Review and manage explorers
Review and manage explorers
- Access an explorer
- Review the graphical and numerical metrics that are available by default
- Manage graphical and numerical metrics
- Set the date interval over which you want to review search usage data
- Set a period used to establish the trends in numerical metric boxes
- Add one or more global dimension filters to refine search usage analytics data
- Narrow a report to a dimension value
- Exclude a dimension value from a report
- See the list of dimension value related search results without leaving the usage analytics report
- See which documents were opened following a user query
- Manage predefined filters
- Edit predefined and custom filters
- Add dimensions or metrics to the data table
- Report on queries that surrounded a custom event
- Export the content of a usage analytics explorer
- Export usage analytics data based on your current filters
- Manage the access to the explorer
- Apply a template to an explorer
- Rename an explorer
- Remove an explorer
- Share an explorer
- Required privileges
You can use the Reports (platform-ca | platform-eu | platform-au) page in the Analytics section of the Coveo Administration Console navigation menu to review the data collected by Coveo Usage Analytics (Coveo UA).
By default, a Coveo organization comes with three default explorers that can also be used as templates to create other explorers. These pre-configured explorers present search usage metrics in numeric, graphical, and tabular format. The indicator values are presented for a selectable date interval. You can add metrics and dimensions to the table to better evaluate the search solution (see Dimensions and Metrics).
|
|
Note
The usage analytics data that you can review can be limited by your permissions. |
Access an explorer
-
On the Reports (platform-ca | platform-eu | platform-au) page, click the explorer that you want to open, and then click Open in the Action bar.
Note-
The following message appears on the page when Coveo UA isn’t activated for your Coveo organization:
This section is not available for your Organization.Contact Coveo Support to activate Coveo UA for your Coveo organization.
In explorers, the time series at the top and the table at the bottom are independent entities, meaning that changes in the table such as removing metrics or adding metric filters won’t be replicated in the time series nor the time series be affected by them. The contrary is also true, adding metrics in the time series won’t add them in the table.
-
-
When needed, enter Edit mode:
On the explorer, click Edit in the upper-right corner.
Changes that you made before accessing Edit mode are kept. Therefore, you must remove these changes (if unwanted) before saving the explorer.
Review the graphical and numerical metrics that are available by default
On the explorer, review the available metric values:
|
|
Notes
|
-
Click Event Count
This clickable box reports click counts.
NoteThis box is only available by default in the Activity pre-configured explorer.
-
Search Event Count
This clickable box reports search counts.
-
Search Events With Clicks
NoteThis box is only available by default in the Search Relevance pre-configured explorer and it replaces the Search Event Count box.
This clickable box reports counts of search events resulting in at least one click.
-
Visit Count
This clickable box reports the total count of visits, which are the number of visits regardless of unique IP addresses and user names for the selected date interval and filters (see Usage analytics metrics).
-
Timeline
This time series shows the number of clicks, searches, or visits per day by default, depending on the user selection (see Interval).
NoteThe timeline uses your browser’s time zone.
-
The table presents the data for the selected date range, filters, dimensions, and metrics.
NoteRelevance metrics (Average Click Rank, Search Event Clickthrough, and Relevance Index) values (if any) have a color that represents if the value is good (green), neutral (black), or poor (red) depending on predefined thresholds.
The predefined thresholds for each metric are the following:
-
Average Click Rank: 1-3 = good (green), 3-6 = neutral (black), and > 6 = poor (red)
-
Search Event Clickthrough: > 60% = good (green), 40-60% = neutral (black), and < 40% = poor (red)
-
Relevance Index: > 0.7 = good (green), 0.5-0.7 = neutral (black), and < 0.5 = poor (red)
For example:
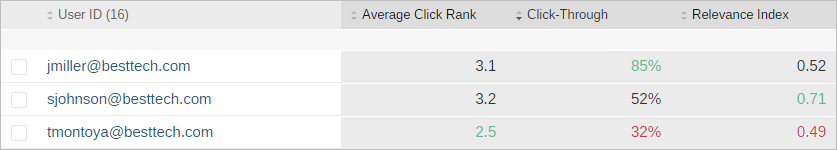
ExampleThe
Activitytable shows a list for the User Query dimension with the Click Event Count, Search Event Count, and Visit Count metrics.You can sort the table by a dimension or a metric by ascending or descending order by clicking the corresponding column header.
-
Manage graphical and numerical metrics
On the explorer, you can:
Add one or more graphical and numerical metrics
-
In Edit mode, click
 next to the metrics box.
next to the metrics box. -
Select one or more metrics to be shown in the time series and in the metrics box:
-
Click the links (Search, Click, and Custom) to browse metrics by event type, and then select the one(s) of your choice (see Usage analytics metrics).
-
Click All, and then use the Search metrics box to find and select the metric(s) of your choice.
-
-
Under Selected Metrics, review the metrics order in the box by dropping the metrics to the place of your choice.
-
When you report on a custom event and on a search or click event (you added a filter or selected a dimension or metric related) at the same time, or on an all event category metric or dimension (for example, Unique User IP and Browser), choose to Create a relation using the Last search or the Visit between the event categories.
Notes-
Last search links each custom event to the user query immediately preceding (if any) and Visit links each custom event to all queries performed during the user visit in which the custom event happened.
-
The Create a relation using parameter has no effect when you report only on search and click events.
-
Your selection here is automatically replicated in the time series to match metrics total value.
-
-
Click More to access advanced settings.
-
In the More section:
-
Choose how the data is grouped in the time series by selecting one of the following interval values: Automatic, Hour, Day, Week, or Month. By default, Automatic is selected.
Note-
When you choose Automatic, the data is grouped in the time series based on the interval value that most fits the selected date range:
Selected date range Interval value 181 days and more
Month
60 to 180 days
Week
60 hours to 59 days
Day
1 to 59 hours
Hour
Less than an hour
Minute
-
The interval can be modified at any time.
Leading practiceA mix of this feature with the date interval selection offers more possibilities.
For example, you want to investigate hour by hour what happened during an activity drop that occurred on October 30, 2021.
-
In the upper-right corner, click the box containing the actual date range to access the Report Period dialog, and then select October 30, 2014 (see Set the date interval).
-
Click
 .
. -
Select the Hour interval.
-
Click Apply.
You see, for each hour, the hourly total value of each metric you selected to be shown in the time series. This way you can know exactly the hour the drop started.
-
-
When you want to see metric trends over the selected period, select the Display trend data option (see Determine trends).
-
When you want to see metric values on top of every time series points, select the Display metric data option.
-
Under Data Display, select the time series to be shown using Line or Barcharts.
-
Click Apply.
-
Remove one or more graphical and numerical metrics
-
In Edit mode, click
 next to the metrics box.
next to the metrics box. -
Under Selected Metrics, click the minus sign (-) next to the metric(s) you want to remove from the time series and the metrics box.
-
Click Apply.
Determine trends
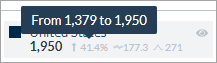
Compare specific data with data from a prior period (see Set a period used to establish the trends in numerical metric boxes).
|
|
Note
When available and selected to be displayed, the trend indicator (up or down arrow) shows the percentage of increase or decrease for a metric in comparison with the same selected period that preceded (week, month, year…).
|
Set the date interval over which you want to review search usage data
On the explorer, in Edit mode, do one of the following:
-
At the top section of the explorer, in the time series, click and hover over an area:
|
|
Notes
|
-
In the upper-right corner, you can go from the actual date interval selected (last week, month…) to the previous period or next period by clicking
 and
and  respectively or you can click the box containing the actual date range (for example,
respectively or you can click the box containing the actual date range (for example,  - by default the last 7 complete days) to access the Report Period dialog, and then select the date range you want to review (see Set the period to review search usage data).
- by default the last 7 complete days) to access the Report Period dialog, and then select the date range you want to review (see Set the period to review search usage data).
|
|
Note
You can select a period that’s incomplete (for example, the current month), in which case your date range selection will always include the latest available events until the period ends (for example, the first day of the following month). For example, you’re reviewing data per Month and want to see how statistics are trending for the first two weeks of the current month, so you click |
Set a period used to establish the trends in numerical metric boxes
|
|
If you want trends to be shown in the numerical metric boxes, you must select the Display trend data option (see Trend option). |
-
On the explorer, in Edit mode, click the box containing the actual date range in the upper-right corner.
-
In the Report Period panel that appears, in the Compare to section, click the Previous Period, Previous Month, Previous Year, or Custom Period link to set the period to compare the current selected search usage data with.
The trends in the numerical metric boxes are automatically updated based on your selection.
Notes-
By default, the Previous Period is used to compare.
-
The explorer remembers your date range selection so you don’t have to set it each time the report is displayed.
-
-
Click Save in the upper-right corner.
Add one or more global dimension filters to refine search usage analytics data
On the explorer, do one of the following:
-
Hover your cursor over the dimension value for which you want to add a filter.
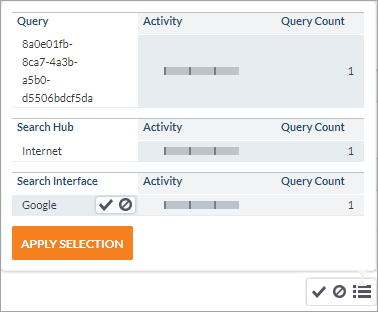
-
Click
 next to the dimension value.
next to the dimension value. -
In the window that appears, select one or many dimension values you want to exclude
 or to narrow to
or to narrow to .
-
Click Apply selection.
The selected filter(s) appear in the top bar.

-
-
On the explorer, in Edit mode, access the dialog to add global dimension filters by clicking
(see Add global dimension filters).
Narrow a report to a dimension value
On the explorer, do one of the following:
-
Click
next to the dimension value.
-
Select the checkbox next to the dimension value, and then click include.
Exclude a dimension value from a report
On the explorer, do one of the following:
-
Click
 next to the dimension value.
next to the dimension value. -
Select the checkbox next to the dimension value, and then click exclude.
See the list of dimension value related search results without leaving the usage analytics report
On the explorer, click ![]() next to the dimension value.
next to the dimension value.
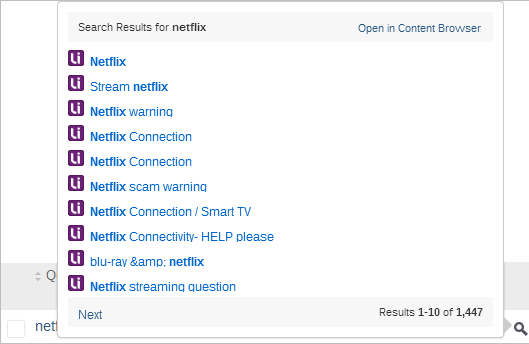
You can click Next to see other search results for the dimension value.
|
|
Notes
|
See which documents were opened following a user query
On the explorer, click ![]() next to a Keyword or User Query dimension value.
next to a Keyword or User Query dimension value.
|
|
Note
The Search Relevance explorer opens in a new browser tab with a filter on the query or keyword value (for example, |
Manage predefined filters
The page may contain one or more predefined filters that are always applied when you access the page to show more meaningful data.
On the explorer, in Edit mode, click X next to the predefined filter labels to remove those filters.
The Search cause is not interfaceLoad hidden filter is applied to the Keyword page to exclude the queries that are automatically generated to present default search results when users initially access the search interface and didn’t yet enter keywords in the search box.
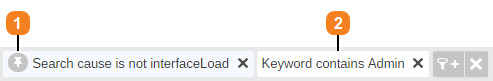
1 Predefined filter (identifiable by its light blue background and its pin icon)
2 Manually entered filter (white background)
Edit predefined and custom filters
On the explorer, in Edit mode:
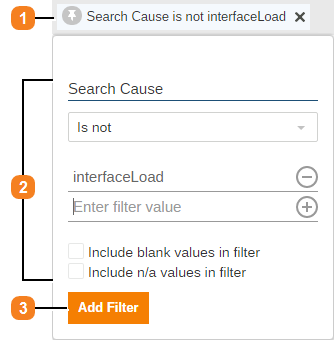
1 Click the filter label
2 Edit the filter content
3 Click Add Filter
Add dimensions or metrics to the data table
-
On the explorer, in Edit mode, click
 next to the table header.
next to the table header. -
In the Available dimensions and Available metrics lists, do one of the following to select one or more dimensions and/or metrics to be shown in the table:
-
Click the links (Search, Click, and Custom) to browse dimensions and metrics by event type, and then select the one(s) of your choice (see Dimensions and Metrics).
-
Click All, and then use the Filter box to find and select the dimension(s) and metric(s) of your choice.
ExampleCountry and Search Event Count
-
-
In the Advanced Settings section:
-
(Optional) Click
, and then create one or more metric filters (see Add dimension and metric filters in cards).
-
In the Value Destination Link box, set destination links when clicking table values (see Set destination links on card title and values).
Metric filters are ONLY applied to the table content. Therefore, numerical metric count(s) (Click Event Count, Search Event Count, etc.) next to the line graph won’t be affected by the filter(s).
For example, you only want to know the user IDs that have 20 clicks or more, so you add the following filter:
Click Event Count is greater than 20. The click event count next to the time series (1186) isn’t the same as the sum of the click event counts in the table (214).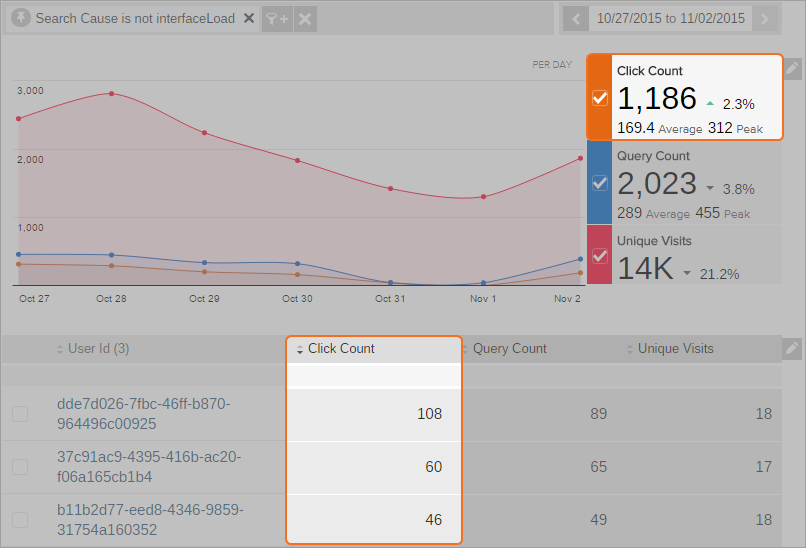
-
Under Sort Direction, decide the metric value sort order, by selecting Ascending or Descending.
-
Set the number of rows per page in the table.
In the Rows box, enter the number of rows per page.
NoteBy default, the table has ten rows per page.
-
-
Click Apply.
The table is updated to add a column for the selected dimension or metric.
ExampleIf you first select the Country dimension, the table displays metric values for United States, Canada, etc. You further slice and dice the data by adding the Device dimension to get all Country+Device combinations such as United States using Firefox, United States using Chrome, Canada using Chrome, etc. If you then remove Country, the table only shows the metric values for the various devices.
NoteYou can remove dimensions and metrics from a data table by hovering over the dimension or metric name, clicking
 in Edit mode, and then saving your modifications.
in Edit mode, and then saving your modifications.
Report on queries that surrounded a custom event
-
On the explorer, in Edit mode, click
 next to the table header.
next to the table header. -
Search and select User Query and one or more dimensions or metrics related to custom events to display [that is, Event Type, Custom Event Value, Custom Event Count…] (see Usage analytics dimensions and Usage analytics metrics).
-
Under Create a relation using, select Last search to link each event to the search event immediately preceding (if any) or select Visit to link each event to all queries performed during the user visit in which the event happened (see Visit ID).
Notes-
Your selection here is automatically replicated in the time series to match metrics total value.
-
We recommend that you select Last search in situations where the last query performed by the user is the reason why they did the custom event.
For example, in Salesforce, when agents attached a result to a case (
caseAttach), the last query they made gave them the results they used to do the custom event.On the other hand, we recommend that you select Visit in situations where all the queries performed by the user during the visit didn’t resolved their matter.
For example, when one of your clients creates a case (
caseCreate), they, more often than not, tried to get the information they needed by querying on the subject of their matter before doing the custom event. You can then use these queries to create knowledge base article(s) and therefore fill the content gap.
-
-
Click Apply.
-
Create a filter on a dimension value (see Add filter).
ExampleCustom Event Value is caseCreate.When you selected Last search, in the User Query column, you see the query that immediately preceded all the custom event you filter on.
When you selected Visit, in the User Query column, you see all queries performed during the user visit in which the custom event(s) you filter on happened.
Export the content of a usage analytics explorer
On the explorer, at the lower-right corner of each data table in explorers (pre-configured or custom), click ![]() to export the table content as a CSV file (see Data exports).
to export the table content as a CSV file (see Data exports).
|
|
Note
When you have more than one hundred thousand results, this dialog appears: 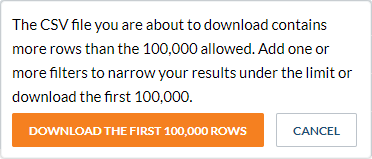
Click Download the First 100,000 Rows or click Cancel to add one or more filters (see Add one or more global dimension filters to refine search usage analytics data). |
Export usage analytics data based on your current filters
-
On the explorer, click
 in the upper-right corner, and then select Export raw data using current filters.Note
in the upper-right corner, and then select Export raw data using current filters.NoteThis function exports all the data of your Coveo organization (not only the dimensions and metrics appearing on the page) that meets the criteria (date interval and other filters). When you only want to download the content of a report table, rather use the other export feature (see Export the content of a usage analytics explorer and Data exports).
-
On the Data Exports (platform-ca | platform-eu | Data platform-au) page, download the newly created export (ZIP file) on your computer (see Download an export).
Manage the access to the explorer
|
|
Notes
|
On the explorer, access the Manage Report Access dialog (click ![]() in the upper-right corner, and then select Manage report access), and then define who has access to the explorer (see Manage access to reports).
in the upper-right corner, and then select Manage report access), and then define who has access to the explorer (see Manage access to reports).
Apply a template to an explorer
-
On the explorer, click
 in the upper-right corner, and then select Apply template.
in the upper-right corner, and then select Apply template. -
In the Select a Template panel that appears, select the template of your choice, and then click Select Template (see Explorer templates).
-
Click Save in the upper-right corner.
|
|
Note
This option is useful when you’ve deleted one of the three pre-configured explorers. |
Rename an explorer
-
On the explorer, in Edit mode, change the explorer name by clicking and editing the original name in the upper-left corner.
ExampleYou want to analyze the workflow of anonymous and authenticated users so you changed the Audience Copy page name to Users Workflow.
-
Optionally, enter an explorer description.
-
Click Save in the upper-right corner.
Remove an explorer
On the explorer, click ![]() in the upper-right corner, and then select Delete.
in the upper-right corner, and then select Delete.
|
|
Note
If you inadvertently delete one of the pre-configured explorers, you can recreate them by applying the related template to an explorer and saving it (see Apply a template to an explorer). |
Share an explorer
On the explorer, in Edit mode, before you save an explorer, in your browser address bar, copy the URL and share the link to any colleagues who have the required privileges to review explorers within or outside your Coveo organization.
|
|
Notes
|
Required privileges
The following table indicates the required privileges to view and edit explorers from the Reports (platform-ca | platform-eu | platform-au) page and associated panels (see Manage privileges and Privilege reference).
|
|
Note
Access to explorers or part of their content may be further restricted as a function of the member (see Manage access to reports and Manage permission filters). |
| Action | Service - Domain | Required access level |
|---|---|---|
View explorers |
Analytics - Analytics data Analytics - Dimensions Analytics - Named filters Analytics - Permission filters Analytics - Reports Organization - Organization |
View |
Edit explorers |
Analytics - Analytics data Analytics - Dimensions Analytics - Named filters Analytics - Permission filters Organization - Organization |
View |
Analytics - Data exports Analytics - Reports |
Edit |
|
Analytics - Administrate |
Allowed |