Manage query parameter rules
Manage query parameter rules
A query parameter is a component of a query that can be specified either through the query string or in the JSON body of a user query. The Query parameters section of the Query Pipelines (platform-ca | platform-eu | platform-au) page lets members with the required privileges create query parameter rules to override search parameter values for every query that matches a condition.
These rules can be added without having to modify the search interface code. By default, the list of query parameters in a query pipeline is empty. Therefore, the query parameters in the search interface code are used.
Query parameter rules are defined independently for each pipeline. These parameters are useful in customizing the search experience, allowing for the override of default values for every query that matches a defined condition.
You want to enable or disable the query syntax based on a user or group. For administrators, you set a rule that enables advanced query syntax whenever they’re performing a search. This includes allowing specific query operators or search fields that are typically not available to general users. On the other hand, for general users, the default search parameters would apply, with the advanced syntax options remaining disabled.
|
|
Note
Query parameter rules have priority over the same parameters set in the search interface code. |
Prerequisites
Before creating a rule, first make sure that you have the following:
-
Access to a search page
You need access to a Coveo-powered search interface to be able to test the rule that you create.
-
An existing query pipeline
The queries from the search page must travel through a specific query pipeline.
-
Required privileges
You need specific privileges to be able to add and edit rules in a query pipeline.
Once you meet these requirements, you can create a rule on the Query Pipelines (platform-ca | platform-eu | platform-au) page. To test the rule, use the A/B test feature to compare the results of the rule with the results of the original pipeline.
Access the Query parameter subtab
To manage query parameter rules in a query pipeline:
-
On the Query Pipelines (platform-ca | platform-eu | platform-au) page, click the query pipeline in which you want to manage rules, and then click Edit components in the Action bar.
-
On the page that opens, select the Advanced tab.
-
In the Advanced tab, on the left side of the page, select Query parameters.
Add or edit query parameter rules
You can add query parameter rules to a query pipeline to override the current parameter value for every query that matches a condition.
-
In the upper-right corner of the page, click Add rule, or double-click an existing rule you want to edit.
-
On the Add a Query Parameter Rule subpage, select the parameter to which you want to add a rule, and then click Next.
NoteIf you can’t find the parameter you’re looking for, you can look for it in the Filter by parameter name field.
-
On the Rule configuration panel, do one of the following:
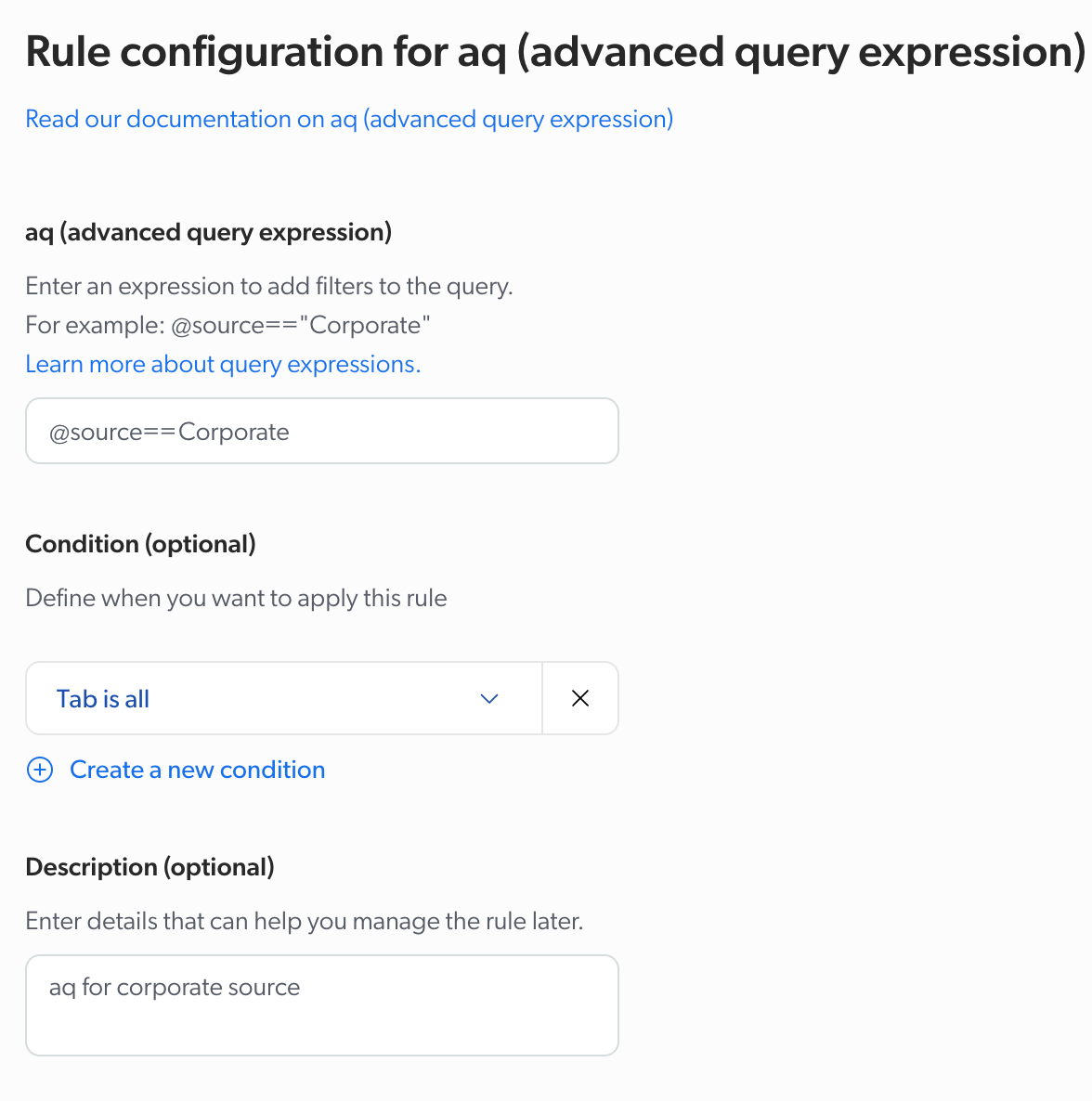
If you selected a string parameter
Select or enter the value of the parameter with which you want to replace the actual parameter value.
If you selected an integer parameter
Enter the number with which you want to replace the actual parameter value.
If you selected a Boolean parameter
Select whether to enable or disable the parameter.
-
Under Condition (optional), select a query pipeline condition in the dropdown menu or create a new one.
-
Under Description (optional), enter information that will help you manage the rule in the future.
-
Depending on whether you’re creating a new rule or editing an existing one, click Add rule or Save.
|
|
You can check who created or last modified a given query parameter rule by inspecting the Details column of the Query parameters subtab. 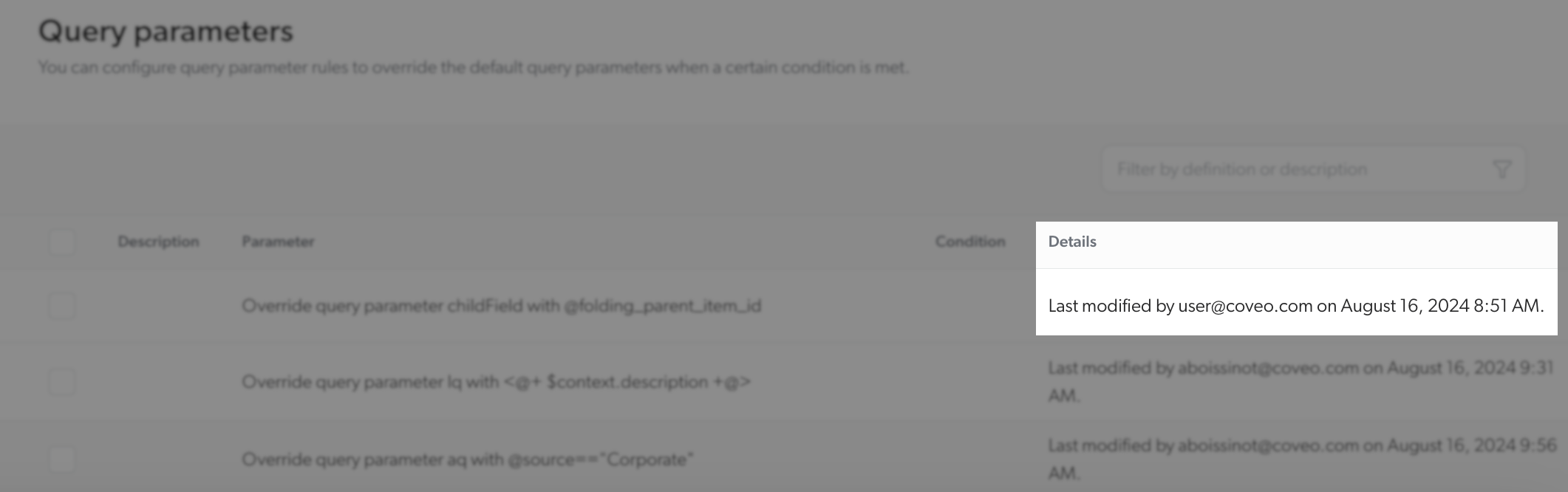
|
Duplicate query parameter rules
When creating query parameter rules in a query pipeline, you may want to create a new rule that’s similarly configured to an existing one. An efficient way to do this is to duplicate the existing rule and then modify it as needed.
-
In the Query parameters subtab, select each checkbox next to the rules you want to duplicate within the same pipeline.
-
In the Action bar, click Duplicate.
The duplicated query parameter rules appear at the bottom of the list in the pipeline component tab.
Copy query parameter rules to another pipeline
When you have more than one query pipeline that serve different purposes but require similar rules, you may want to copy query parameter rules from one pipeline to another.
-
In the Query parameters subtab, select each checkbox next to the rules you want to copy to another pipeline.
-
In the Action bar, click More, and then click Copy to.
-
In the dialog that appears, select the target pipeline to which you want to copy the rules, and then click Copy.
Delete query parameter rules
You can delete query parameter rules from a query pipeline.
-
In the Query parameters subtab, select each checkbox next to the rules you want to delete.
-
In the Action bar, click More, and then Delete.
-
Click Delete to confirm.
Change the rule order
Query pipeline rules are executed in the order in which they appear on the page until a condition is satisfied.
-
Select the checkbox next to the rule for which you want to change the position.
-
In the Action bar, click Move up or Move down to change the position of the rule.
Reference
The query parameters in this section can be modified when creating query parameter rules. For the list of query parameters that can be used when sending requests to the Search API, see Query parameters.
aq (advanced query expression)
The advanced query expression, typically generated by code (for example, when toggling facet values).
|
|
Note
When logging a usage analytics event for a query, the |
You want to avoid content from being filtered by a certain facet selection. The Source facet of your search interface contains the Tutorial video and Tutorial web facet values, which both lead to complementary content.
Therefore, you create a rule by doing the following:
-
In the aq (advanced query expression) field, you enter the following expression:
(@source=="Tutorial video" OR @source=="Tutorial web"). -
Under Condition, you create the condition:
Query contains Tutorial.
Child field
The @-prefixed name of the field to use to be able to identify an item as a child of another item in a folded query result.
Use a field whose value points to the Parent field value of the intended parent.
Whenever an item is a child of another item, its childField value must be identical to the parentField value of that other item.
|
|
Notes
|
Catalog ID
The unique identifier of the catalog entity to use for the query in a Coveo for Commerce solution.
cq (constant query expression)
The constant query expression, typically populated with expressions that must apply to all queries sent from a specific search interface (for example, from a specific tab). Once evaluated, the result sets of those expressions are kept in a special cache.
|
|
Avoid including dynamic content in the constant query expression. Otherwise you risk filling up the cache with useless data, which can have a negative impact on performance. |
|
|
Notes
|
When your employees perform queries, you want to show results that are internal. Therefore, you create a rule by doing the following:
-
In the cq (constant query expression) field, you enter
@targetAudience==internal. -
Under Condition, you create the condition:
Context[useGroup] is employee.
Debug
Whether to force a successful response to include debug information.
Default: false
|
|
Notes
|
dq (disjunction query expression)
The disjunction query expression, typically populated by Coveo ML ART models to ensure that relevant items are included in the query results.
This expression is merged with the other parts of the query expression using the OR operator.
Therefore, the resulting query expression is ((q AND aq) OR dq) AND cq.
For further information on query expressions, see Understanding the query expression.
|
|
This parameter overrides the generated disjunction query expression ( |
Enable Did You Mean
Whether to enable the Did You Mean feature of the index, which populates the queryCorrections property of a successful response with keyword correction suggestions.
Default: false
|
|
Notes
|
Enable duplicate filtering
Whether to filter out duplicates, so that items resembling one another only appear once in the query results.
Default: false
|
|
Notes
|
Enable ML Did You Mean
Whether to enable the Coveo ML query suggestions Did You Mean feature, which populates the queryCorrections property of a successful response with keyword correction suggestions.
Default: false
|
|
Notes
|
Enable query syntax
Whether to interpret advanced Coveo query syntax as such in the basic query expression (see the q (basic query expression and Lowercase operators parameters).
Default: true
|
|
Note
While the Enable query syntax parameter is set to |
-
After analyzing usage analytics data, you noticed that special characters such as
(,[,],{,},-, and&created content gaps. Therefore, you create a rule where you set the the Enable query syntax parameter tofalseso the index interprets those special characters as spaces. -
You want to ignore operators for your clients, but not for your internal users, so you set a condition on the identity. Therefore, you create a rule where you set the Enable query syntax parameter to
falseand under Condition, you create the condition:Identity is anonymous. -
You want to ignore all operators but still want to use
AND,OR, andNOT. Therefore, you create a rule where you set the Enable query syntax parameter tofalseand under Condition, you create the condition:Query doesn’t contain "and" or Query doesn’t contain "or" or Query doesn’t contain "not".
Enable term permutations
Whether to enable the term permutations feature in the query pipeline.
Default: false
When set to true, the term permutations feature expands the keywords used in the user query to search for different variations of the same query by using casing variations and character transitions.
In your Coveo index, you have support articles and user manuals that relate to the TP 213 v4 product.
You realize that your clients and support agents are often querying TP213v4 to find related information.
This results in some of your users not finding the information they’re looking for.
Therefore, you create a rule where you set the Enable term permutations parameter to true to ensure that all usage variations of TP213v4 are taken into account when queried.
Therefore, when searching for TP213v4, a user will obtain a query similar to the following:
TP213v4 OR ((TP 213 v4) OR (TP213 V4) OR (tp2 13 V4))|
|
The term permutations feature expands every keyword used in a query. Since each queried keyword is affected by the feature, this may lead to query performance issues. Therefore, this feature should only be used when necessary and under certain conditions. |
Excerpt length
The maximum length of result excerpts (in number of characters). An excerpt is a segmented text generated at query time by the index from the body of an item. When a query is performed, the excerpt yields relevant item body sections in which the queried terms are highlighted.
An excerpt includes the most relevant sentences in which the queried keywords appear, in the order in which they appear in the item, up to the specified number of characters.
Default: 200
|
|
Note
The maximum length you set using this parameter also applies to retrieved first sentences, if those are included in the results (see the Retrieve first sentences parameter). |
When your clients are on a specific tab, you want to show longer descriptions than in the other tabs. Therefore, you create a rule by doing the following:
-
In the Excerpt length field, you enter
500. -
Under Condition, you link create the condition:
Tab is Books.
Filter field
The @-prefixed name of the field to use to group items into distinct folded query results.
Use a field whose value is identical for all items to group under the same folded query result.
Filter field range
The maximum number of items to include in the childResults array of a folded query result.
Default: 5
Forward language to Coveo index
Controls whether the language of the user’s interface is used when interpreting the query.
Default: false
When set to true, the language of the user’s interface is included in the search request sent to the Coveo index.
This means that the interpretation and processing of the user’s query are influenced by their language setting, potentially enhancing the relevance of the returned search results.
It can be particularly useful for stem expansion.
|
|
This parameter should be used in combination with the |
If a user’s interface is in French and the Forward language to Coveo index parameter is set to true, the language information is included in the search request sent to the Coveo index.
French content is therefore prioritized in the search results, making the results more relevant to the user’s language preference.
Index
The identifier of the index mirror to forward the request to. If you don’t specify an index value, any index mirror could be used.
|
|
Note
Passing an |
Locale
The locale of the current user. Must comply with IETF’s BCP 47 definition.
Coveo ML models use this information to provide contextually relevant output.
Moreover, this information can be referred to in query expressions and QPL statements by using the $locale object.
|
|
Note
When logging a usage analytics event, the |
Logical index
The identifier for a logical group of indexes that have been configured to include items from the same sources.
If you don’t specify a logicalIndex value, the default grouping will be used, typically including all indexes.
Default: default
Logical index aggregation
Whether to aggregate the results from all indexes in the logical index group.
Lowercase operators
Whether to treat the AND, NEAR, NOT, and OR keywords in the basic query expression (see the q parameter) as Coveo query syntax operators, even if those keywords are in lowercase.
|
|
Note
Setting this parameter to |
Default: false
You want to allow customer to use the AND and OR operators even if they write them in lowercase.
When you ignore the operators, where the Enable query syntax is set to false, you must add a rule to exclude AND and OR, otherwise the operators won’t be considered.
Therefore, you create a rule where to set the Lowercase operators parameter to true.
lq (large query expression)
The large query expression, typically populated with a case description, long textual query, or any other form of text that can help refine a query.
The Coveo ML Intelligent Term Detection (ITD) feature can extract relevant keywords from the large query expression and inject those keywords in the basic query expression (see the q parameter).
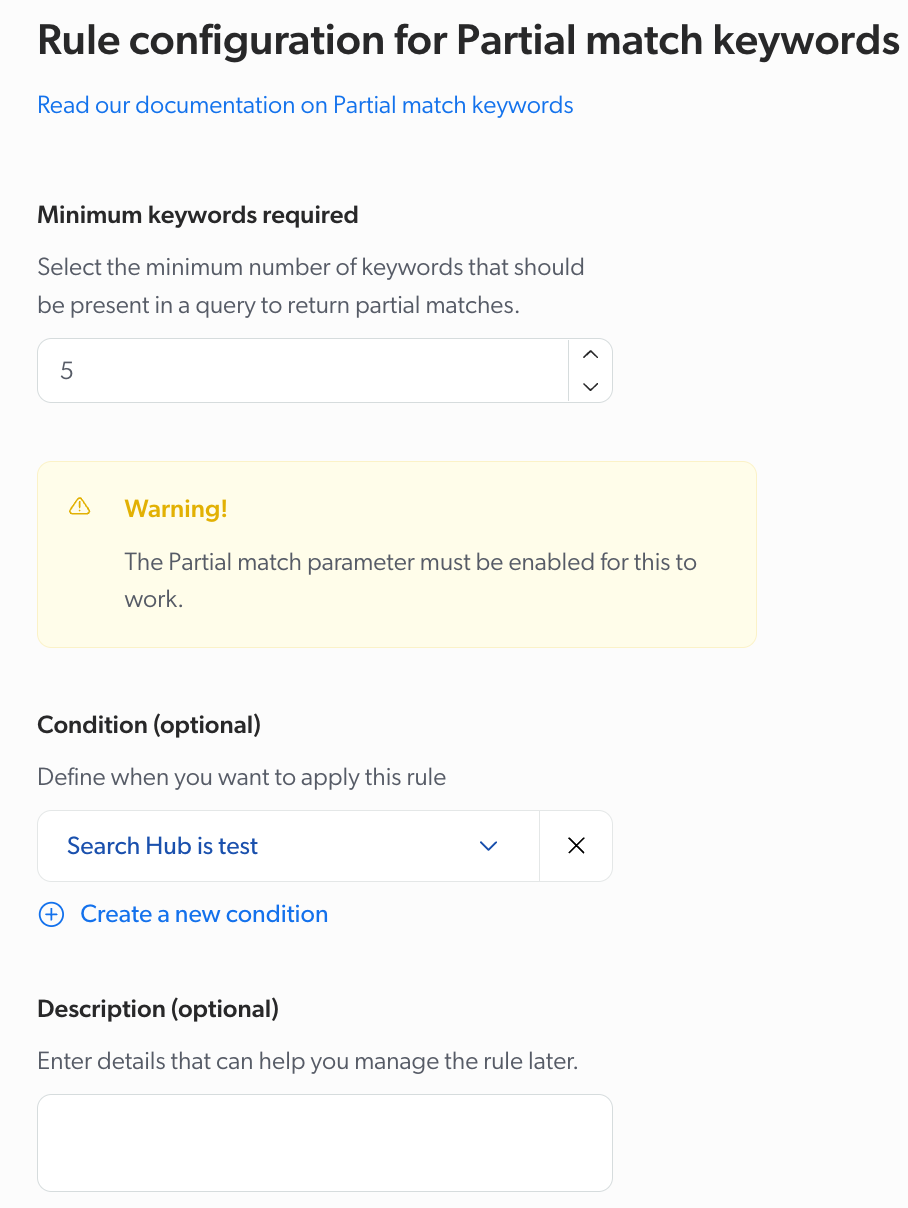
lq Partial match keywords
The minimum number of keywords that need to be present in the lq (large query expression) to convert it to a partial match expression in case the Coveo ML Intelligent Term Detection (ITD) feature can’t extract relevant keywords from the large query expression. For further information on query expressions, see Understanding the query expression.
Default: 5
|
|
Note
This parameter applies as a fallback setting when no Coveo ML ART model is available in the query pipeline to process a query that contains a non-null large query expression ( |
lq Partial match max keywords
The maximum number of keywords from the large query expression (see the lq parameter) that will be included in the partial match expression in case the Coveo ML Intelligent Term Detection (ITD) feature can’t extract relevant keywords from the large query expression.
Default: 100
|
|
Notes
|
lq Partial match threshold
An absolute or relative value indicating the minimum number of partial match expression keywords an item must contain to match the large query expression in case the Coveo ML Intelligent Term Detection (ITD) feature can’t extract relevant keywords from the large query expression.
Default: 50%
If specified, the lq Partial match threshold parameter value must be one of the following:
-
a 32-bit unsigned integer (for example,
3) -
a percentage value between 0% and 100% (for example,
75%) -
an empty string (
"") -
the
allstring
|
|
Notes
|
Maximum age
The maximum age (in milliseconds) of the cached query results.
If the results of a specific request are available in the cache, and if those results are no older than the maximumAge value, the service returns those results rather than forwarding a new query to the index.
Such cache hits improve responsiveness but still count as queries in your queries per month (QPM) count.
Default: -1
|
|
Note
This parameter is automatically overridden when |
Maximum timeout
The maximum time (in milliseconds) limit for the query to execute before timing out.
ML Did You Mean max candidates
The maximum number of Coveo ML Did You Mean candidates to request from the QS model.
Default: 3
ML Did You Mean min score
The minimum score a query suggestion may have to be allowed as a candidate for the Coveo ML query suggestions Did You Mean feature.
For best results, value should typically be in range [0.8, 2].
Default: 1.0
ML Did You Mean use facet count
Whether to use facet counts for the Coveo ML Did You Mean feature.
Default: false
Number of results
The number of results to return.
Along with the firstResult parameter, this allows you to retrieve a specific page of result items.
This parameter also defines the maximum number of results which can be returned by the Coveo ML Content Recommendations (CR) and Product Recommendations (PR) features.
Default: 10
|
|
Note
The maximum |
|
|
Don’t set this parameter in the query pipeline if your search interface contains a |
When your clients search for find a store, you’ll want the results returned to only be the articles that help them find stores.
You also need a featured result rule on that specific article for the same query.
Therefore, you create a rule by entering 1 in the Number of results field to ensure that only the most relevant article is returned.
Parent field
The @-prefixed name of the field to use to be able to identify an item as a parent in a folded query result.
Use a field whose value can uniquely identify each item.
All items whose childField value is identical to the parentField value of another item are considered children of that other item.
|
|
Notes
|
Partial match
Whether to convert a basic expression containing certain keywords to a partial match expression, so that any item containing a specific amount of those keywords will match the expression.
If you don’t set this parameter to true, an item must contain all the basic expression keywords to match the expression.
See Taking advantage of the partial match feature to learn how to leverage this feature.
Default: false
|
|
Notes
|
q (basic query expression)
The basic query expression, typically the keywords entered by the end user in a query box. For further information on query expressions, see Understanding the query expression.
|
|
Note
When logging a usage analytics event for a query, the |
|
|
This parameter overrides the query expression that the user enters in the search box. Therefore, it’s strongly recommended to add a condition for your rule to be applied. |
Query correction
Whether to enable the Query correction feature. You can choose whether the feature suggests alternatives or automatically applies keyword corrections to the query expression.
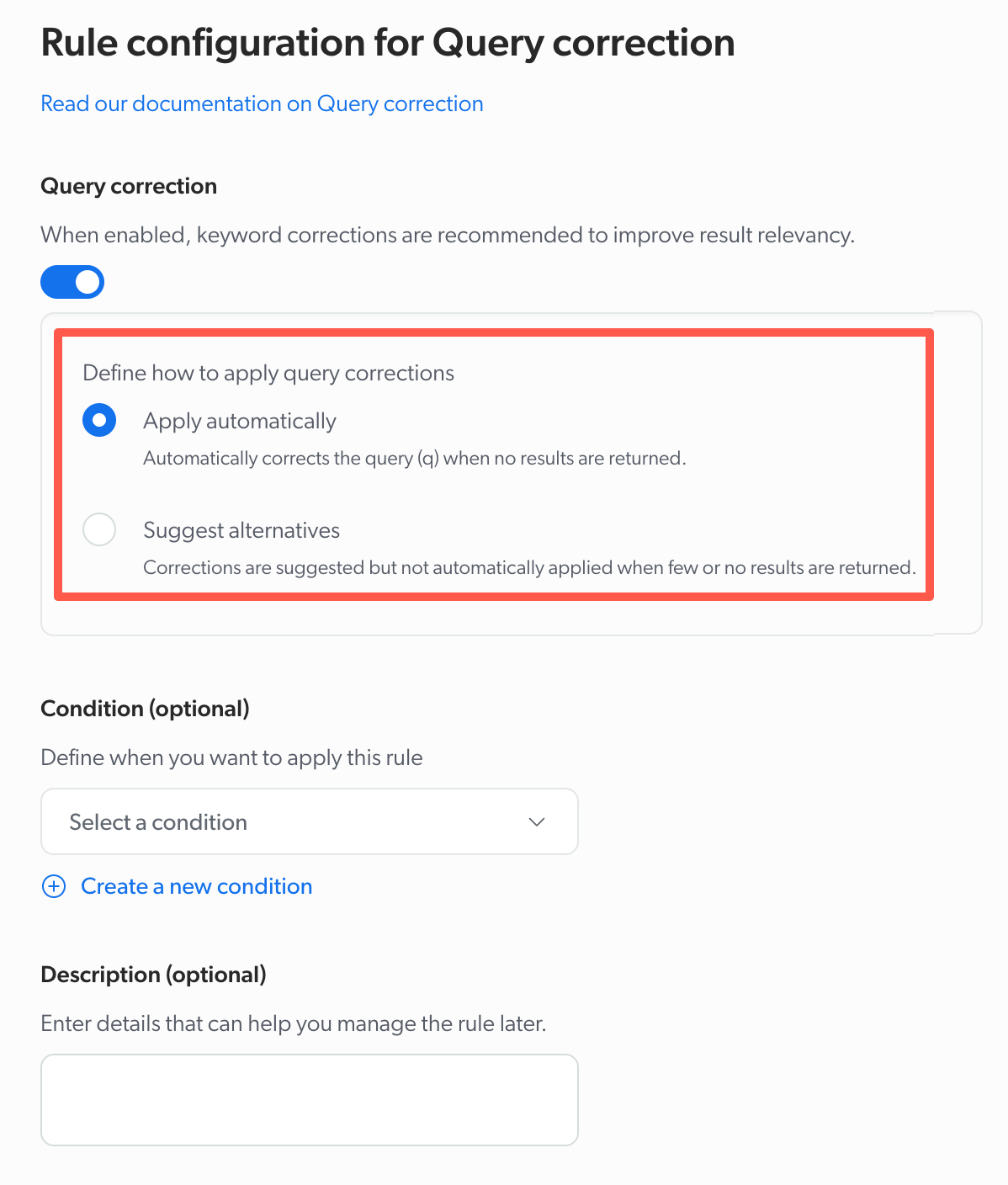
A user is trying to find books by the author Michael Crichton, but they misspell the author’s name as Michael Crighton.
Since the Query correction parameter is enabled, the name is automatically corrected to Michael Crichton, and the user is presented with the correct results.
Question mark
Whether to enable the question mark character (?) in the wildcard feature of the index to expand basic expression keywords (see the q parameter) containing the question mark character (?) to the possible matching keywords.
See Using wildcards in queries for the complete parameter definition.
Default: false
|
|
Note
Setting this parameter to |
You want to allow clients to use the ? wildcard, especially since you set operators to be ignored (Enable query syntax is set to false).
You also set the Wildcards parameter to true, which is required for the questionMark parameter to be effective.
Therefore, you create a rule where you set the Question mark parameter to true.
Recommendation
The recommendation interface identifier from which the query originates.
Retrieve first sentences
Whether to include the first sentences of textual items in the query results.
First sentences are typically useful when rendering result items such as emails, since the first few sentences of these kinds of items are often more relevant than a contextually generated excerpt (see the Excerpt length parameter).
Default: false
|
|
Note
The maximum length of the retrieved sentences (in number of characters) is determined by the value of the |
You want to always show the first sentence of items.
This sentence will be truncated if longer than the excerpt.
If the sentence is short (for example, title of an email), the rest of the normal excerpt will be shown until the excerptLength is reached.
Therefore, you create a rule by doing the following:
-
You set the Retrieve first sentences parameter to
true. -
Under Condition, you create the condition:
Query is Email.
Search hub
The first level of origin of the request, typically the identifier of the graphical search interface from which the request originates. Coveo ML models use this information to provide contextually relevant output.
|
|
Notes
|
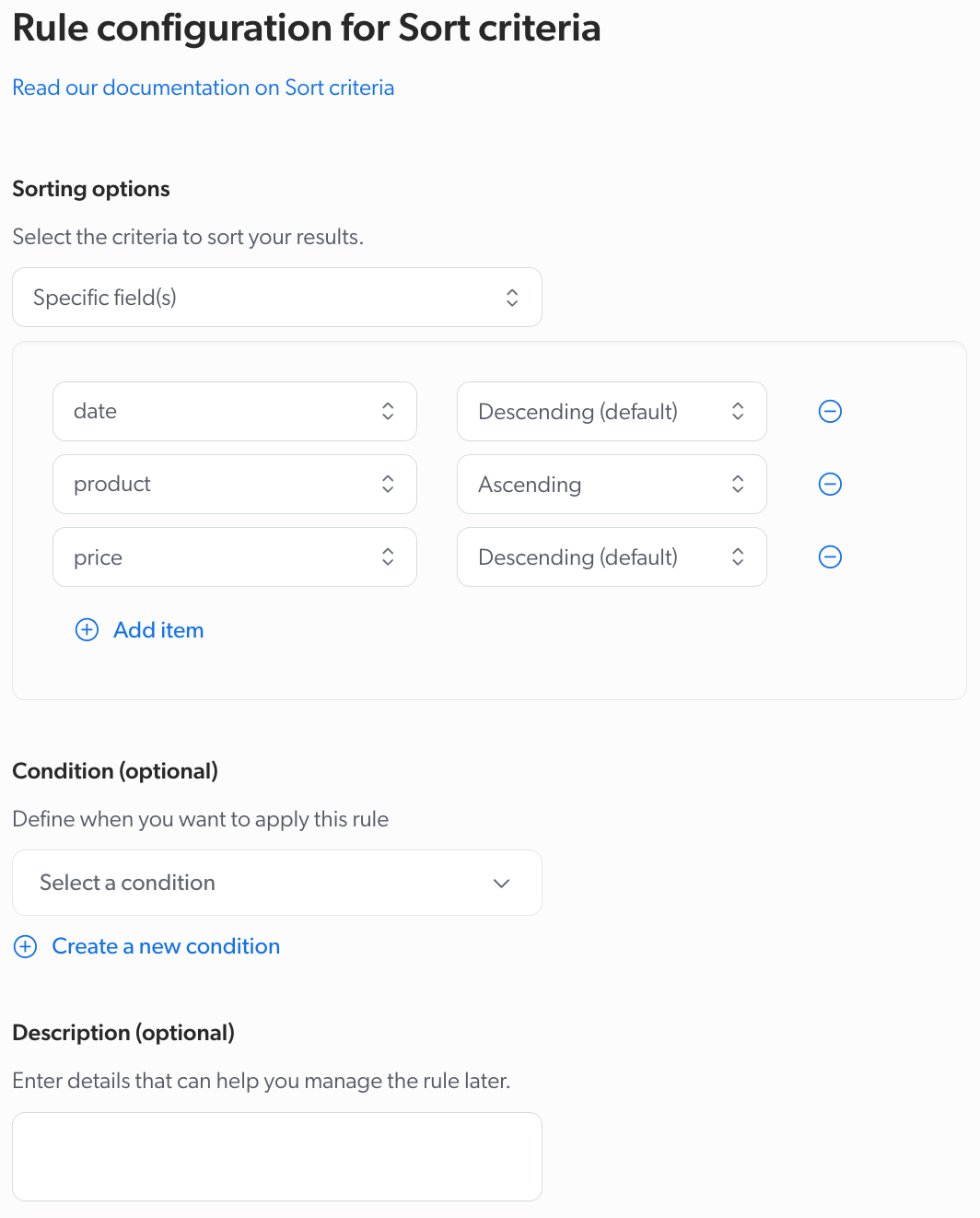
Sort criteria
The criteria to use for sorting the query results. Allowed values:
-
Relevance (default): Uses standard index ranking factors (adjacency, TDIDF, etc.) and custom ranking expressions (QREs and QRFs) to compute a ranking score for each query result item, and sorts the query results by descending score value.
ExampleYou’re managing a knowledge base for new employees. By selecting Relevance, you ensure that content such as training materials and onboarding guides are displayed at the top of the search results while still considering other factors such as the number of views and the last modified date.
-
Ranking expression: Uses only custom ranking expressions (QREs and QRFs) to compute a ranking score for each query result item, and sorts the query results by descending score value.
ExampleYour e-commerce site, Barca Sport, carries a collection of premium soccer cleats that you want to promote. You’ve already created a ranking expression rule that boosts the score of this item by
100. By selecting Ranking expression as the sort criteria, you ensure that other ranking factors are ignored, and that the premium soccer cleats are displayed at the top of the search results. -
No sort: Doesn’t apply any specific sorting logic to the query results. Items are returned in an order determined by the index’s internal system, which isn’t based on specific criteria such as date or relevance.
ExampleYour company’s intranet includes a collection of announcements. By selecting No Sort, results are displayed as they are retrieved by the index, without applying any specific sorting logic. This can be useful for a query like "latest announcements," where you want to see the announcements as they exist in the system, without additional ordering applied.
-
Specific fields: Sort using the value of a specific sortable field.
ExampleYour e-commerce site, Barca Sport, offers a wide range of products. When setting the Sort criteria, you select Specific fields, first by selecting
datein descending order (showing the newest items first), and thenproductin ascending order (alphabetically organizing products with the same release date).For a query like
running shoes, the newest shoes are displayed first. If multiple shoes were added on the same date, they’re listed alphabetically.
|
|
Notes
|
Summary length
The length of the automatically generated item summary. The Coveo Platform uses a linguistic algorithm that relies on term frequency and proximity to generate an item summary made of sentences identified to be the most important ones in the item. This summary is generated independently from the query, as opposed to a result item excerpt, which is generated based on query keywords.
Default: 0
Tab
The second level of origin of the request, typically the identifier of the selected tab in the graphical search interface from which the request originates. Coveo ML models use this information to provide contextually relevant output.
|
|
Note
When logging a usage analytics event for a query, the |
Wildcards
Whether to enable the wildcards feature of the index in order to expand basic expression keywords (see the q parameter) containing wildcard characters (*) to the possible matching keywords (see Using wildcards in queries).
Default: false
You want to allow your clients to use wildcards, especially since you create a rule where the Enabled query syntax parameter is set to false.
Therefore, you create a rule where you set the Wildcards parameter to true.
QPL syntax
Use the following query pipeline language (QPL) syntax to define a statement expressing the queryParamOverride feature:
override <query | querySuggest> <queryParameterOverrides><query | querySuggest>
This is one of the two options:
-
query: modifies parameters in search requests (that is, inGETorPOSTrequests to the/rest/search/v2route). -
querySuggest: modifies parameters in query suggestion requests (that is, inGETorPOSTrequests to the/rest/search/v2/querySuggestroute).
<queryParameterOverrides>
A comma-separated list of parameter-value pairs, where each parameter is a valid query/query suggestion parameter and each value must be a valid value for the specified query/query suggestion parameter (see Query parameters).
Order of execution
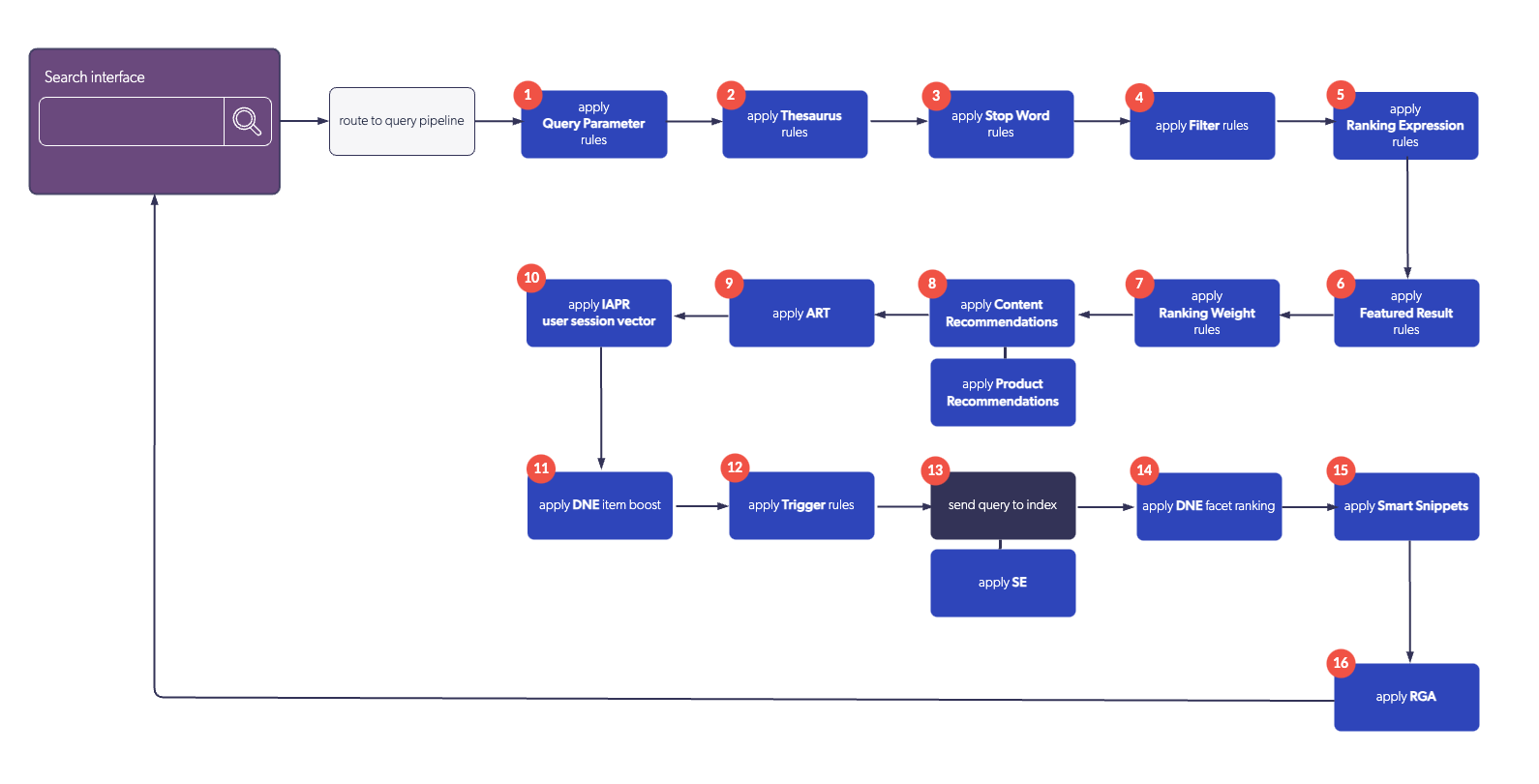
The following diagram illustrates the overall order of execution of query pipeline features:
Required privileges
By default, members with the required privileges can view and edit elements of the Query Pipelines (platform-ca | platform-eu | platform-au) page.
The following table indicates the required privileges for members to view or edit query parameter rules (see Manage privileges and Privilege reference).
| Action | Service - Domain | Required access level |
|---|---|---|
View query parameter rules |
Organization - Organization |
View |
Edit query parameter rules |
Organization - Organization |
View |
Search - Query pipelines |
Edit |