Manage stop word rules
Manage stop word rules
Stop words are words that are filtered out of a query in order to give more importance to keywords. This provides users with more relevant search results. The stop word list for a Coveo organization index is empty by default, but with the required privileges, you can add stop word rules in the Coveo Administration Console.
Stop words are defined independently for each query pipeline. Depending on your specific needs, you may want to add a list of words to ignore from queries. For instance, you might ignore industry-specific words that appear in many of your items and offer little differentiation between items in search results.
On a medical website, words such as cause, symptoms, and treatment tend to appear frequently in articles across the site.
These words are often used in queries but they don’t help differentiate between articles on the site.
You therefore create a stop word rule for each of these words.
So when a user searches for headache or migraine treatment, the query sent to the index is headache migraine.
The search results will be more relevant as the focus is on the keywords headache and migraine rather than the generic term treatment.
Prerequisites
Before creating a rule, make sure that you have the following:
-
Access to a search page
You need access to a Coveo-powered search interface to be able to test the rule that you create.
-
An existing query pipeline
The queries from the search page must travel through a specific query pipeline.
-
Required privileges
You need specific privileges to be able to add and edit rules in a query pipeline.
Once you meet these requirements, you can create a rule on the Query Pipelines (platform-ca | platform-eu | platform-au) page. To test the rule, use the A/B test feature to compare the results of the rule with the results of the original pipeline.
Order of execution
The following diagram illustrates the order of execution of query pipeline features:
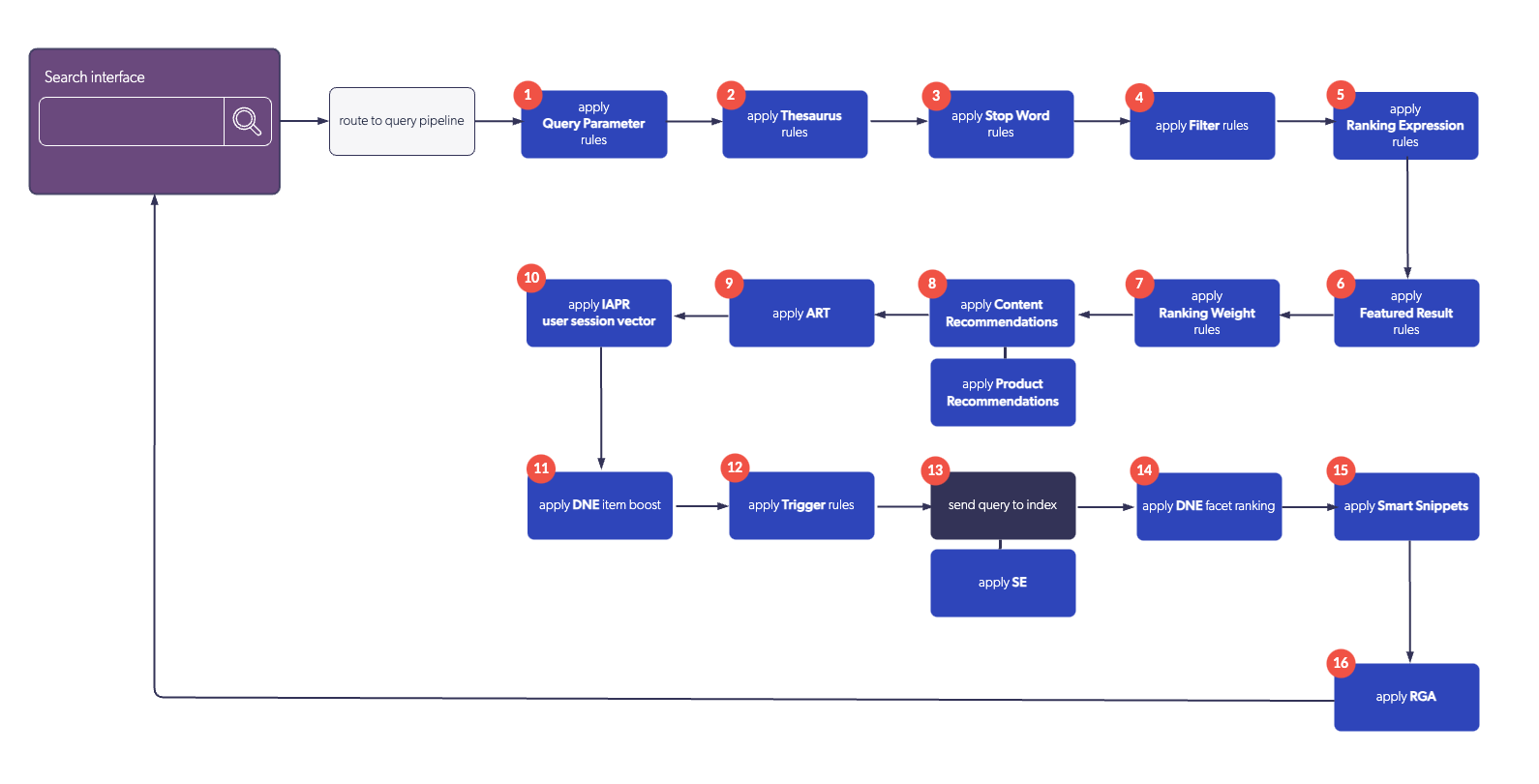
|
|
Note
Query pipeline stop word rules are not applied to the query that’s used by RGA, CPR, SE, and Smart Snippet models.
These models always use the raw basic query expression ( |
Access the "Stop words" subtab
-
On the Query Pipelines (platform-ca | platform-eu | platform-au) page, click the query pipeline you want to modify, then select Edit components in the Action bar.
-
On the page that opens, select the Search terms tab.
-
In the Search terms tab, on the left side of the page, select Stop words.
Add or edit stop word rules
-
Do one of the following:
-
If you’re creating a new rule, click Add stop word.
-
If you’re editing an existing rule, click the rule you want to edit.
-
-
Under Stop word, add or edit the words that will be ignored when they appear in queries. Type one or more words separated by commas, and then press Enter.
-
(Optional) Click Add condition to set a condition under which the stop word rule applies.
-
In the Select a condition panel that opens, in the dropdown menu, select one of the available conditions, or create a new one by clicking Create a new condition.
-
Click Apply condition.
-
Your rule is now active.
Duplicate stop word rules
You can duplicate a stop word rule to use as a starting point for new rules within the same query pipeline.
-
Click
next to the rule you want to duplicate, and then click Duplicate. The duplicated rule appears at the bottom of the list.
-
Edit the duplicated rule as required.
Delete stop word rules
-
Click
next to the rule you want to delete, and then click Delete. The rule is removed from the list.
Your deleted rules will stop being effective immediately in the target pipeline.
|
|
|
Leading practices
When managing stop word rules, consider the following recommendations and tips:
-
The index assigns a semantic value to every word by considering their frequency in the index. Frequent words in indexed items are considered to carry less meaning. Consequently, the index already attributes minimal ranking weight for the occurrence of these words in search results. Therefore, it’s recommended to add stop word rules only for specific use cases.
NoteYou might consider adding stop word rules to exclude bad keywords from queries to not impact the Coveo ML model learning process. However, if end users perform queries containing only banned words, the model learning process could be affected depending on the returned search results.
For more information on the management of the blocklist words, see Blocklists.
-
Apply conditions:
Typically, stop word rules should only apply when a certain condition is fulfilled.
In general, you should associate the rule, and/or the query pipeline it’s defined in, to a condition. Without a condition, the stop word rule would apply to all queries.
-
Consider using the Partial match feature:
For implementations where users tend to enter lengthy natural language queries, employing the Partial match feature can simplify search results by eliminating the need for exhaustive stop word definitions. This option lets you define a minimum number of keywords to be found in a search result before this search result is returned. As a result, the index favors the most important keywords and stop words become optional.
-
Consider how stop words affect ART models:
When creating stop word rules, the words specified in the rule don’t get passed to the ART models, which means that the Automatic Relevance Tuning (ART) models don’t learn from these words and won’t associate them with user interactions. However, it’s important to note that these models also have their own stop word list that can be managed through the Advanced model configuration API. These stop words help reduce the impact of common words when generating recommendations, however, a model only starts excluding them after accumulating sufficient interaction data.
Therefore, it’s recommended to regularly review ML model training data to ensure that stop word rules aren’t adversely affecting the quality of the recommendations.
-
Test your stop words:
When creating stop word rules, you should always perform tests to ensure that your stop words don’t negatively impact the search experience in cases other than the one you’re trying to improve.
Stop word special cases
Stop word rules remove the specified words from queries only when they appear in combination with other keywords. They aren’t removed when they’re the only word in the query, because otherwise the removal could create an invalid expression.
Coveo indexes all words contained in your source items, including the stop words. This allows Coveo to manage exceptions and keep stop words in the query in the following cases:
-
Stop words within a phrase search.
ExampleA user is looking for an item that contains a very specific phrase and encloses the phrase between double-quotes in the search box:
"in the plan for year 2025"The words
in,the, andforare stop words, but since the phrase is enclosed in double-quotes, all keywords in this query are sent to the index, so only items containing these keywords in the same order and as contiguous occurrences are returned. -
A query containing only stop words.
ExampleA user searches for:
to be or not to beIf all the keywords of this query are stop words, they’re all kept and sent to the index.
-
A stop word is an argument of the
NOTorNEARoperators.Examples-
A user searches for:
how NEAR:10 export, meaning the user is looking for items containing bothhowandexportoccurring within ten words from each other.The word
howhas been set as a stop word. However, since it’s an argument of theNEARoperator, it will be kept to return items containing bothhowandexportwithin ten words from each other. -
A user searches for:
(NOT how export), meaning the user is looking for items containingexportbut nothow.The word
howhas been set as a stop word.
If
howis a stop word, because it’s an argument of theNOToperator, and theNOToperator has precedence over the implicitANDoperator, it will be kept to return items containing bothhowandexport. -
-
A stop word also has a plural form.
ExampleAn online store sells a variety of wristwatches. Since the majority of their products contain the word
watchorwatches, searching for these words doesn’t provide relevant results, as customers are looking for either specific brands or types of watches. Therefore, you add bothwatchandwatchesto your stop words list to ensure that the search results are more relevant. You must add both forms since the plural form isn’t automatically removed when the singular form is a stop word.
Required privileges
The following table indicates the privileges required to view or edit stop word rules. Learn more about the Privilege reference or how to manage privileges.
| Action | Service - Domain | Required access level |
|---|---|---|
View stop word rules |
Organization - Organization |
View |
Edit stop word rules |
Organization - Organization |
View |
Search - Query pipelines |
Edit |