.
|
|
Notes
|
On a community site, a public form allows end users to submit cases to a customer support team.
As the end user is filling the form, contextually relevant query results are automatically displayed as potential solutions to deflect the case. Those results are regularly updated while the end user fills the form. Each update triggers a new query that counts against the query quota, although the entire form-filling user action is pushed as a single search event to Coveo UA.
User entitlement
For search interfaces used by authenticated users, search entitlement is based on the number of users, rather than the number of queries. In the Consumption (platform-ca | platform-eu | platform-au) dashboard, if your license agreement includes user-based search entitlements, you should typically select an entitlement metric for each appropriate search hub.
For search interfaces identified as per-user, Coveo tracks the number of distinct users that performed queries in the past months. The exact number of months depends on the entitlement:
| Entitlement | Period accounted for |
|---|---|
Agent Users |
3 months |
Intranet Users |
12 months |
Platform Intranet Users |
12 months |
Platform Agents |
3 months |
Platform Portal Users |
12 months |
Salesforce Service Cloud Agents |
3 months |
Salesforce Sales Cloud Users |
12 months |
Salesforce Platform Users |
12 months |
Salesforce Community Cloud Users |
12 months |
ServiceNow CSM Agent Users |
3 months |
ServiceNow Fulfillers |
3 months |
ServiceNow ITSM Users |
12 months |
ServiceNow HRSD Users |
12 months |
Dynamics Customer Engagement Users |
3 months |
|
|
Notes
|
At any time, if the total number of users for an entitlement exceeds the maximum value allowed by the license, the license should be revised.
In this context, unless otherwise specified by the license, queries made from per-user search interfaces don’t count against any of the query quotas.
What’s a user?
A user is an identity passed when a query is made in a Coveo-powered search interface (for example, search page, insight panel, etc.).
-
On an authenticated Intranet search page, each employee counts as a distinct user.
-
In the context of Coveo for Salesforce, each authenticated Salesforce user (for example, support agent) using the search interface counts as a distinct user.
|
|
Note
When performing a query using many identities, only the first one counts as a distinct user. For example, if a query is run using the following identities:
In that case, only |
Access a resource consumption graph
You can access a graph to visualize resource consumption evolution for a given search hub over the selected month or the last 12 months. The graph, however, currently accounts for queries only.
In the Consumption (platform-ca | platform-eu | platform-au) dashboard, click a search hub, and then click View Graph in the Action bar.
|
|
Note
The graph displays the daily record of the total number of queries made in the current month. As such, future days reflect the most recent total recorded. 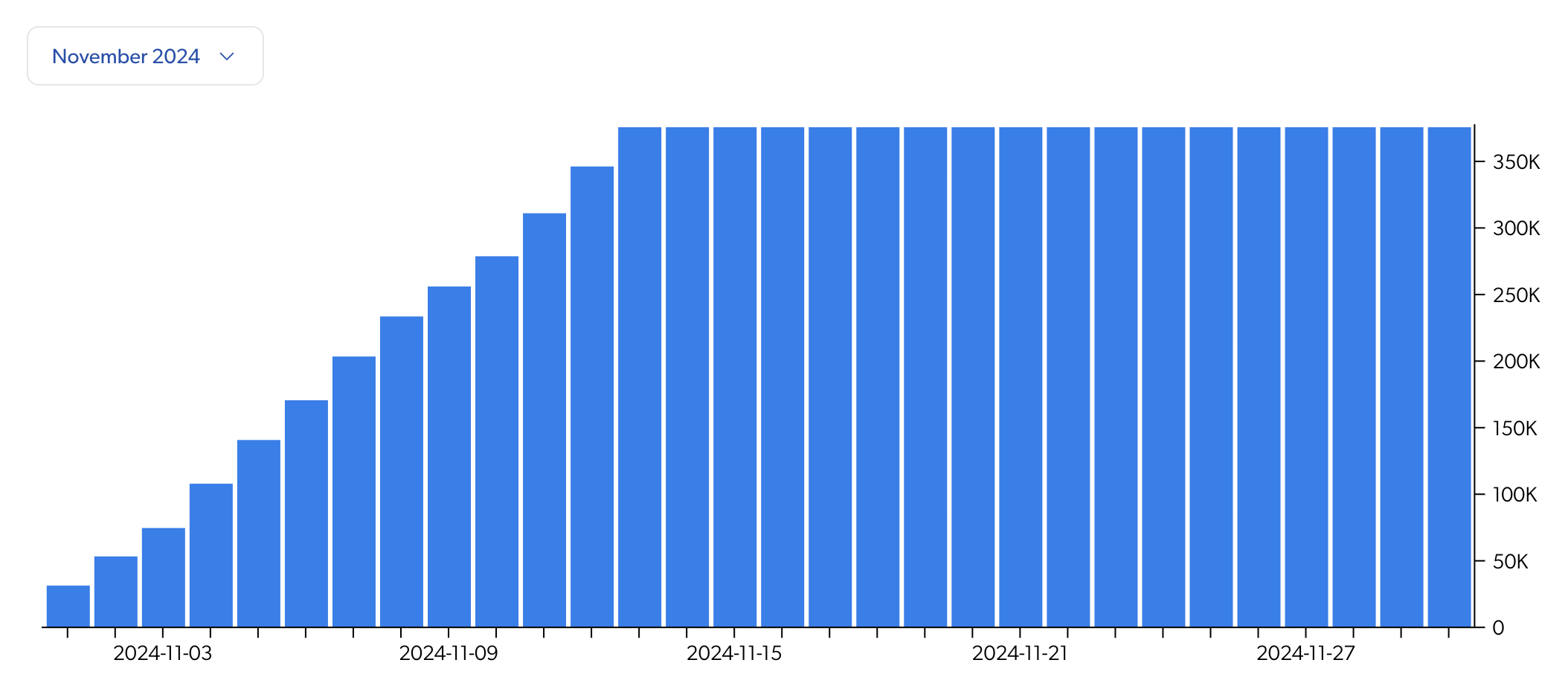
|
Access query logs
You can access an HTML log file listing the queries made in the selected search hub during the selected month, along with their date and time, query expression, etc. The information in this file can be useful when troubleshooting query usage.
In the Consumption (platform-ca | platform-eu | platform-au) dashboard, click a search hub, and then click one of the following in the Action bar:
-
View Query Logs to open the log in a new browser tab.
-
Download Query Logs to download the HTML log file.
Required privileges
The following table indicates the privileges required to view or edit elements of the Consumption (platform-ca | platform-eu | platform-au) dashboard and associated panels (see Manage privileges and Privilege reference).
| Action | Service - Domain | Required access level |
|---|---|---|
| View the Consumption dashboard and related activities |
Organization - Activities Organization - Organization Search - Search Usage Metrics |
View |
| Edit the entitlement metric of a search hub |
Organization - Activities Organization - Organization |
View |
|
Search - Search Usage Metrics |
Edit | |
| View or download a list of the queries performed in a hub during a certain month |
Organization - Activities Organization - Organization Search - Query Logs Search - Search Usage Metrics |
View |