About the query expression
About the query expression
Every time a query is sent to a Coveo organization index, the various parts of the query expression are merged into a single combined query expression which can be read as follows:
((q AND lq AND aq) OR dq) AND cqIn other words, in order for an item to be returned as a query result, that item must satisfy the constant query expression (cq), along with either:
-
The basic (
q) and advanced (aq) query expressions -
The {disjunction-query-expression-dq}
This article explains the typical purpose of each part of the query expression.
Basic query expression (q)
The basic query expression (q) typically comes directly from end-user input, such as when an end user is typing keywords in a search box.
As such, this part of the query expression can be altered by query pipeline Stop words and Thesaurus rules, and also serves as the main input for several index features such as:
-
Partial match (For more information, see Taking advantage of the partial match feature)
-
Did You Mean (For more information, see Query Correction feature)
-
Excerpt generation
-
Keyword highlighting
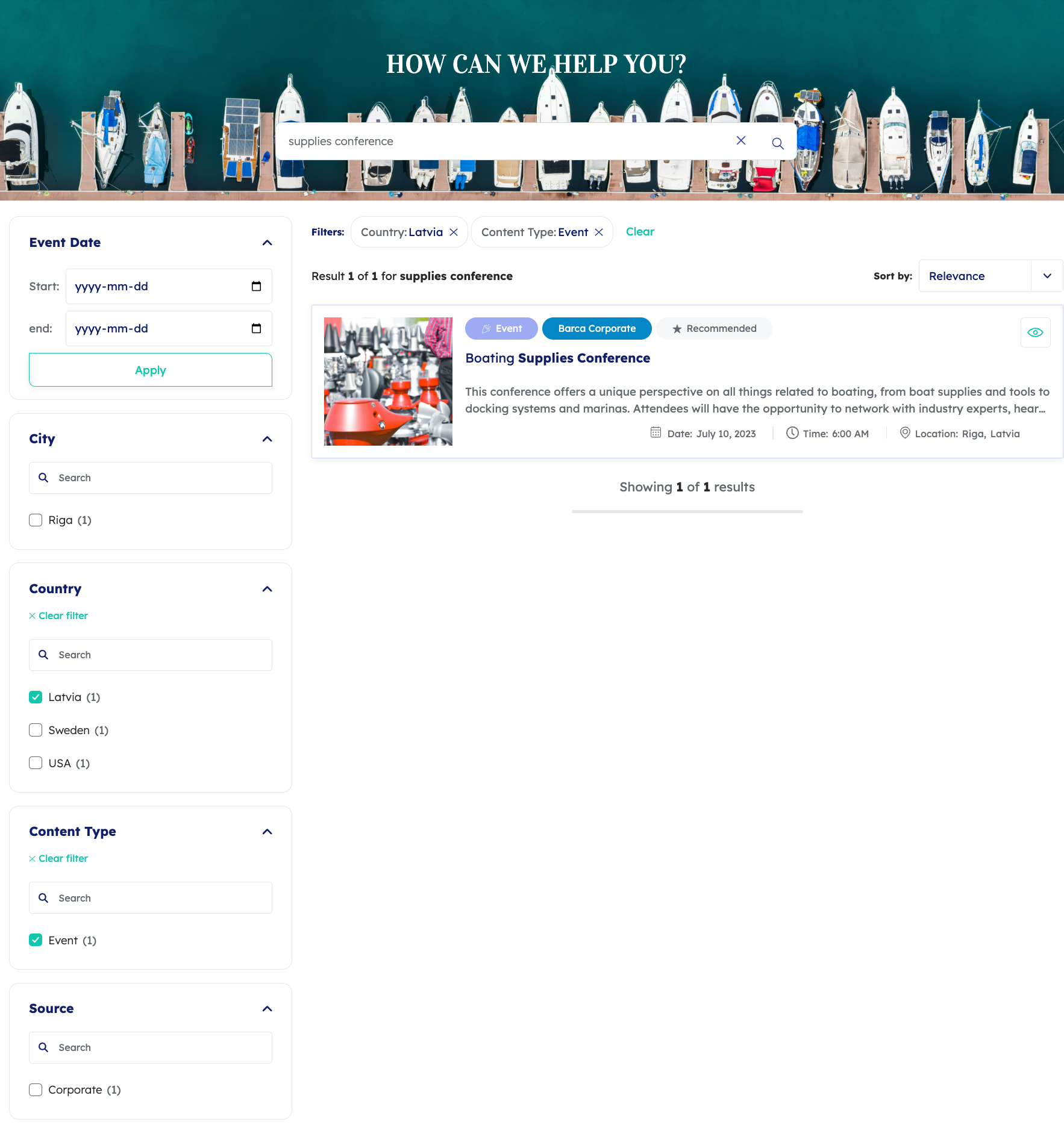
A customer triggers a query from a customer service search interface.
The query consists of the keywords what are barca environment policies.
Therefore, the q part of the combined query expression has the value what are barca environment policies.
This basic query expression returns the following search results:
|
|
Note
In a Coveo JavaScript Search Framework interface, the |
Advanced query expression (aq)
The advanced query expression (aq) is typically created by client-side logic, such as when the end user interacts with facet values or similar search interface elements intended to be used as query result filters.
This part of the query expression is assumed to be code-generated, and can take full advantage of the Coveo query syntax.
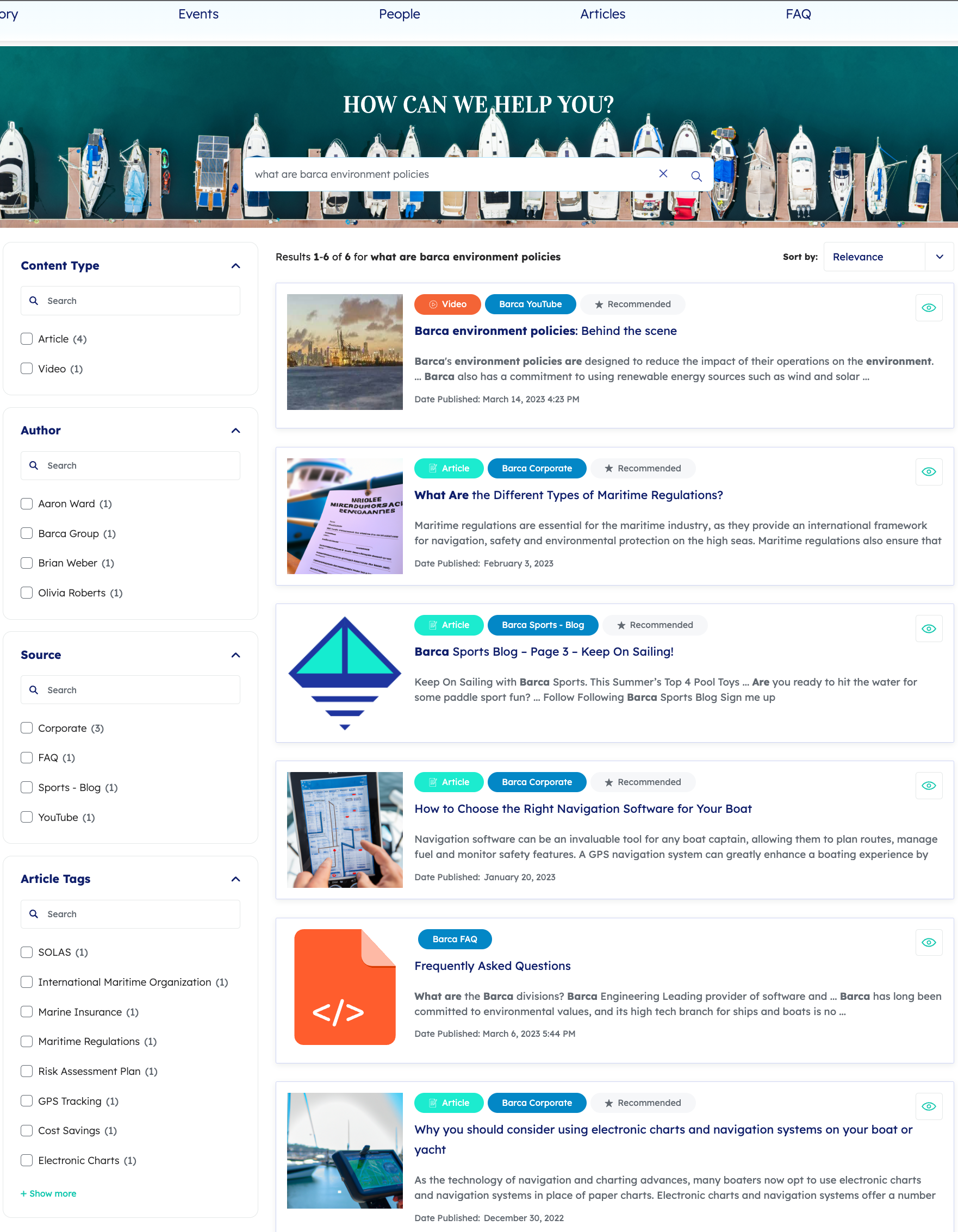
A support agent selects the SOLAS and Marine Insurance value on the Article Tags facet and the Corporate value on the Source facet on a customer service search interface, which triggers a new query.
The aq value changes to @articletags==("Marine Insurance", "SOLAS") and @source== "Corporate".
This advanced query expression returns the following search results:
Disjunction query expression (dq)
The disjunction query expression (dq) is typically generated by an Automatic Relevance Tuning (ART) Coveo Machine Learning (Coveo ML) model to ensure relevant items are included in the query results, regardless of matching keywords.
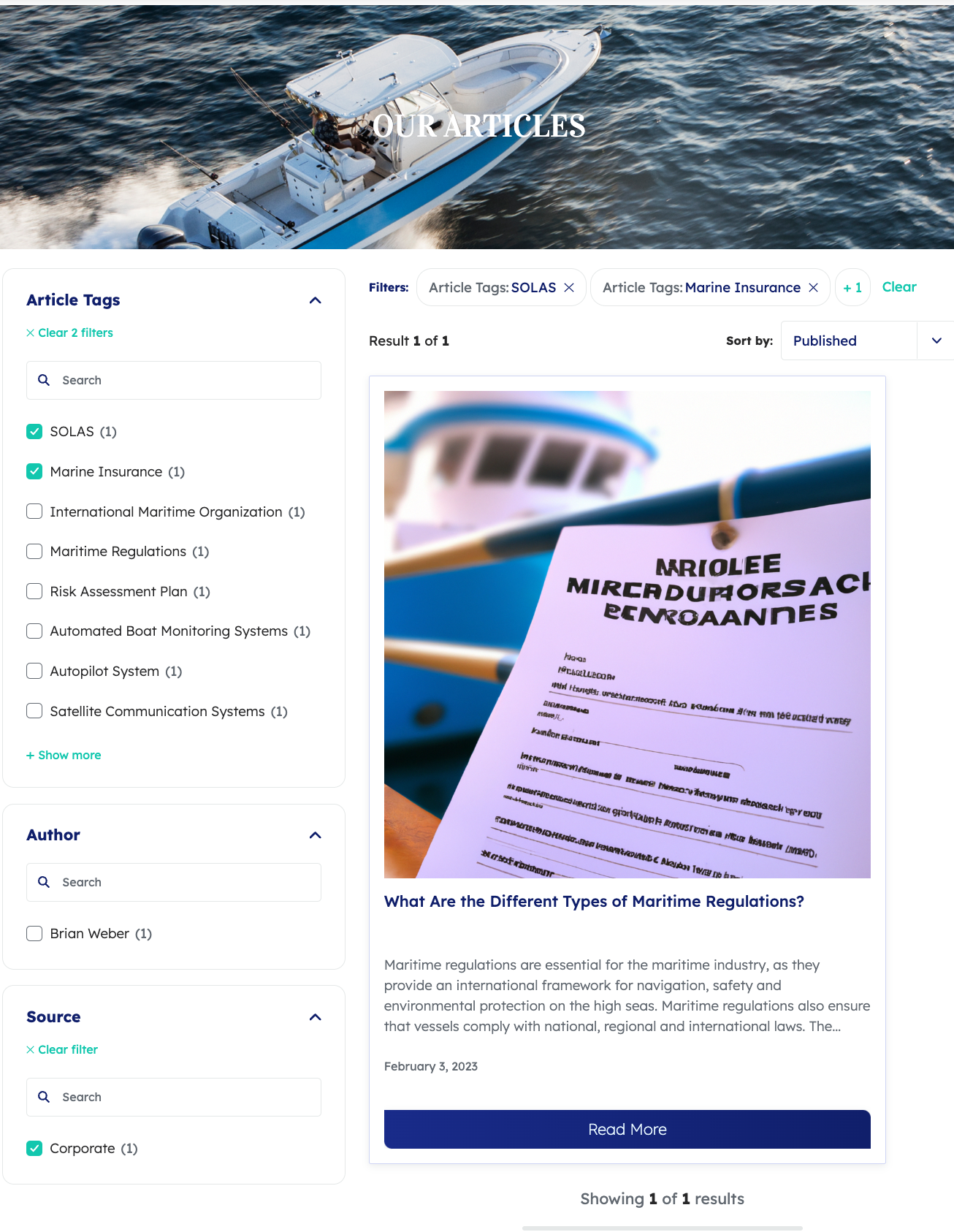
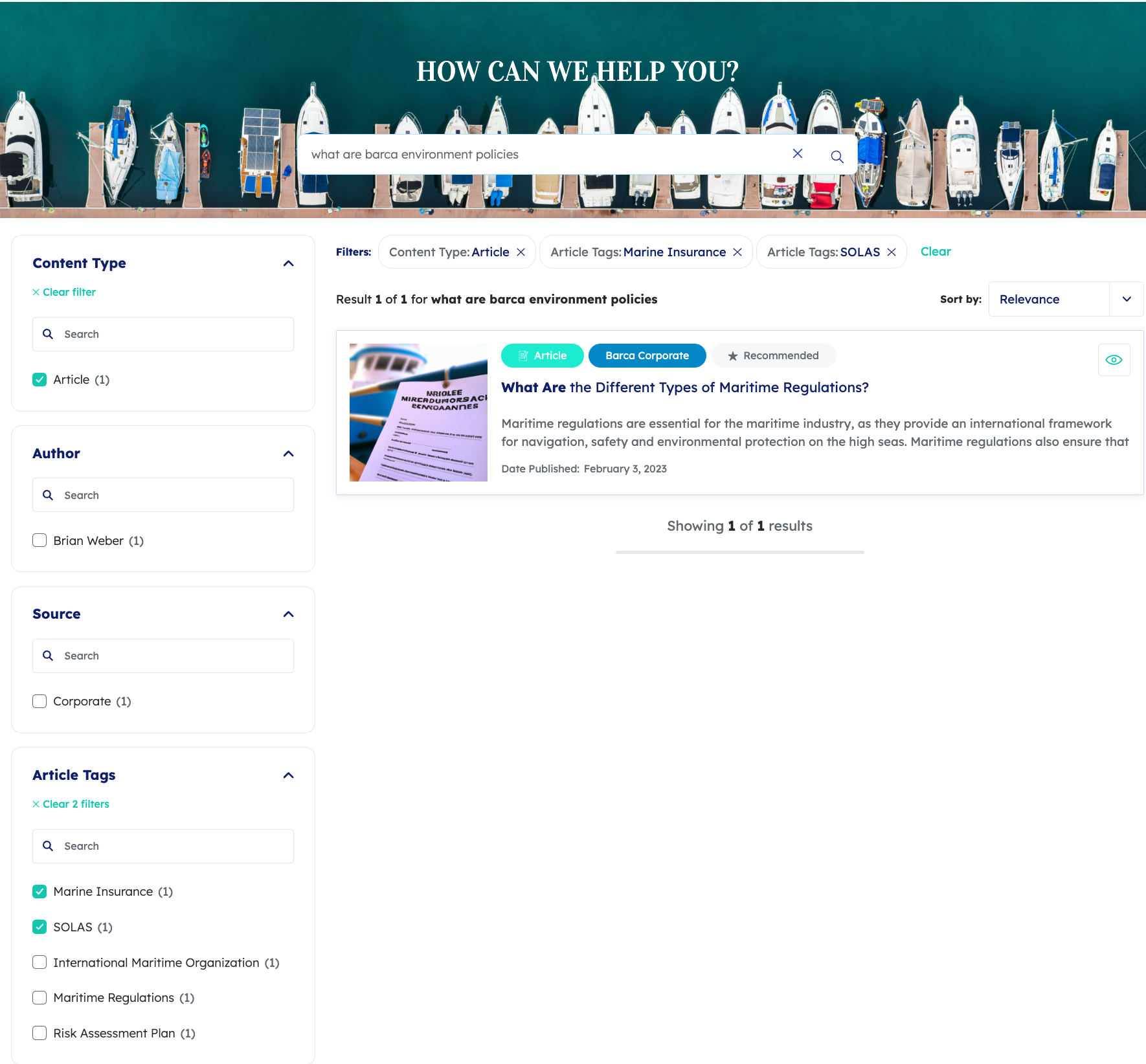
A customer triggers a query from a customer service search interface.
The ART model on the assigned query pipeline has learned a pattern based on the current context that agents often find the information in the article titled What are the Different types of Maritime Regulations useful when they initially search for what are barca environment policies.
This article is indexed as an item in a source with the permanentid aadd742687c62910d6dc8347304ec2cedfd0b06d5b4d2794a925ce5688bd.
Therefore, the dq is assigned the value @permanentid=aadd742687c62910d6dc8347304ec2cedfd0b06d5b4d2794a925ce5688bd.
This disjunction query expression returns the following search results:
|
|
Note
An ART model won’t attempt to populate the |
|
|
The constant and disjunction query expressions should never be used for any query pipeline feature that affects the ranking of results. Instead, you should use either the basic or advanced query expressions. |
Constant query expression (cq)
The constant query expression (cq) is very similar to the advanced query expression but must hold expressions that are constant for all users of a specific search interface or search tab (for example, search scope).
The results of evaluating these expressions are kept in a special index cache to avoid re-evaluating them on each query.
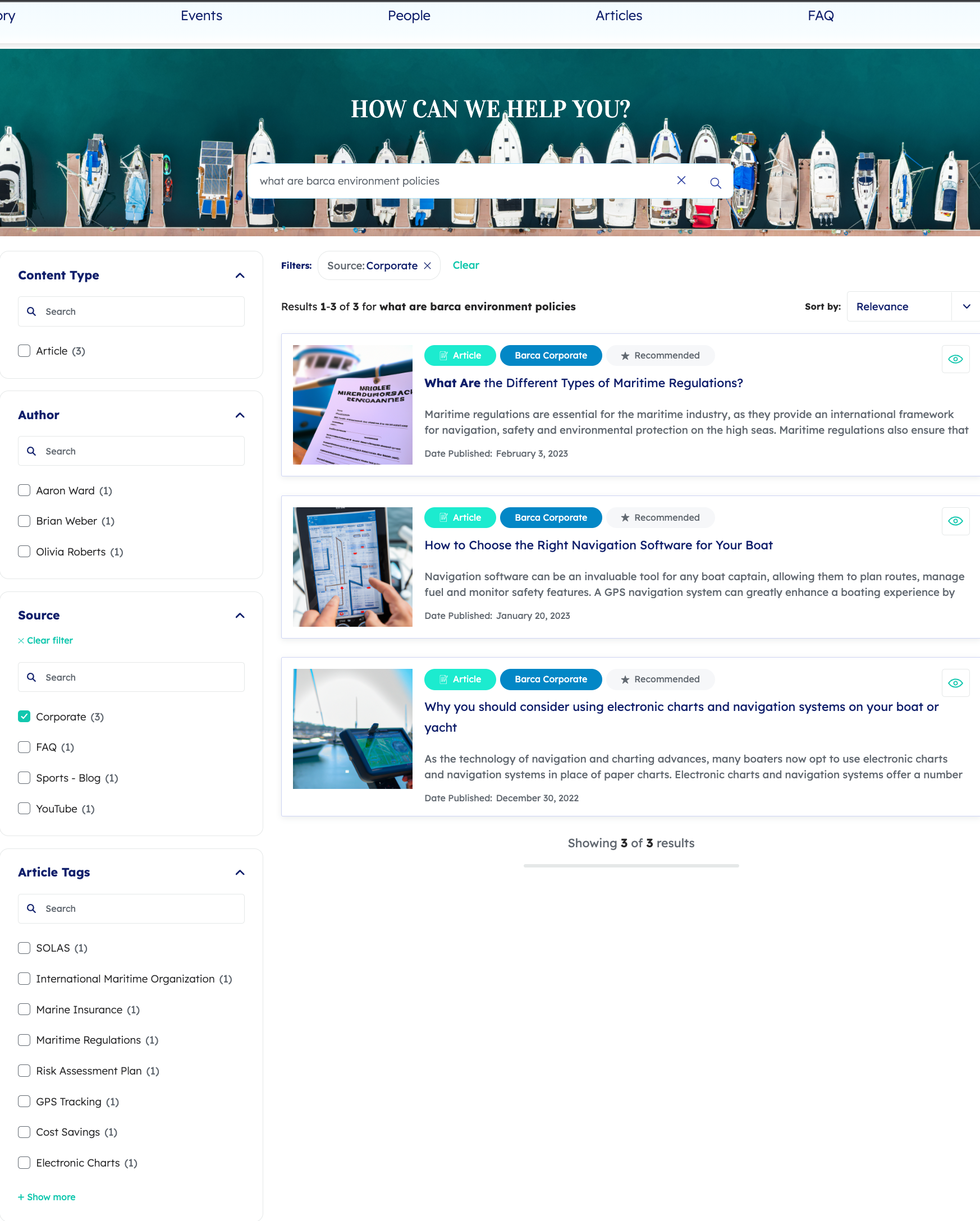
A customer selects the value Corporate for the Source facet on the customer service search interface.
The selected tab has the value @source=="Corporate", so the cq value is also @source=="Corporate" until a different tab is selected.
This constant query expression returns the following search results:
|
|
|
Large query expression (lq)
The large query expression (lq) is typically leveraged by case deflection and insight panel search interfaces to send lengthy textual data (for example, a case description) along with a query.
A Coveo ML ART model with Intelligent Term Detection (ITD) enabled can extract contextually relevant keywords from the large query expression and use those keywords to refine the basic query expression (q).
A support agent triggers a query from an insight panel search interface.
The lq contains the case description of a customer requesting help.
The ART model on the assigned query pipeline uses {intelligent-term-detection-abr} to extract relevant terms from the case description, based on the current context (see How does Intelligent Term Detection (ITD) work?).
Combined Query Expression Examples
A customer interacts with the search page as follows:
-
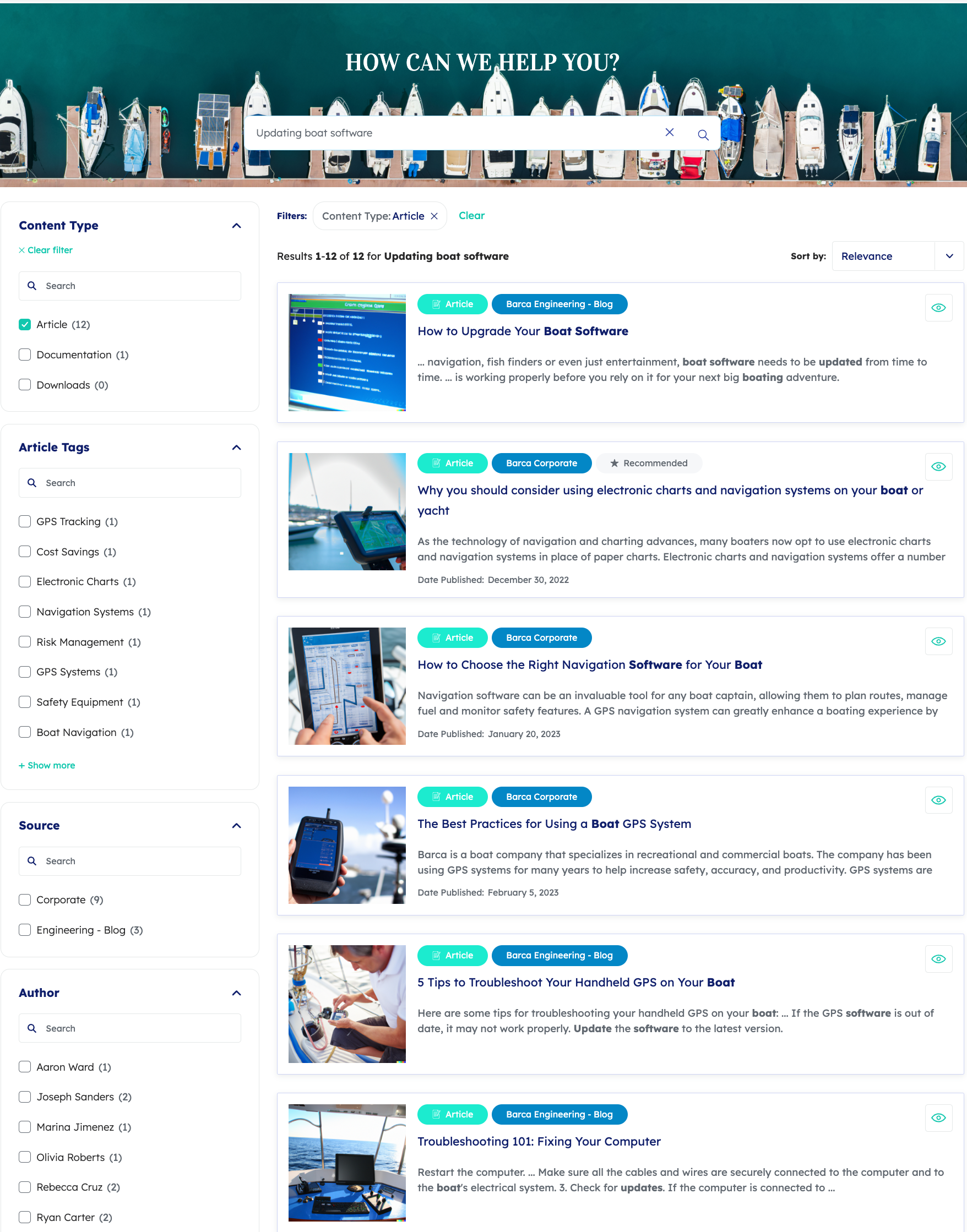
The customer triggers a query containing the keywords
Updating boat software. -
They interact with the Content Type facet, changing the advanced query expression to
@contenttype=="Article". -
The ART model on the assigned query pipeline has learned a pattern based on the current context that customers often were interested in looking at the article titled
The Best Practices for Using a Boat GPS Systemwhen they searched forUpdating boat software. This article has apermanentidvalue ofz0f0rcprlia27wg8ov6q4347f4hjnc55nzu6nl8rnzn1p56ugf1235fvhrg8. Therefore, thedqis assigned the value@permanentid=z0f0rcprlia27wg8ov6q4347f4hjnc55nzu6nl8rnzn1p56ugf1235fvhrg8This results in the following combined query expression:
((Updating boat software AND @contenttype=="Article") OR @permanentid=z0f0rcprlia27wg8ov6q4347f4hjnc55nzu6nl8rnzn1p56ugf1235fvhrg8)
This combined query expression returns the following search results:
A support agent is interacting with a customer service search interface to assist a customer with their product. The support agent interacts with the search interface as follows:
-
The support agent triggers a query containing the keywords
Supplies conference. -
The support agent selects the value
Latviafrom the Country facet, setting the advanced query expression to@country="Latvia". -
The support agent is authenticated on the customer service search interface, so their generated search token enforces the filter
@contenttype=="Article". This ensures that only article items appear in the query results, so thecqvalue is@contenttype=="Article". -
The ART model on the assigned query pipeline uses Intelligent Term Detection (ITD) to extract the terms
suppliesandconferencefrom the case description.This results in the following combined query expression:
((%~ Or([Required:60%],"Supplies conference) ~%) AND @country="Latvia") AND @contenttype=="Event"
This combined query expression returns the following search results: