QueryParamOverride: Query pipeline feature
QueryParamOverride: Query pipeline feature
A query pipeline statement expressing the queryParamOverride query pipeline feature modifies query parameter values before the search (or Coveo Machine Learning (Coveo ML) Query Suggestion (QS)) request is processed any further by the Search API.
|
|
Leading practice
Typically, a statement expressing the In general, you should ensure that this is the case by associating such a statement, and/or the query pipeline it’s defined in, to a global condition. |
|
|
Note
In the Coveo Administration Console, you can manage statements expressing the |
The following diagram shows the process of a query being sent to the Search API and the order of execution of query pipeline features.

Syntax
Use the following query pipeline language (QPL) syntax to define a statement expressing the queryParamOverride feature:
override <query | querySuggest> <queryParameterOverrides>|
|
Note
An override statement can modify only one query parameter at a time.
Adding multiple parameters in a single statement will result in an error, such as:
|
<query | querySuggest>
This is one of the two options:
-
query: modifies parameters in search requests (that is, inGETorPOSTrequests to the/rest/search/v2route). -
querySuggest: modifies parameters in query suggestion requests (that is, inGETorPOSTrequests to the/rest/search/v2/querySuggestroute).
<queryParameterOverrides>
A parameter-value pair where the parameter is a valid query or query suggestion parameter, and the value is a valid input for that parameter (see Query parameters). Only one parameter-value combination is supported per override statement.
Example
You create a global condition with the following QPL definition:
Global condition:
when $context[userRole] is "powerUser"In an empty query pipeline named Testing override, you create four distinct statements, each expressing the queryParamOverride feature, with the following QPL definitions:
Statement 1
override querySuggest enableWordCompletion: trueStatement 2
override querySuggest count: 3Statement 3
override query enableQuerySyntax: trueStatement 4
override query wildcards: trueYou associate these statements to the global condition statement you created before.
In a graphical search interface, an end user types in a search box which has been configured to provide Coveo Machine Learning (Coveo ML) query completion suggestions, causing a querySuggest request to be sent with a partial basic query expression (q) to the Search API on each new keystroke:
querySuggest payload
{
"q": "query pip",
"context": {
"userRole": "powerUser"
}
}Since the query suggestion operation goes through the Testing Override query pipeline and satisfies the global condition, the querySuggest override statement is applied.
As a result the following things happen:
-
The query suggestions are ordered by which suggestion best completes the last word being typed by the end user in the search box (because of
enableWordCompletion: true). -
A maximum of three query completion suggestions is returned (because of
count: 3).
|
|
Successful response - 200 OK |
The end user ignores the query completion suggestions, and finally inputs an expression which includes a wildcard character (*) and advanced query syntax (@source==docs.coveo.com) before submitting the query:
Query payload
{
"context": {
"userRole": "powerUser"
},
"q": "query pip* @source==docs.coveo.com"
}Since the query goes through the Testing Override query pipeline and satisfies the global condition, the query override statement is applied.
As a result the following things happen:
-
The index only return items whose
@sourcefield value is equal todocs.coveo.com(because ofenableQuerySyntax: true). -
The index only return items whose content includes both the
querykeyword and a keyword that starts withpip(because ofwildcards: true).
Reference
The query parameters in this section can be modified when creating query parameter rules. For the list of query parameters that can be used when sending requests to the Search API, see Query parameters.
aq (string)
The advanced query expression, typically generated by code, such as when toggling facet values.
|
|
Note
When logging a usage analytics event for a query, the |
-
You want to ignore existing advanced queries containing a query ranking expression (QRE).
-
Parameter type to override:
Query -
Parameter name:
aq -
Parameter value type:
String -
Parameter value:
-
Condition:
Advanced query contains QRE(see Create a condition)
-
-
You want to avoid content from being filtered by a certain facet selection. The Source facet of your search interface contains the Tutorial video and Tutorial web facet values, which both lead to complementary content.
-
Parameter type to override:
Query -
Parameter name:
aq -
Parameter value type:
String -
Parameter value:
(@source=="Tutorial video" OR @source=="Tutorial web") -
Condition:
Query contains Tutorial(see Create a condition)
-
childField (string)
The @-prefixed name of the field to use to be able to identify an item as a child of another item in a folded query result.
Use a field whose value points to the parentField value of the intended parent.
Whenever an item is a child of another item, its childField value must be identical to the parentField value of that other item.
|
|
Notes
|
commerce.catalogId (string)
The unique identifier of the catalog entity to use for the query in a Coveo for Commerce solution.
cq (string)
The constant query expression, typically populated with expressions that must apply to all queries sent from a specific search interface (for example, from a specific tab). Once evaluated, the result sets of those expressions are kept in a special cache.
|
|
Avoid including dynamic content in the constant query expression. Otherwise you risk filling up the cache with useless data, which can have a negative impact on performance. |
|
|
Notes
|
When your employees perform queries, you want to show results that are internal.
-
Parameter type to override:
Query -
Parameter name:
cq -
Parameter value type:
String -
Parameter value:
@targetAudience==internal -
Condition (see Create a condition):
-
Context -
Key:
userGroup -
Value:
employee
-
debug (boolean)
Whether to force a successful response to include debug information.
Default: false
|
|
Notes
|
dq (string)
The disjunction query expression, typically populated by Coveo ML ART models to ensure that relevant items are included in the query results.
This expression is merged with the other parts of the query expression using the OR operator.
Therefore, the resulting query expression is ((q AND aq) OR dq) AND cq.
For further information on query expressions, see Understanding the query expression.
|
|
This parameter overrides the generated disjunction query expression ( |
enableDidYouMean (boolean)
Whether to enable the Did You Mean feature of the index, which populates the queryCorrections property of a successful response with keyword correction suggestions.
Default: false
|
|
Notes
|
enableDuplicateFiltering (boolean)
Whether to filter out duplicates, so that items resembling one another only appear once in the query results.
Default: false
|
|
Notes
|
enableMLDidYouMean (boolean)
|
|
This feature is in an experimental state. |
Whether to enable the Coveo ML query suggestions Did You Mean feature, which populates the queryCorrections property of a successful response with keyword correction suggestions.
Default: false
|
|
Notes
|
enableQuerySyntax (boolean)
Whether to interpret advanced Coveo query syntax as such in the basic query expression (see the q and lowercaseOperators parameters).
Default: true
|
|
Note
While the |
-
After analyzing usage analytics data, you noticed that special characters such as
(,[,],{,},-, and&created content gaps. Therefore, you setenableQuerySyntaxtofalseso the index interprets those special characters as spaces.-
Parameter type to override:
Query -
Parameter name:
enableQuerySyntax -
Parameter value type:
Boolean -
Parameter value:
false
-
-
You want to ignore operators for your clients, but not for your internal users, so you set a condition on the identity.
-
Parameter type to override:
Query -
Parameter name:
enableQuerySyntax -
Parameter value type:
Boolean -
Parameter value:
false -
Condition:
Identity is anonymous(see Create a condition)
-
-
You want to ignore all operators but still want to use
AND,OR, andNOT, so you can add a condition that ignores the rule if the operator is in the query.-
Parameter type to override:
Query -
Parameter name:
enableQuerySyntax -
Parameter value type:
Boolean -
Parameter value:
false -
Condition:
Query doesn’t contain "and" or Query doesn’t contain "or" or Query doesn’t contain "not"(see Create a condition)
-
Enable term permutations
Whether to enable the term permutations feature in the query pipeline.
Default: false
When set to true, the term permutations feature expands the keywords used in the user query to search for different variations of the same query by using casing variations and character transitions.
In your Coveo index, you have support articles and user manuals that relate to the TP 213 v4 product.
You realize that your clients and support agents are often querying TP213v4 to find related information.
This results in some of your users not finding the information they’re looking for.
By setting the Enable term permutations parameter to true, you ensure that all usage variations of TP213v4 are taken into account when queried.
Therefore, when searching for TP213v4, a user will obtain a query similar to the following:
TP213v4 OR ((TP 213 v4) OR (TP213 V4) OR (tp2 13 V4))|
|
The term permutations feature expands every keyword used in a query. Since each queried keyword is affected by the feature, this may lead to query performance issues. Therefore, this feature should only be used when necessary and under certain conditions. |
Excerpt length
The maximum length of result excerpts (in number of characters). An excerpt is a segmented text generated at query time by the index from the body of an item. When a query is performed, the excerpt yields relevant item body sections in which the queried terms are highlighted.
An excerpt includes the most relevant sentences in which the queried keywords appear, in the order in which they appear in the item, up to the specified number of characters.
Default: 200
|
|
Note
The maximum length you set using this parameter also applies to retrieved first sentences, if those are included in the results (see the |
When your clients are on a specific tab, you want to show longer descriptions than in the other tabs.
-
Parameter type to override:
Query -
Parameter name:
excerptLength -
Parameter value type:
Number -
Parameter value:
500 -
Condition:
Tab is Books(see Create a condition)
Filter field
The @-prefixed name of the field to use to group items into distinct folded query results.
Use a field whose value is identical for all items to group under the same folded query result.
filterFieldRange (integer [int32])
The maximum number of items to include in the childResults array of a folded query result.
Default: 5
firstResult (integer [int32])
The 0-based position of the first result to return in the non-paginated result set.
Along with the numberOfResults parameter, this allows you to retrieve a specific page of result items.
Default: 0
forwardLanguageToCoveoIndex (boolean)
Controls whether the language of the user’s interface is used when interpreting the query.
Default: false
When set to true, the language of the user’s interface is included in the search request sent to the Coveo index.
This means that the interpretation and processing of the user’s query are influenced by their language setting, potentially enhancing the relevance of the returned search results.
It can be particularly useful for stem expansion.
|
|
This parameter should be used in combination with the |
If a user’s interface is in French and forwardLanguageToCoveoIndex is set to true, the language information is included in the search request sent to the Coveo index.
French content is therefore prioritized in the search results, making the results more relevant to the user’s language preference.
index (string)
The identifier of the index mirror to forward the request to.
If you don’t specify an index (or #indextoken-string[indexToken]) value, any index mirror could be used.
|
|
Note
Passing an |
indexToken (string)
The identifier of the index mirror to forward the request to.
If you don’t specify an indexToken (or index) value, any index mirror could be used.
|
|
Note
Passing an |
isGuestUser (boolean)
Whether the current user is anonymous. Coveo ML models may use this information to provide contextually relevant output.
|
|
Note
When logging a usage analytics event for a query, the |
locale (string)
The locale of the current user. Must comply with IETF’s BCP 47 definition.
Coveo ML models use this information to provide contextually relevant output.
Moreover, this information can be referred to in query expressions and QPL statements by using the $locale object.
|
|
Note
When logging a usage analytics event, the |
logicalIndex (string)
The identifier for a logical group of indexes that have been configured to include items from the same sources.
If you don’t specify a logicalIndex value, the default grouping will be used, typically including all indexes.
Default: "default"
lowercaseOperators (boolean)
Whether to treat the AND, NEAR, NOT, and OR keywords in the basic query expression (see the q parameter) as Coveo query syntax operators, even if those keywords are in lowercase.
|
|
Note
Setting this parameter to |
Default: false
You want to allow customer to use the AND and OR operators even if they write them in lowercase.
When you ignore the operators (enableQuerySyntax set to false), you must add a condition to exclude AND and OR.
Otherwise, operators won’t be considered.
-
Parameter type to override:
Query -
Parameter name:
lowercaseOperators -
Parameter value type:
Boolean -
Parameter value:
true
lq (string)
The large query expression, typically populated with a case description, long textual query, or any other form of text that can help refine a query.
The Coveo ML Intelligent Term Detection (ITD) feature can extract relevant keywords from the large query expression and inject those keywords in the basic query expression (see the q parameter).
lqPartialMatchKeywords (integer [int32])
The minimum number of keywords that need to be present in the large query expression (see the lq parameter) to convert it to a partial match expression in case the Coveo ML Intelligent Term Detection (ITD) feature can’t extract relevant keywords from the large query expression.
For further information on query expressions, see Understanding the query expression.
Default: 5
|
|
Note
This parameter applies as a fallback setting when no Coveo ML ART model is available in the query pipeline to process a query that contains a non-null large query expression ( |
lqPartialMatchMaxKeywords (integer [int32])
The maximum number of keywords from the large query expression (see the lq parameter) that will be included in the partial match expression in case the Coveo ML Intelligent Term Detection (ITD) feature can’t extract relevant keywords from the large query expression.
Default: 100
|
|
Notes
|
lqPartialMatchThreshold (string)
An absolute or relative value indicating the minimum number of partial match expression keywords an item must contain to match the large query expression in case the Coveo ML Intelligent Term Detection (ITD) feature can’t extract relevant keywords from the large query expression.
Default: 50%
If specified, the lqPartialMatchThreshold value must be one of the following:
-
A 32-bit unsigned integer (for example,
3) -
A percentage value between 0% and 100% (for example,
75%) -
An empty string (
"") -
The
allstring
|
|
Notes
|
maximumAge (integer [int32])
The maximum age (in milliseconds) of the cached query results.
If the results of a specific request are available in the cache, and if those results are no older than the maximumAge value, the service returns those results rather than forwarding a new query to the index.
Such cache hits improve responsiveness but still count as queries in your queries per month (QPM) count.
Default: -1
|
|
Note
This parameter is automatically overridden when |
maximumTimeoutMs (integer [int32])
The maximum time (in milliseconds) limit for the query to execute before timing out.
mlDidYouMeanMaxCandidates (integer [int32])
The maximum number of Coveo ML Did You Mean candidates to request from the QS model.
Default: 3
mlDidYouMeanMinScore (number [double])
The minimum score a query suggestion may have to be allowed as a candidate for the Coveo ML query suggestions Did You Mean feature.
For best results, value should typically be in range [0.8, 2].
Default: 1.0
mlDidYouMeanUseFacetCount (boolean)
Whether to use facet counts for the Coveo ML Did You Mean feature.
Default: false
numberOfResults (integer [int32])
The number of results to return.
Along with the firstResult parameter, this allows you to retrieve a specific page of result items.
This parameter also defines the maximum number of results which can be returned by the Coveo ML Content Recommendations (CR) and Product Recommendations (PR) features.
Default: 10
|
|
Note
The maximum |
|
|
Don’t set this parameter in the query pipeline if your search interface contains a |
When your clients search find a store, you’ll want the results returned to only be the articles that help them find stores.
You also need a featured result rule on that specific article for the same query (see Manage featured result rules).
-
Parameter type to override:
Query -
Parameter name:
numberOfResults -
Parameter value type:
String -
Parameter value:
1
parentField (string)
The @-prefixed name of the field to use to be able to identify an item as a parent in a folded query result.
Use a field whose value can uniquely identify each item.
All items whose childField` value is identical to the parentField value of another item are considered children of that other item.
|
|
Notes
|
partialMatch (boolean)
Whether to convert a basic expression containing at least partialMatchKeywords to a partial match expression, so that any item containing at least partialMatchThreshold of those keywords will match the expression.
If you don’t set this parameter to true, an item must contain all the basic expression keywords to match the expression.
See Taking advantage of the partial match feature to learn how to leverage this feature.
Default: false
|
|
Notes
|
partialMatchKeywords (integer [int32])
The minimum number of keywords that needs to be present in a basic expression to convert it to a partial match expression.
Default: 5
|
|
Notes
|
See Taking advantage of the partial match feature to learn how to leverage this feature.
partialMatchThreshold (string)
An absolute or relative value indicating the minimum number (rounded up) of partial match expression keywords an item must contain to match the expression.
If specified, the partialMatchThreshold value must be either of the following:
-
A 32-bits unsigned integer (for example,
3) -
A percentage value between 0% and 100% (for example,
75%) -
The empty string (
"") -
The
allstring
Default: 50%
|
|
Notes
|
See Taking advantage of the partial match feature to learn how to leverage this feature.
q (string)
The basic query expression, typically the keywords entered by the end user in a query box. For further information on query expressions, see Understanding the query expression.
|
|
Note
When logging a usage analytics event for a query, the |
|
|
This parameter overrides the query expression that the user enters in the search box. Therefore, it’s strongly recommended to add a condition for your rule to be applied. |
queryCorrection.enabled (boolean)
Whether to enable the Query correction feature to correct misspelled keywords or to suggest alternatives.
queryCorrection.options.automaticallyCorrect (string)
Whether to automatically apply or suggest keyword corrections to the query expression.
|
|
Note
The |
questionMark (boolean)
Whether to enable the question mark character (?) in the wildcard feature of the index to expand basic expression keywords (see the q parameter) containing the question mark character (?) to the possible matching keywords.
See Using wildcards in queries for the complete parameter definition.
Default: false
|
|
Note
Setting this parameter to |
You want to allow clients to use the ? wildcard, especially since you set operators to be ignored (enableQuerySyntax is set to false).
You also set the wildcards parameter to true, which is required for the questionMark parameter to be effective.
-
Parameter type to override:
Query -
Parameter name:
questionMark -
Parameter value type:
Boolean -
Parameter value:
true
recommendation (string)
The recommendation interface identifier from which the query originates.
retrieveFirstSentences (boolean)
Whether to include the first sentences of textual items in the query results.
First sentences are typically useful when rendering result items such as emails, since the first few sentences of these kinds of items are often more relevant than a contextually generated excerpt (see the excerptLength parameter).
Default: false
|
|
Note
The maximum length of the retrieved sentences (in number of characters) is determined by the value of the |
You want to always show the first sentence of items.
This sentence will be truncated if longer than the excerpt.
If the sentence is short (for example, title of an email), the rest of the normal excerpt will be shown until the excerptLength is reached.
-
Parameter type to override:
Query -
Parameter name:
retrieveFirstSentences -
Parameter value type:
Boolean -
Parameter value:
true -
Condition:
Query is Bulletin(see Create a condition)
searchHub (string)
The first level of origin of the request, typically the identifier of the graphical search interface from which the request originates. Coveo ML models use this information to provide contextually relevant output.
|
|
Notes
|
sortCriteria (string)
The criteria to use for sorting the query results. Allowed values:
-
Relevance (default): Uses standard index ranking factors (adjacency, TDIDF, etc.) and custom ranking expressions (QREs and QRFs) to compute a ranking score for each query result item, and sorts the query results by descending score value.
ExampleYou’re managing a knowledge base for new employees. By selecting Relevance, you ensure that content such as training materials and onboarding guides are displayed at the top of the search results while still considering other factors such as the number of views and the last modified date.
-
Ranking expression: Uses only custom ranking expressions (QREs and QRFs) to compute a ranking score for each query result item, and sorts the query results by descending score value.
ExampleYour e-commerce site, Barca Sport, carries a collection of premium soccer cleats that you want to promote. You’ve already created a ranking expression rule that boosts the score of this item by
100. By selecting Ranking expression as the sort criteria, you ensure that other ranking factors are ignored, and that the premium soccer cleats are displayed at the top of the search results. -
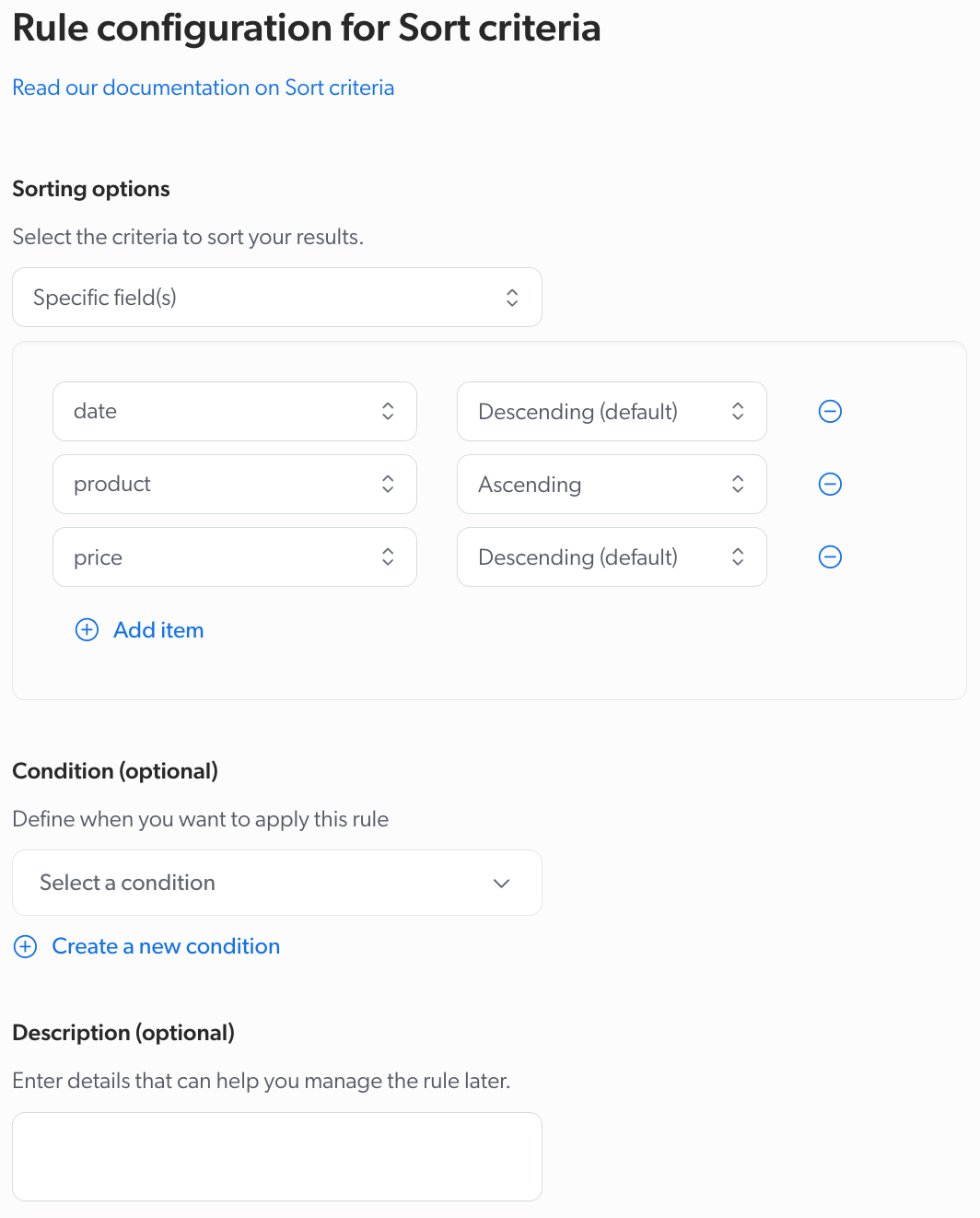
Specific fields: Sort using the value of a specific sortable field.
ExampleYour e-commerce site, Barca Sport, offers a wide range of products. When setting the Sort criteria, you select Specific fields, first by selecting
datein descending order (showing the newest items first), and thenproductin ascending order (alphabetically organizing products with the same release date).For a query like
running shoes, the newest shoes are displayed first. If multiple shoes were added on the same date, they’re listed alphabetically.
|
|
Notes
|
staticQuery (boolean)
Whether to execute this query in a way that doesn’t count against the allowed number of queries per month (QPM) of a Coveo organization, but may produce cached or outdated query results (see Rendering static content using persistent queries).
Default: false
|
|
Note
Setting this parameter to |
summaryLength (integer [int32])
The length of the automatically generated item summary. The Coveo Platform uses a linguistic algorithm that relies on term frequency and proximity to generate an item summary made of sentences identified to be the most important ones in the item. This summary is generated independently from the query, as opposed to a result item excerpt, which is generated based on query keywords.
Default: 0
tab (string)
The second level of origin of the request, typically the identifier of the selected tab in the graphical search interface from which the request originates. Coveo ML models use this information to provide contextually relevant output.
|
|
Note
When logging a usage analytics event for a query, the |
wildcards (boolean)
Whether to enable the wildcards feature of the index in order to expand basic expression keywords (see the q parameter) containing wildcard characters (*) to the possible matching keywords (see Using wildcards in queries).
Default: false
You want to allow your clients to use wildcards (*, ?), especially since you set operators to be ignored (enableQuerySyntax set to false).
-
Parameter type to override:
Query -
Parameter name:
wildcards -
Parameter value type:
Boolean -
Parameter value:
true
Query Suggest parameters
The Query Suggest parameters listed in this section are those that can be defined in the Swagger UI when you use the Query Suggest endpoint. For the complete list of available query parameters, see QS parameters.
debug (boolean)
See debug for the complete parameter definition.
enableWordCompletion (boolean)
See enableWordCompletion for the complete parameter definition.
locale (string)
|
|
This parameter override has been moved from Query suggest parameters and can now be leveraged in the Query Suggestion model association. |
See locale for the complete parameter definition.
q (string)
See q for the complete parameter definition.
|
|
This parameter overrides the query expression that the user enters in the search box. Therefore, it’s strongly recommended to add a condition for your rule to be applied. |
searchHub (string)
See searchHub for the complete parameter definition.
tab (string)
See tab for the complete parameter definition.
Unsupported parameters
The following parameters are NOT supported:
-
actionsHistory -
analytics -
categoryFacets -
commerce -
context -
dictionaryFieldContext -
disableQuerySyntaxNoteWe recommend that you use the
enableQuerySyntaxparameter instead. -
facets -
facetOptions -
fieldsToExclude -
fieldsToInclude -
groupBy -
mlParameters -
pipeline -
queryFunctions -
sortField -
userActions
QPL syntax
Use the following query pipeline language (QPL) syntax to define a statement expressing the queryParamOverride feature:
override <query | querySuggest> <queryParameterOverrides><query | querySuggest>
This is one of the two options:
-
query: modifies parameters in search requests (that is, inGETorPOSTrequests to the/rest/search/v2route). -
querySuggest: modifies parameters in query suggestion requests (that is, inGETorPOSTrequests to the/rest/search/v2/querySuggestroute).
<queryParameterOverrides>
A comma-separated list of parameter-value pairs, where each parameter is a valid query/query suggestion parameter and each value must be a valid value for the specified query/query suggestion parameter (see Query parameters).