About the query pipeline routing algorithm
About the query pipeline routing algorithm
When a query is sent to the Search API, a routing algorithm is executed to determine which query pipeline in the target Coveo organization will process this query.
The following diagram illustrates the process of a query being routed to a query pipeline.[1]
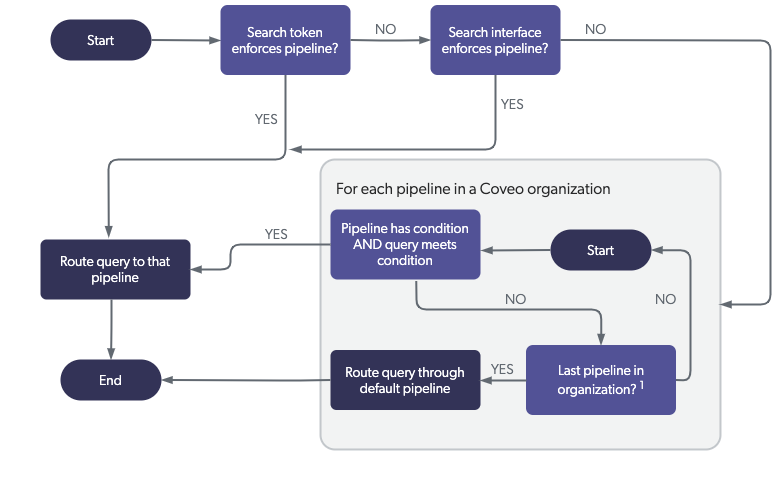
When a query is sent to the Search API:
-
If the search token enforces a pipeline, go to Step 4 using the search token-enforced pipeline (bypassing its condition, if any).
-
Otherwise, if the search interface enforces a pipeline, go to Step 4 using the search interface-enforced pipeline (bypassing its condition, if any).
-
Otherwise, for each pipeline that has a condition in the Coveo organization:
|
|
Notes
|